Chapter 8.
Reasons for Entrepreneurial Failure
中文參考課件:
Contents:
1.Think like a game
2.Benefit from failure
Objectives:
Understand the key reasons for entrepreneurial failure
How to think like a game in entrepreneurship
Understand how to benefit from failure
Understand equity distribution in startups
Don’t fear with Failure
Entrepreneurship is Marathon, not a sprint: It takes patience, persistence, and perseverance.
Entrepreneurial failure is not the end of a story.
In fact, if you learn the right lessons, failure can be the foundation of any entrepreneur’s future success.
The newness of entrepreneurial activity will often to failure but entrepreneurs should able to rise up and try again.
Most successes come from a succession of failure. Entrepreneurs learn from failure.
I did not fail but I simply found 10000 ways that did not work! - Thomas Edison
Why do most startups fail?
According to the study by Shikhar Ghosh at Harvard Business School,75%of startups fail.
Key Reasons for entrepreneurial failure :
Lack of focus
Lack of motivation, commitment, and passion
Too much pride, resulting in an unwillingness to see or listen
Taking advice from the wrong people
Lacking good mentorship
Lack of general and domain-specific business knowledge: finance, operations, and marketing
Raising too much money too soon
Another study by CB insights.
Key Reasons for entrepreneurial failure :
No market need
Ran out of cash
Not the right team
Got outcompete
Pricing/cost issue
Poor product
Need/lack of business model
Poor marketing 9.Ignore customers
8.1 Think like a game
Game also called “ Strategic Science”.
The game provides a systematic thinking environment in the context of interacting with people, judge how they react, and helps to find the decision best for the situation.
Games have been around as long as human civilization.
If you’re looking for a powerful approach that synthesizes modern product development with world-class game design – and a toolkit to help you innovate smarter and drive engagement from the ground up – you’ve found it.
Leading companies Disney, Netflix, NY times use game thinking for their success.
Game thinking?
| 1.What is the topic and agenda? | What is your goal or target you want to achieve? What are the rules to follow? |
| 2. Who is the player? | Who is the main player and whose interest and action affect? |
| 3. What is the goal? | What is the extent of each person’s damage or gain? What actions will affect the gain of others? |
| 4. How much do I know? | How much information do I have? What strategy might the other party implement? How to formulate our own strategy based on the opponent strategy? |
| 5. How much does the opponent know? | How will the opponent develop their strategy based on what they know about me and each other? |
| 6. What are the possible outcomes? | Among all the outcomes, which one is most likely to happen? Is that outcome good for me? |
Game theory?
Mathematician John Von Neumann and Economist Oscar Morgenstern in 1940.
Game theory is a theoretical framework to conceive social situations among competing players and produce optimal decision-making of independent and competing actors in a strategic setting.
Using game theory, real-world scenarios for such situations as pricing competition and product releases (and many more) can be laid out and their outcomes predicted.
Scenarios include the prisoner's dilemma and the dictator game among many others.
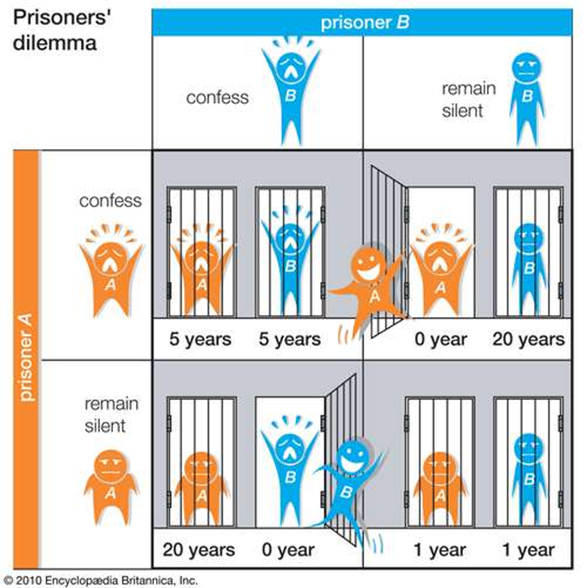
Prisoner's Dilemma
This is a well-known example of Game theory.
Consider two criminals who are arrested for a crime. Police had no hard evidence to convict them. Then officials remove prisoners from that cell and take into the separate chambers to question each one separately.
Officials present four deals
1.If both confess, they will each receive 5 years in prison.
2.If Prisoner 1 confess, but Prisoner 2 remain silent, Prisoner 1will be free and Prisoner 2 will get 20 years
3.IfPrisoner 2 Confess, but Prisioner1 remains silent, Prisoner 1 will get 20 years and Prisoner 2 will be free.
4.If both remain silent then they will both get 1 year in prison
Game theory in Economics and Business
Game theory in business is useful for modeling competing for the behavior of economic agents.
The business has several strategic choices and may face dilemmas in product development, pricing, and marketing strategies.
Game theory can be characterized by an oligopoly. Which is competing companies agreement for a lower pricing structure.
Game theory provides hypothetical material implications in marketing strategies to waging war decisions, ideal auctions, voting styles, etc.


