Chapter 6 The Monetary System
LECTURE VIDEO学习视频8:
Bank Capital, Leverage, and the Financial Crisis of 2008–2009
More realistically, a bank gets funds not only from accepting deposits, but also from issuing debt and equity.
Definition of bank capital: the resources that a bank obtains from issuing equity to its owners.
It not only makes loans and holds reserves but also buys financial securities, such as stocks and bonds.
While, in China, commercial banks are not allowed to engage in trust investment and stock investment.
The bank decides how to allocate its resources among different assets based on their risk and return, as well as on any regulations.
Definition of leverage: the use of borrowed money to supplement existing funds for purposes of investment.
Definition of leverage ratio: the ratio of assets to bank capital.
Because of leverage, a small change in assets can lead to a large change in owner’s equity.
For example:
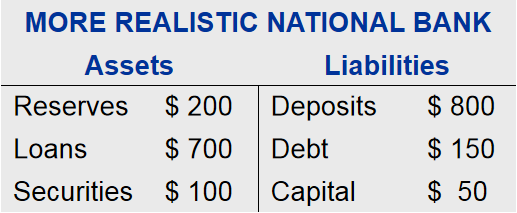
In this example, leverage ratio is 20, which means that for every $20 in assets, $1 is from the bank’s owners, $19 is financed with borrowed money.
(1) If bank's assets rise in value by 5% because some of the securities the bank was holding rose in price.
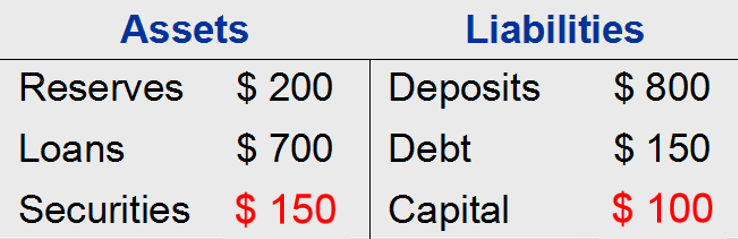
$1,000 of assets would now be worth $1,050. While, bank capital rises from $50 to $100, by 100%.
So, for a leverage rate of 20, a 5% increase in the value of assets increases the owners' equity by 100%.
(2) If bank's assets fall in value by 5% because some people who borrowed from the bank default on their loans.
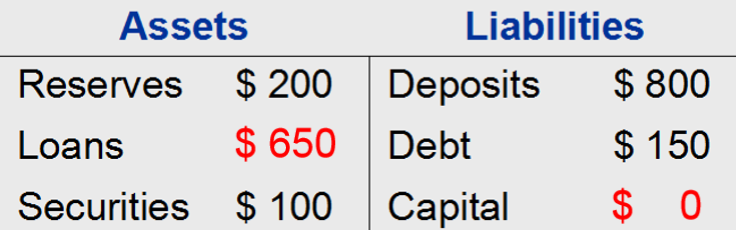
$1,000 of assets would be worth $950. While, value of the owners' equity falls to zero, by 100%.
So, for a leverage ratio of 20, a 5% fall in the value of the bank assets leads to a 100% fall in bank capital.
(3) We can infer that if tha value of assets were to decrease by more than 5%, the bank's assets would fall below its liabilities, bank capital was negative.
In this case, the bank would be insolvent and it would be unable to pay off its debt holders and depositors in full.
Therefore, bank regulators require banks to hold a minimum amount of capital, called capital requirement, intended to ensure banks will be able to pay off depositors and debts.
In 2008 and 2009, many US banks found themselves with too little capital after the incurred sizable losses on their assets.
The shortage of capital induced banks to reduce their lending, called credit crunch.
Credit crunch will inturn depress the economic activities.
To address this problem, The U.S. Treasury and the Fed put billions of dollars into the banking system to increase the bank capital.
The goal of capital injection by the US government is to recapitalize the banking system so that bank lending can return to its normal level.
【10分钟速成课:经济学】第12集 - 金融危机Financial Crisis
ACTIVE LEARNING:
Additional video about credit crisis in U.S. durin 2007-2009


