Chapter 2 MEASURING THE COST OF LIVING
LECTURE VIDEO 学习视频6:
Correcting Economic Variables for the Effects of Inflation
a. Dollar Figures from Different Times
1) To change dollar values from one year to the next, we can use this formula:
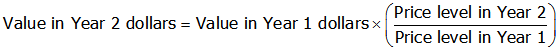
2) Example: Babe Ruth’s 1931 salary in 2009 dollars:
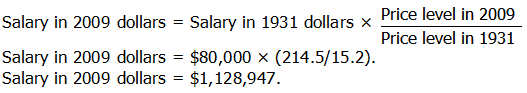
b. Indexation
1) Definition of indexation: the automatic correction of a dollar amount for the effects of inflation by law or contract.
2) As mentioned above, many government transfer programs use indexation for the benefits. The government also indexes the tax brackets used for federal income tax.
3) There are uses of indexation in the private sector as well. Many labor contracts include cost-of-living allowances (COLAs).
c. Real and Nominal Interest Rates
1) Example: Sally Saver deposits $1,000 into a bank account that pays an annual interest rate of 10%. A year later, she withdraws $1,100.
2) What matters to Sally is the purchasing power of her money.
a) If there is zero inflation, her purchasing power has risen by 10%.
b) If there is 6% inflation, her purchasing power has risen by about 4%.
c) If there is 10% inflation, her purchasing power has remained the same.
d) If there is 12% inflation, her purchasing power has declined by about 2%.
e) If there is 2% deflation, her purchasing power has risen by about 12%.
3) Definition of nominal interest rate: the interest rate as usually reported without a correction for the effects of inflation.
4) Definition of real interest rate: the interest rate corrected for the effects of inflation.



