-
1 The History&...
-
2 Torment of&n...
-
3 Lexical chun...
-
4 Bilingual tr...

01 Read the following passage and complete the exercises that follow.

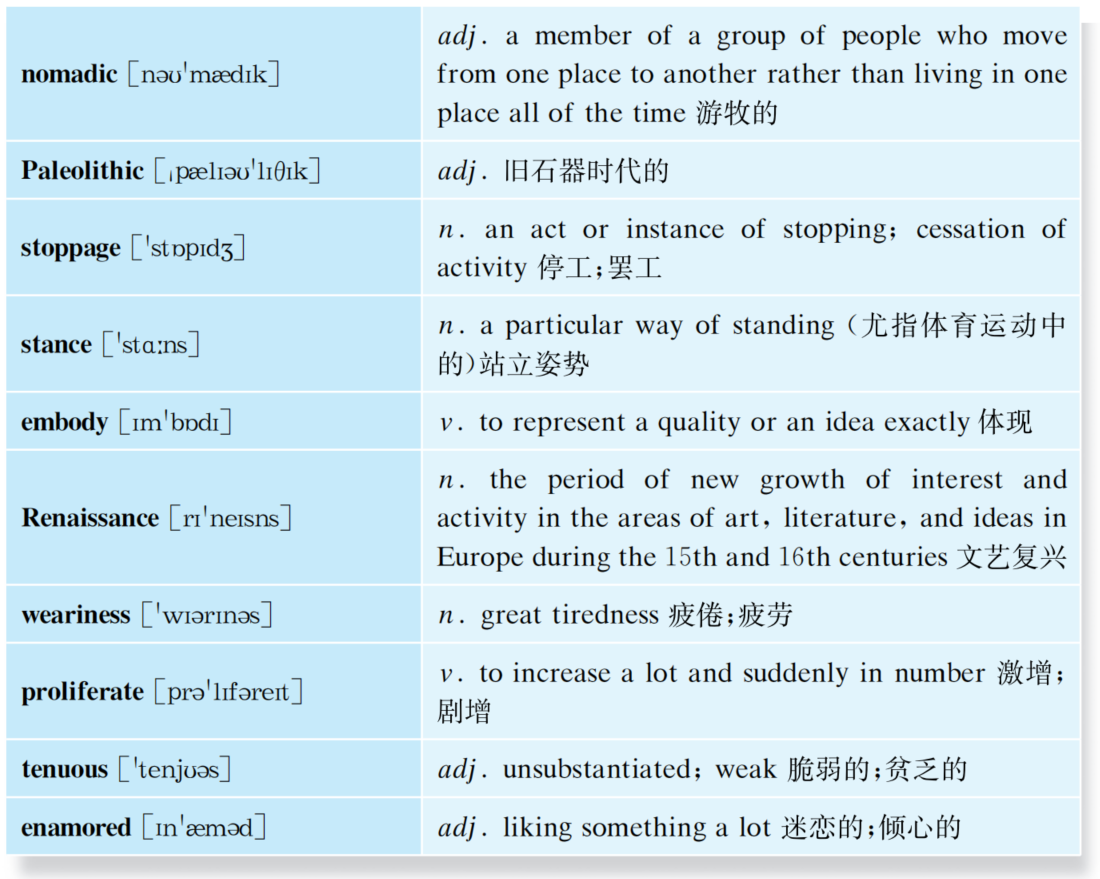
The History of Fitness
Lance C. Dalleck, M.S. and Len Kravitz, Ph.D.
Introduction
As we enter the 21st century, one of the greatest accomplishments to be celebrated is the continuous pursuit of fitness since the beginning of man's existence. Throughout prehistoric times, man's quest for fitness has been driven by a desire to survive through hunting and gathering. Today, though no longer driven by subsistence requirements, fitness remains paramount to health and well-being. This article will highlight historical events and influential individuals who have shaped the history of fitness beginning with primitive man up to the foundation of the modern fitness movement.
