Chapter 4 Saving, Investment and Financial System
LECTURE VIDEO学习视频5:
Government policies can affect the economy's saving and investment.
a. Policy 1: Saving Incentives
The tax on interest income and dividend income sustantially reduces the after-tax future return from current saving and ,as a result, reduces the incentive for people to save.
Many economists suggest tax reform aimed at increasing saving to stimulate investment and growth.
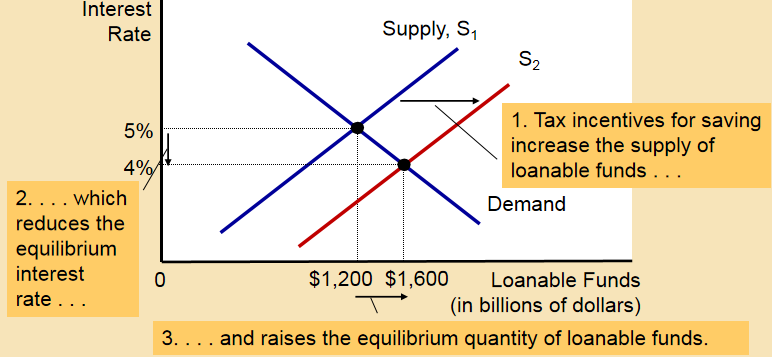
Suppose that the government changes the tax code to encourage greater saving.
This will cause an increase in saving, shifting the supply of loanable funds to the right.
The equilibrium interest rate will fall and the equilibrium quantity of funds will rise.
Thus, if a reform of the tax laws encouraged greater saving, the result would be lower interest rates and greater investment.
b. Policy 2: Investment Incentives
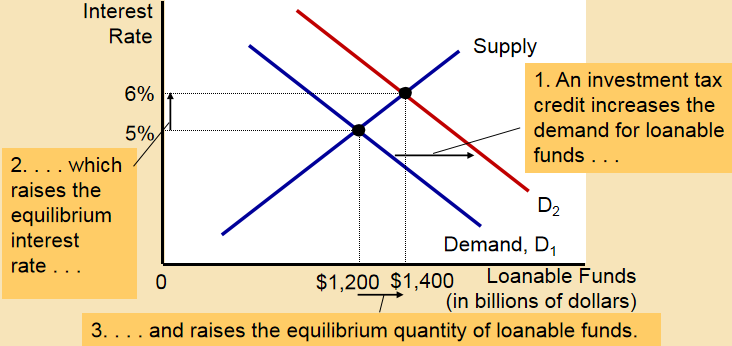
Investment tax credit 投资赋税优惠 lowers taxes for any firm building a new factory or buying new equipment.
In other words, the use of an investment tax credit will benefit firms which do the new invstments.
This will cause an increase in investment, causing the demand for loanable funds to shift to the right.
The equilibrium interest rate will rise, and the equilibrium quantity of funds will increase as well.
Thus, if a reform of the tax laws encouraged greater investment, the result would be higher interest rates and greater saving.
c. Policy 3: Budget Deficit/Surplus
A budget deficit occurs if the government spends more than it receives in tax revenue. Governments finance budget deficits by borrowing in the bond market, called the government debt.
A budget surplus, tax revenue exceeding government spending, can be used to repay some of the previous government debt.
A balanced budget means the government spending exactly equals to tax revenue.
This implies that public saving (T – G) falls (rises), which will lower (improve) national saving.
Suppose that the government starts with balanced budget where the public saving equals zero.
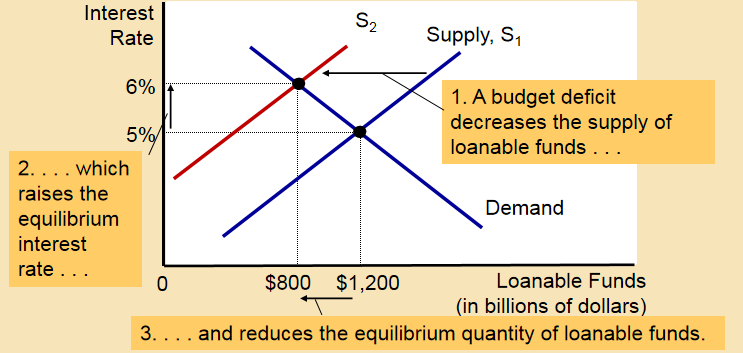
Then, the government starts running a budget deficit because of a tax cut or a spending increase.
Thus, the public saving turns to be a negative figure, which decreases the national saving.
The supply of loanable funds will shift to the left. The equilibrium interest rate will rise, and the equilibrium quantity of funds will decrease.
Thus, When the government reduces national saving by running a budget deficit, the interest rate rises and investment falls.
When the government borrows to finance its budget deficit, leaving less funds available for investment, thus it crowds out household and firms that otherwise would borrow to finance investment.
The decrease in investment because of government borrowing is called crowding out.
Since investment is important for long-run economic growth, government budget deficits reduce reduce the economy's growth rate and future standard of living in the long run.
Government budget surpluses work in the opposite way. The supply of loanable funds increases, the equilibrium interest rate falls, and investment rises.


