02 Read the following passage and answer these questions.

Types and risks of plastic surgery
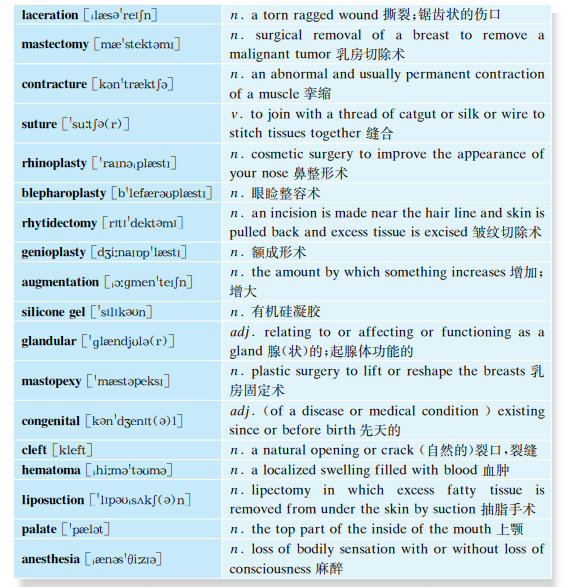
Plastic surgery is any surgery performed for cosmetic or reconstructive purposes. As far as reconstructive surgery is concerned, it is performed to correct functional impairments caused by burns; traumatic injuries, such as facial bone fractures and breaks; congenital abnormalities, such as cleft palates or cleft lips; developmental abnormalities; infection and disease; and cancer or tumors. Reconstructive plastic surgery is usually performed to improve function, but it may be done to approximate a normal appearance.
The most common reconstructive procedures are tumor removal, laceration repair, scar repair, hand surgery, and breast reduction plasty.
Some other common reconstructive surgical procedures include breast reconstruction after a mastectomy for the treatment of cancer, cleft lip and palate surgery, contracture surgery for burn survivors, and creating a new outer ear when one is congenitally absent.
Plastic surgeons use microsurgery to transfer tissue for coverage of a defect when no local tissue is available. Free flaps of skin, muscle, bone, fat, or a combination may be removed from the body, moved to another site on the body, and reconnected to a blood supply by suturing arteries and veins as small as 1 to 2 millimeters in diameter.
As for cosmetic surgery, it is an elective or optional procedure that is performed on normal parts of the body with the only purpose of improving a person’s appearance and/or removing signs of aging. Procedures are either surgical, such as rhinoplasty or facelift, or nonsurgical procedures include Botox and laser hair removal.
Plastic surgery can be performed on all areas of the head, neck and body.
For the head, common procedures include blepharoplasty (reshaping of the eyelids or the application of permanent eyeliner), labiaplasty /lip enhancement (the former involves surgical reduction and reshaping of the labia; the latter is surgical improvement of lips' fullness through enlargement),rhinoplasty (reshaping of the nose), otoplasty (reshaping of the ear, most often done by pinning the protruding ear closer to the head), rhytidectomy (removal of wrinkles and signs of aging from the face), browplasty (elevates eyebrows, smooths forehead skin), genioplasty (augmentation of the chin with an implant, usually silicone, by sliding genioplasty of the jawbone or by suture of the soft tissue), cheek augmentation(implants to the cheek) and midface lift (tightening of the cheeks). Neck lift is used to tighten lax tissues in the neck. This procedure is often combined with a facelift for lower face rejuvenation.
Common procedures for the breasts include breast augmentations, enlarging the breasts by means of fat grafting, saline, or silicone gel prosthetics; reduction mammoplasty ("breast reduction"), removing skin and glandular tissue in women with gigantomastia and for men with gynecomastiato reduce back and shoulder pain; and mastopexy, lifting or reshaping of breasts to make them less saggy, often after weight loss (after a pregnancy, for example).
Abdominoplasty involves surgically removing excess skin and fat from the middle and lower part of the abdomen and sometimes tightening the abdominal muscles.
For people who are unhappy with the appearance of their buttocks and seek younger and perky buttocks, buttock lift (removing excess skin and firming the buttocks) and buttock augmentation (enhancement of the buttocks using silicone implants or fat grafting) might be the solutions.

Risks of Plastic Surgery
Plastic surgery, like any type of surgery, is not without risks. Plastic surgery procedures can result in complications ranging from an unattractive or unnatural final result to scarring or even death.
Poor Cosmetic Outcome: This may be the greatest fear of a plastic surgery patient: a result that not only fails to improve appearance but actually makes one's appearance worse than before the surgery.
Scarring: One of the greatest risks to achieving an attractive outcome, scarring is not always predictable, but can be controlled in most cases. Patients can decrease the risk of scarring by not smoking, eating well after surgery and following the surgeon's directions during recovery.
Nerve Damage or Numbness: In some cases, nerves may be damaged or severed during any surgical procedure. The result is more obvious, however, if it is a facial nerve. When those nerves are injured, the outcome can be the inability to make facial expressions or drooping of the eyes or mouth.
Infection: All surgeries carry a risk of infection. Proper wound care and frequent hand washing can minimize or prevent an infection.
Hematoma: A hematoma is a collection of blood outside of a blood vessel. A hematoma can develop after surgery; this typically results in an area being swollen and bruised in appearance, with a pocket of blood beneath. In some cases, this is minor, but a hematoma can be large enough to cause pain and even decrease blood flow through the area. In the case of a large hematoma, the surgeon may choose to remove some of the collected blood with a syringe or other similar method.
Death: Every surgery has a risk of death. While that risk may be less than one percent, it's possible for death to occur during the most minor of surgeries. In many cases, this is due to a reaction to anesthesia.
Anesthesia Issues: Most patients tolerate anesthesia without difficulty; however, anesthesia-related complications are the leading cause of cosmetic surgery deaths. The risk is very slight, but it does exist, which is why even elective procedures need to be taken seriously.
The best way to reduce the risk of a bad outcome is to choose the surgeon who performs the procedure wisely. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, are extremely important before surgery, as non-smokers heal faster and have less scarring. In addition, eating a healthy diet before and after the procedure can speed healing and improve wound closure, which also minimizes scarring.
(Source: https://www.verywellhealth.com/)

 01 View a video clip and define the term “plastic surgery” using the most suitable expressions.
01 View a video clip and define the term “plastic surgery” using the most suitable expressions.






