★ About Earned Value Analysis
EVA is a method to jointly consider the impact of time, cost, and project performance on any analysis of current project status(状态).
EVA also allows the project team to make future projections(预测、推断) of project status based on its current state.
At any point in the project’s development we are able to calculate both schedule and budget efficiency factors (the efficiency with which budget is being used relative to the value that is being created) and use those values to make future projections about the estimated cost and schedule to project completion.
Earned value directly links all three primary project success metrics (度量指标)(cost, schedule, and performance); this methodology is extremely valuable because it allows for regular updating of a time-phased budget to determine schedule and cost variances.
The key to effective use of EVM lies in providing accurate and up-to-date information on the project, particularly in terms of the percentage of work packages completed.
★EVM – Terminology of Earned Value(挣值分析专业术语)
1. BCWS(PV) = Planned value: a cost estimate of budgeted resources scheduled across the project’s life cycle
2. BCWP(EV) =Earned value: the real budgeted cost, or value, of the work that has actually been performed to date
3. ACWP(AC) = Actual cost of work performed: the cumulative total costs incurred in accomplishing the various project work packages
4. Schedule performance index(进度绩效指数)
SV = BCWP-BCWS=(EV – PV)
SPI = EV/PV : the earned value to date divided by the planned value of work scheduled to be performed
5. Cost performance index(费用绩效指数)
CV = BCWP-ACWP=(EV- AC)
CPI = (EV/AC): the earned value divided by the actual, cumulative cost of the work performed to date
BAC = Budgeted cost at completion: represents the total budget for a project
挣值分析方法介绍
Reviewing questions(复习思考):
1 .挣值分析案例一
背景:某装饰工程公司承接一项酒店装修改造工程,前 5 个月各月完成费用情况如下表 所示。合同总价 1500 万元,总工期 6 个月。
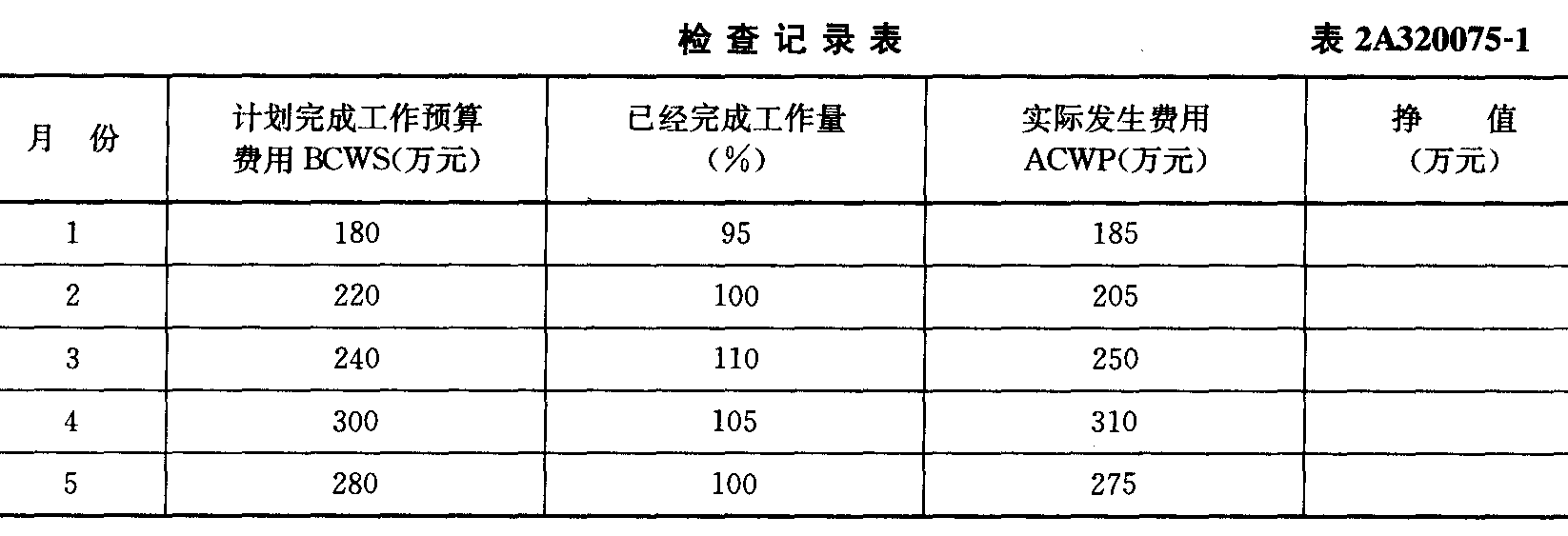
问题 利用挣值法分析当下成本与进度状况。
【参考 答案 】
指标解释以及计算规则:
①已完成工作预算费用(挣值): BCWP=已完成工程量×预算单价
②计划完成工作预算费用:BCWS=计划工程量×预算单价
③已完成工作实际费用:ACWP,即到某一时刻为止,已完成的工作(或部分工作)所实际花费的总金额。
在这三个费用值的基础上,可以确定挣值法的四个评价指标。
①费用偏差CV: CV=BCWP-ACWP 当CV为负值时,即表示项目运行超出预算费用;当CV为正值时,表示项目运行节支,实际费用没有超出预算费用。
②进度偏差SV: SV=BCWP-BCWS 当SV为负值时,表示进度延误,即实际进度落后于计划进度;当SV为正值时,表示进度提前,即实际进度快于计划进度。
③费用绩效指数CPI: CPI=BCWP/ACWP 当CPI<1时,表示超支,即实际费用高于预算费用;当CPI>1时,表示节支,即实际费用低于预算费用。
④进度绩效指数SPI: SPI=BCWP/BCWS 当SPI<1时,表示进度延误,即实际进度比计划进度拖后;当SPI>1时,表示进度提前,即实际进度比计划进度快。
从表中可见, 5 个月的累计的计划完成预算费用 BCWS 为 1220 万元,实际完成预算费用 ACWP 为 1 225 万元。 并进行计算,求得5个月末每项工作的BCWP;5个月末总的BCWP为1250 万元
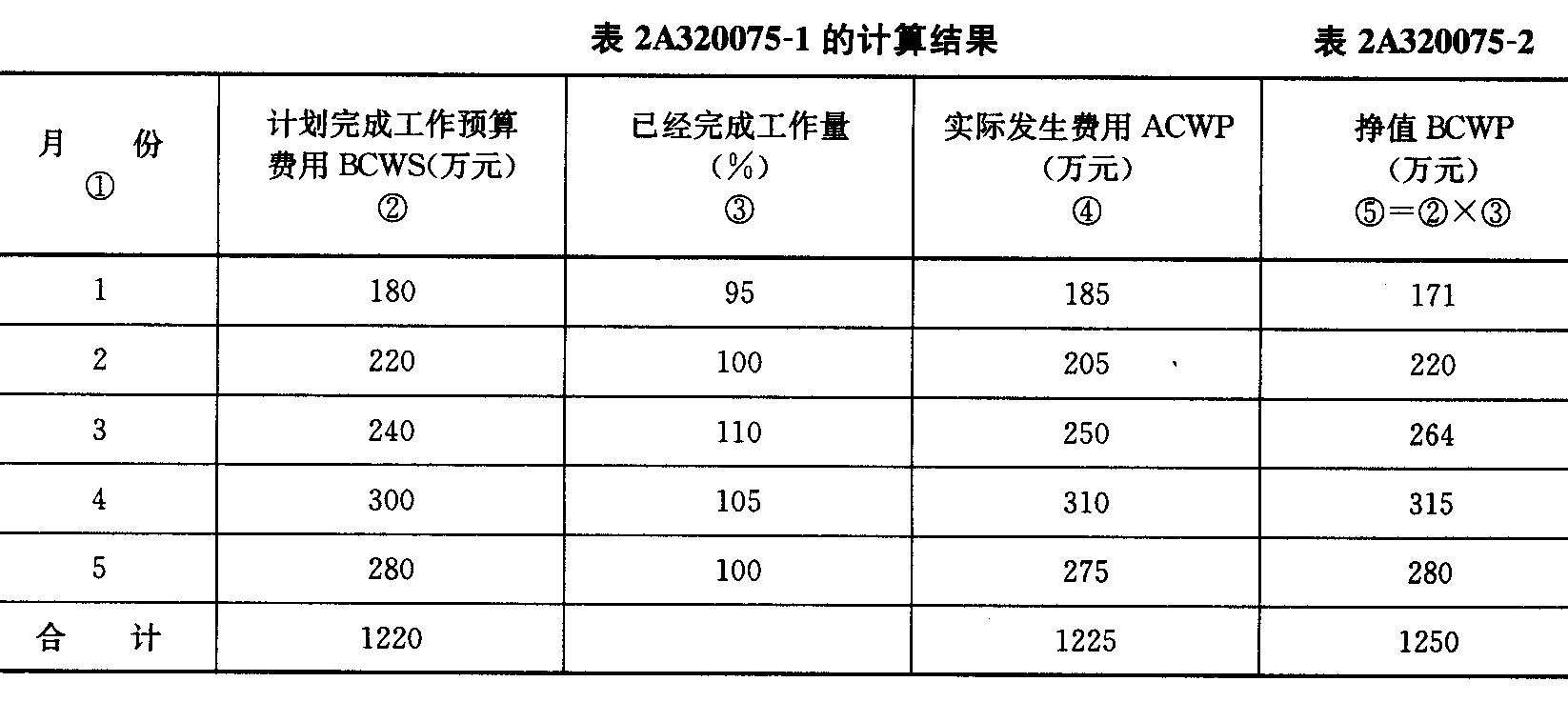
所以:
CV = BCWP — ACWP = 1250 一 1225 = 25 万元,由于 CV 为正,说明费用节约了25万元。
SV = BCWP — BCWS = 1 250 一 1220 = 30 万元,由于 SV 为正,说明进度提前了30万元。
(CPI = BCWP / ACWP = 1250 / 1225 = 1 . 0204 ,由于 CPI 大于 1 ,说明费用节约。)
( SPI = BCWP / BCWS = 1 250 / 1220 = 1 . 0246 ,由于 SPI 大于 1 ,说明进度提前。)
2.挣值分析案例二 (结合网络图)


