3.Development of Business Model
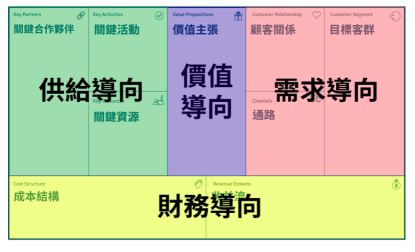
A business model is a conceptual framework that describes how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. To perform these three core tasks Osterwalder an Pigneur(2010) developed a Business model canvas(BMC) comprised of nine building blocks.
Customer segment
Value propositions
Channel
Customer relationships
Revenue streams
Key recourses
Key activities
Key partnership
Cost structures
Customer Segment(CS):
Defines the different groups of people or organizations an enterprise aims to reach and serve. Customer Segments can be broken down into sub-segments if their needs require and justify a distinct offer (e.g. they are reached through different channels, they require different types of relationships, they have substantially different profitabilities, they are willing to pay for different aspects of the offer).
Value Propositions(VP)
The value proposition represents the bundle of products and services that create value for a specific Customer Segment. The Value Propositions may be quantitative(e.g. price, speed of service) or qualitative (e.g. design, customer experience).
Channels(CH)
Channels describe how a company communicates with and reaches its Customer Segments to deliver their Value Proposition. Channels represent a company’s interface with its customers and can include communication, distribution, and sales.
Customer Relationships (CR)
Customer Relationships describe the types of relationships a company establishes with specific Customer Segments and can range from personal relationships to entirely automated interactions. TheCustomer Relationships are a key issue in determining the overall customer experience.
Revenue Streams (RS)
The revenue stream describes how a company will generate cash from each Customer Segment. The Revenue Stream has to take into account how much customers will be willing to pay for the value the company delivers. There are two basic types of revenue streams: revenues from one-time customer payments, and recurring revenues from on-going payments.
Key Resources (KR)
The KeyResources describes the most important assets within a company that makes a business model work. These generally include physical resources (e.g. buildings, vehicles, etc.), intellectual resources(e.g. brands, partnerships, proprietary knowledge, etc.), human resources (e.g.employees), and financial resources (e.g. cash, lines of credit, etc.
Key Activities (KA)
The key activities describe the most important things a company must do to make its business model work. They can be activities to create and offer ValuePropositions, reach markets, maintain Customer Relationships, and earn revenues. General categories for Key Activities include production, problem-solving, and platform/networking.
Key Partnerships (KP)
The KeyPartnerships describes the network of suppliers and partners that make a business model work. Partnerships are essential in most businesses to optimize their business models, reduce risk, or acquire resources. Partnerships can generally be categorized into strategic alliances between-competitors, strategic partnerships between competitors, joint ventures to develop new businesses, and buyer-supplier relationships.
Cost Structure (CS)
The cost structure describes all costs incurred to operate a business model, for example in creating and delivering value, maintaining Customer Relationships, and generating revenue. Cost structures can be divided into fixed costs, variable costs, economies of scale, and economies of scope.
Key elements when developing a business model
Identify your specific audience: Do not target a wide audience narrow down, outline details of your audience
Establish a business process: Understand the activities of your business before going into the market.
Record key business resources: Documentessential resources to ensure your business model is adequately prepared to sustain.
Develop a strong value proposition: Establish what your business offers and why it’s better than competitors are the beginning of a strong value proposition.
Determine key business partners: No business can function without key partners. Select beneficial key partners such as suppliers or advertisers etc..
Create demand generation strategy: Build interests in your business, how customers find you?
Leave room for innovation: Review your model and change it according to the necessity.
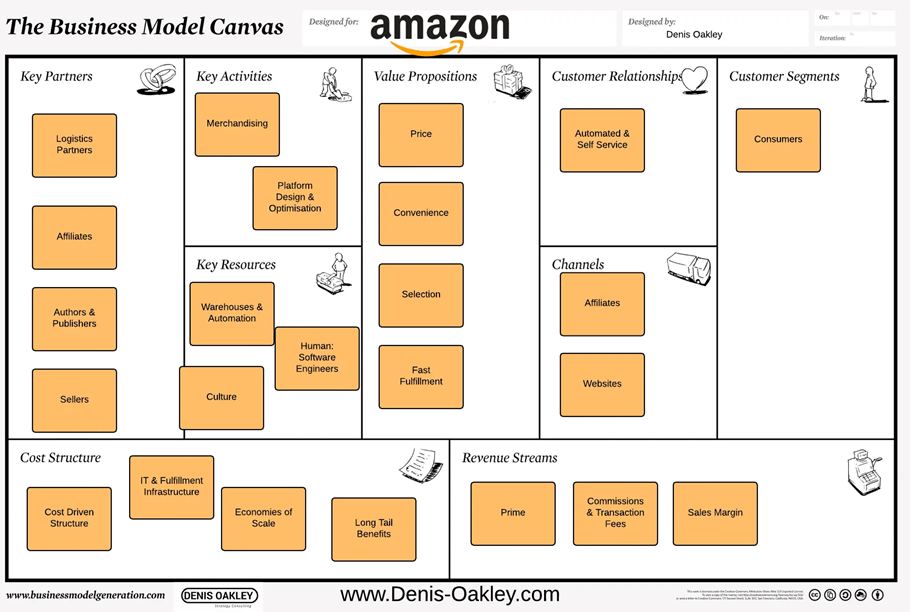
Amazon Business Model Canvas
Amazon solves the problems of many customers. It has an exceptionally powerful business model in the retail e-commerce sector. Known to be the largest online retailer worldwide, Amazon functions at a diverse pace in their product offerings. More and more customers access their sites to purchase the products they are looking for more so at an affordable rate. As long as it continues to develop new ideas and stay ahead of its competition, it is destined to remain at the top.