Primitive man and fitness (pre-10,000 B.C)
Primitive nomadic lifestyles required the continual task of hunting and gathering food for survival. Tribes commonly went on one- or two-day hunting journeys for food and water. Regular physical activity apart from that necessary for hunting and gathering was also a principal component of life. Following successful hunting and gathering excursions, celebration events included trips of six to 20 miles to neighboring tribes to visit friends and family, where dancing and cultural games could often last several hours. This Paleolithic pattern of subsistence pursuit and celebration, demanding a high level of fitness and consisting of various forms of physical activity, defined human life.
Ancient Chinese Civilization (2500-250 B.C.)
In China, the philosophical teachings of Confucius encouraged participation in regular physical activity. It was recognized that physical inactivity was associated with certain diseases (referred to as organ malfunctions and internal stoppages, which sound similar to heart disease and diabetes). Consequently, Kong Fu gymnastics was developed to keep the body in good, working condition. Kong Fu exercise programs consisted of various stances and movements, characterized by separate foot positions and imitations of different animal fighting styles. In addition to Kong Fu gymnastics, other forms of physical activity existed throughout ancient China including archery, badminton, dancing, fencing, and wrestling.
Ancient Greek Civilization (2500-200 B.C.)
Perhaps no other civilization has held fitness in such high regard as ancient Greece. The idealism of physical perfection was one that embodied ancient Greek civilization. The Greeks believed development of the body was equally as important as development of the mind. Physical well-being was necessary for mental well-being, with the need for a strong, healthy body to harbor a sound mind. Gymnastics, along with music, was considered to be the most important classroom topic. A common saying in ancient Greek times was "exercise for the body and music for the soul".
National Period in Europe (1700-1850)
Continental Europe underwent numerous cultural changes following the Renaissance. Fitness remained important and continued to follow trends initiated during the Renaissance. Physical education programs expanded within emerging nations of Europe. Intense feelings for nationalism and independence created the atmosphere for the first modern fitness movement, which came in the form of gymnastics programs. Gymnastics enjoyed immense popularity during this era, becoming especially prevalent in some countries such as Great Britain.
Within Great Britain, medical student Archibald Maclaren spread the word on the benefits of fitness and regular exercise. Marclaren made several observations based on his work, which are remarkably similar to present-day exercise recommendations. Firstly, Marclaren believed the cure for weariness and stress was physical action. Secondly, he noted recreational exercise found in games and sport was not sufficient for attaining adequate fitness levels. Finally, Marclaren realized both growing boys and girls required regular physical exercise. Marclaren also recognized the need for individual variation in fitness training programs.
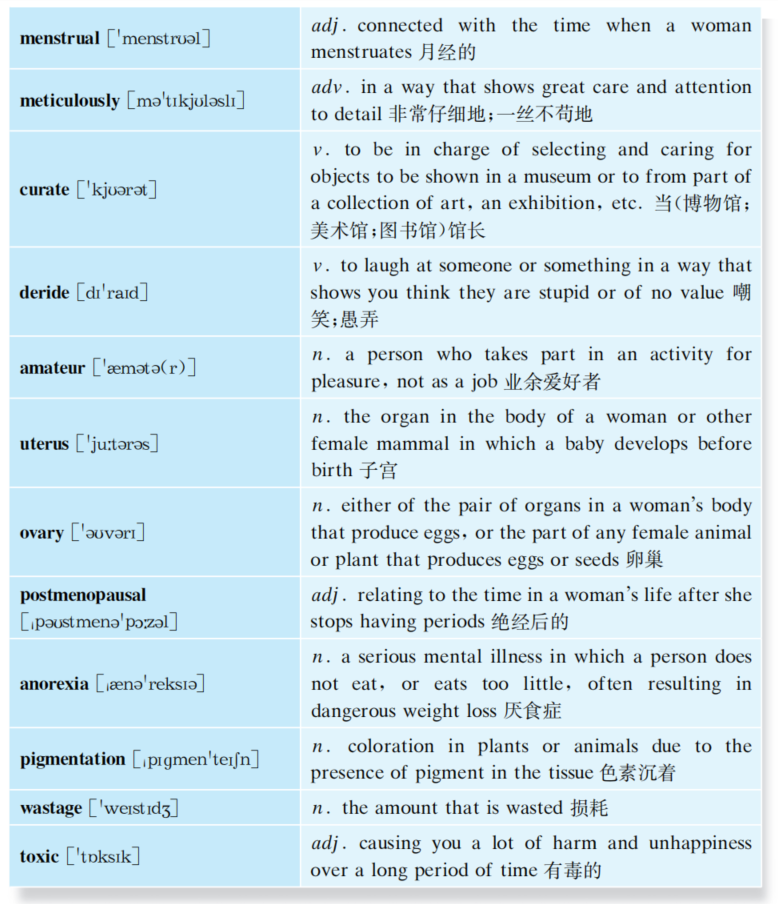
United States (1865-1960s)
One of the most important events with respect to modern fitness in the United States was the Industrial Revolution, which resulted in widespread cultural changes throughout the country. Advancement in industrial and mechanical technologies replaced labor-intensive jobs. Rural life changed to an urban lifestyle. The new city life generally required less movement and work compared to rural life, consequently decreasing levels of physical activity.
