
![]()
![]()
Lee Iacocca the CEO of Chrysler quoted: You can have brilliant ideas, but if you don’t get them across, your ideas won’t get you anywhere.
克莱斯勒的首席执行官Lee Iacocca说过: 你可以有非常棒的点子, 但如果你不付诸执行, 你的想法没有任何用处。
Effective Communication is crucial in any business, but even most importantly in the hospitality and tourism industry as it involves instant encounters and interactions
有效的沟通在任何领域都至为重要, 但在酒店和旅游业尤为重要, 因为它涉及到突发状况和相互作用。
Communication (from Latin commūnicāre, meaning "to share") is the act of conveying intended meanings from one entity or group to another through the use of mutually understood signs and rules.
交流 (来自于拉丁语 commūnicāre, 意思是 "分享") 是通过使用相互理解的符号和规则, 将意图表达的含义从一个实体或群组传达给另一个的行为。
This chapter explores the relationship between effective leadership and communication. It explains the importance of communicating the company’s mission and vision to all stakeholders.
本章探讨了有效领导与沟通的关系。它阐述了将公司的使命和愿景传达给所有利益相关者的重要性。
Everyone in a hospitality and tourism company should learn about the etiquette of communication not only essential for an exceptional service to the guests, but also for being able to handle difficult people and manage conflicts.
接待和旅游公司的每个人都要学习沟通礼仪, 不仅在为宾客提供优质服务方面至关重要, 而且还能学会与不易相处的人打交道以及解决冲突。
In the hospitality businesses we must communicate effectively as we interact with other managers, peers, employees, guests, vendors, and many other persons.
在酒店业, 我们与其他经理, 同行, 员工, 客户, 供应商和许多其他人接触时,必须做到有效沟通。
We must have excellent speaking, listening and writing skills because almost all aspects of the work involve communication.
我们必须拥有出色的口语、听力和写作技能, 因为几乎所有的工作都涉及到沟通。
Managers spend as much as 80% of their day engaging in some form of communication. Their ability to communicate often determines whether they succeed or fail as managers.
经理每天工作80%的时间都是从事不同形式的交流。他们的沟通能力常常决定他们作为管理者是否成功。
Effective communication skills are important in all managerial activities, including recruiting, interviewing, training, coaching, leading and interacting with guests.
有效的沟通技能在所有管理活动中都非常重要,包括招聘、面试、培训、辅导、领导以及与客户交流。
More importantly managers must also be able to communicate organizational information to their employees in a clear and concise way, while at the same time motivating them to perform to the best of their ability.
更为重要的是,管理者必须能够以简洁明了的方式向员工传达组织信息,同时激发他们展现自己最好的能力。
Communication involves much more than just words.
沟通不仅仅是说话。
According to a thorough research performed by Prof. Albert Mehrabian, the act of communication is made up of three elements.
根据Albert Mehrabian教授的深入研究,沟通行为由三要素组成。
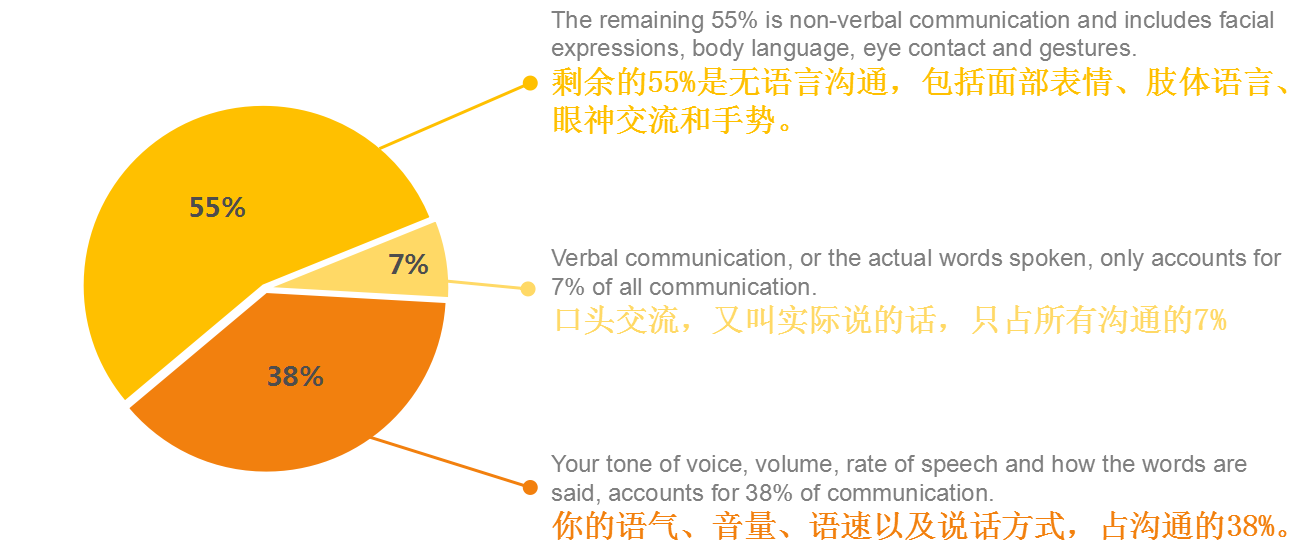
Keeping these findings in mind, communicating in the right way is primordial for any person working in any industry.
牢记这些理论,正确的沟通方式对各行业的员工都是最基本的要求。
The more effectively you communicate, the better you can perform your job and succeed in your career.
你沟通的越有效,你的工作表现就越好,事业成功的几率就更高。


