-
1 How Can ...
-
2 Issues and&n...
-
3 Lexical Chun...
-
4 Bilingual tr...

01 Read the following passage and complete the following exercises.

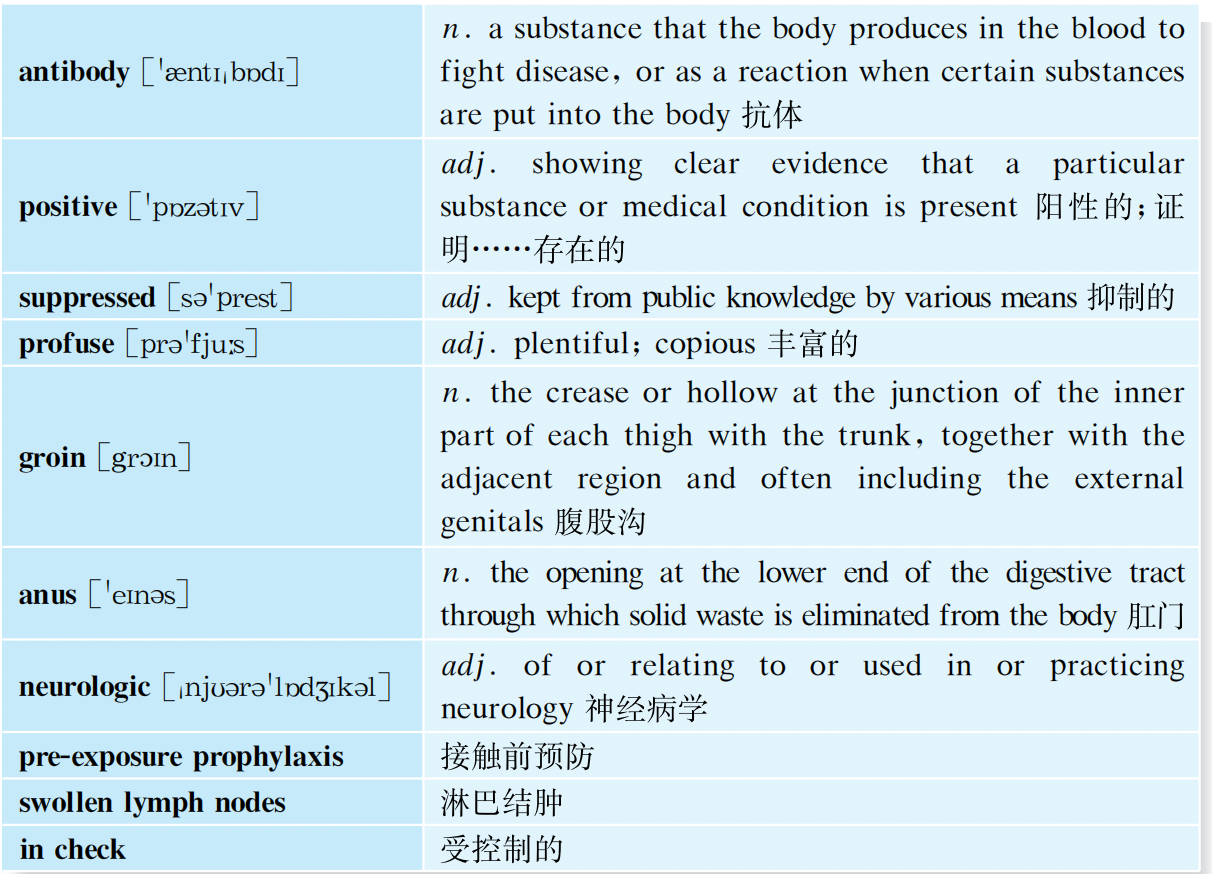
Stages and Symptoms of HIV infection
The symptoms of HIV vary, depending on the individual and what stage of the disease you are in: the early stage, the clinical latency stage, or AIDS (the late stage of HIV infection). Below are the symptoms that some individuals may experience in these three stages. Not all individuals will experience these symptoms.
Early Stage of HIV
Some people infected with HIV are asymptomatic at first. Most people experience symptoms in the first month or two after becoming infected. That’s because your immune system is reacting to the virus as it rapidly reproduces.
This early stage is called acute stage. Symptoms are similar to those of the flu and may last anywhere from a few days to several weeks. About 40% to 90% of people have flu-like symptoms within 2-4 weeks after HIV infection. Other people do not feel sick at all during this stage, which is also known as acute HIV infection. Early infection is defined as HIV infection in the past six months (recent) and includes acute (very recent) infections. Flu-like symptoms can include:
1. Fever
2. Chills
3. Rash
4. Night sweats
5. Muscle aches
6. Sore throat
7. Fatigue
8. Swollen lymph nodes
9. Mouth ulcers

During the first few months of infection, an HIV test may provide a false-negative result. This is because it takes time for the immune system to build up enough antibodies to be detected in a blood test. But the virus is active and highly contagious during this time.
You should not assume you have HIV just because you have any of these symptoms. Each of these symptoms can be caused by other illnesses. And some people who have HIV do not show any symptoms at all for 10 years or more.

After you get tested, it’s important to find out the result of your test. If you’re HIV-positive, you should see a doctor and start HIV treatment as soon as possible. You are at high risk of transmitting HIV to others during the early stage of HIV infection, even if you have no symptoms. For this reason, it is very important to take steps to reduce your risk of transmisson. If you’re HIV-negative, explore HIV-prevention options, like pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), that can help you stay negative.
Clinical Latency Stage
After the early stage of HIV infection, the disease moves into a stage called the clinical latency stage (also called “chronic HIV infection”). During this stage, HIV is still active but reproduces at very low levels. People with chronic HIV infection may not have any HIV-related symptoms, or only mild ones.
For people who aren’t taking medicine to treat HIV (called antiretroviral therapy or ART), this period can last a decade or longer, but some may progress through this phase faster. People who are taking medicine to treat HIV, and who take their medications right way, every day, may be in this stage for several decades because treatment helps keep the virus in check.
It’s important to remember that people can still transmit HIV to others during this phase even if they have no symptoms, although people who are on ART and stay virally suppressed (having a very low level of virus in their blood) are much less likely to transmit HIV than those who are not virally suppressed.
Progression to AIDS
If you have HIV and you are not on ART, eventually the virus will weaken your body’s immune system and you will progress to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), the late stage of HIV infection.
Symptoms can include:
1. Rapid weight loss
2. Recurring fever or profuse night sweats
3. Extreme and unexplained tiredness
4. Prolonged swelling of the lymph glands in the armpits, groin, or neck
5. Diarrhea that lasts for more than a week
6. Sores of the mouth, anus, or genitals
7. Pneumonia
8. Red, brown, pink, or purplish blotches on or under the skin or inside the mouth, nose, or eyelids
9. Memory loss, depression, and other neurologic disorders
Each of these symptoms can also be related to other illnesses. Many of the severe symptoms and illnesses of HIV disease come from the opportunistic infections that occur because your body’s immune system has been damaged.
(Source: https: //www. hiv.gov/hiv-basics/overview/about-hiv-and-aids/symptoms-of-hiv )