At the turn of the century, the most common causes of death were from influenza, polio, rubella, and other infectious diseases. Risk of disease and mortality from infectious diseases were alleviated with the discovery of Penicillin. The cost of industrialization and urbanization became glaringly apparent starting in the 1950s and 1960s. An epidemic of hypokinetic diseases including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and Type II diabetes, never before prevalent, began to be recognized as the leading causes of disease and death. The lifestyle improvements brought in part by the Industrial Revolution had apparently come with an unwanted and alarming cost to health.
Important contributions to fitness came during the 1940s, specifically from Dr. Thomas K. Cureton at the University of Illinois. Cureton not only recognized the numerous benefits of regular exercise, he strived to expand the body of knowledge regarding physical fitness. Among his most important contributions were developing fitness tests for cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, and flexibility. His research resulted in multiple recommendations for the improvement of cardiorespiratory fitness, including the identification of exercise intensity guidelines necessary for improved fitness levels. His suggestions became the fundamental basis behind future exercise programs.
President John F. Kennedy was a major proponent of fitness and its health-related benefits to the American people. He furthered the development of the Presidents Council on Youth Fitness, appointing Bud Wilkinson as head of the council. The name was also changed to the President's Council on Physical Fitness. Kennedy's commitment to fitness can best be summarized when he said, "Physical fitness is the basis for all other forms of excellence."
Dr. Ken H. Cooper, widely recognized as "The Father of the Modern Fitness Movement", is generally credited with encouraging more individuals to exercise than any other individual in history. Cooper advocated a philosophy that shifted away from disease treatment to one of disease prevention. "It is easier to maintain good health through proper exercise, diet, and emotional balance than it is to regain it once it is lost" he said. Early in his career, Cooper stressed the necessity for providing epidemiological data to support the benefits of regular exercise and health. Data from thousands of individuals became the foundation for his aerobic concepts. Aerobics, released in 1968, sent a powerful message to the American people-to prevent the development of chronic diseases, exercise regularly and maintain high fitness levels throughout life. Dr. Cooper's message, programs and ideas established the model from which fitness has proliferated up to modern time.
Lessons From History
The history of fitness portrays some fascinating themes that relate closely to the 21st century. One commonality is the strong association of political might with physical fitness throughout mankind's advancement. In many ways, this shows how impacting our world leaders can be on health and fitness.
The mind-body concept has had a tenuous development. At times, some cultures prescribed spirituality at the expense of the body where as others, such as Greek society, upheld the ideal a sound mind can only be found in a healthy body.
Another interesting development from history is the concept of exercise for the body and music for the soul. Present day fitness programs have evolved this concept harmoniously, with music being a distinctive component to the exercise experience.
It appears that as societies become too enamored with wealth, prosperity and self-entertatinment that fitness levels drop. In addition, as technology has advanced with man, the levels of physical fitness have decreased. History offers little insight how to prevent or turnaround these recourses. Thus, this is a resolution we are challenged with in today's society. Perhaps utilizing all of the extensive research completed on health and fitness in combination with the creative minds now in the fitness industry, we now can solve this part of the fitness puzzle.
(Source: https://www.unm.edu/~lkravitz/Article%20folder/history.html)