The three most common delivery methods are design/bid/build, design/build, and construction management. Combinations(组合) of these strategies may be employed as well. Each has its distinct advantages and disadvantages, but the choice is not always clear and simple. The owner must carefully weigh his or her options to ensure the right choice for the specific project. Now we will discuss them respectively.
★Design/Bid/Build(DBB模式)
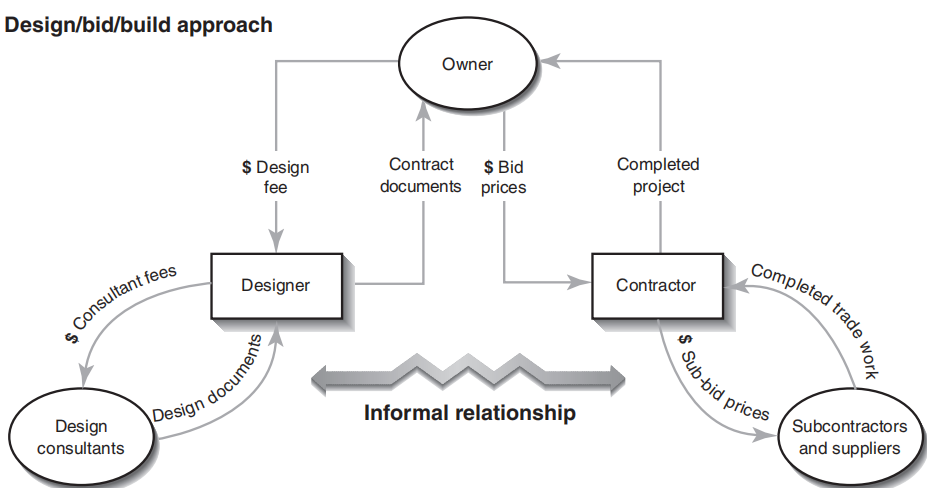
The owner first hires a design professional, who then prepares a design, including complete documents. The design professional is paid a fee. with the complete documents the owner will bid for the lowest price from contractors or negotiates with a specific contractor. The contractor is then responsible for delivering the completed project in accordance with the contract documents. The contractor can choose to subcontract some of the work or have the forces in house to accomplish the task.
Advantages:
☝ It can greatly reduce the level of risks. This model contains contractual protection for the owner. The owner does not have to get heavily involved in the construction process. The contractor and subcontractor will cover all the construction risks.
☝ In most cases, the owner knows the final cost at the beginning of construction.
☝ The owner can enjoy the benefits of open market competition. In the open bidding procedure, the lowest bidder is the winner.
Disadvantages:
☟ The construction professionals does not enter the process until the design is complete, so it's difficult to reduce the time, it's time costing.
(the work proceeds linearly) (工作线性推进)

☟ The construction begins after the completion of design, so the design is not usually reviewed for constructability before it is finished, moreover many economical and effective design features will be ignored.
☟ High risk of major breakdown in relationship. The designer designs the project based on the owner’s instructions. The general contractor prices and schedules the project based on the contract documents alone. There is little chance for interaction among the participates. Moreover, the parties involved view the situation from different perspectives. If unforeseeable conditions arise, the contract has to be renegotiated and revised, which is a source of conflict.
★Design/build(DB模式)
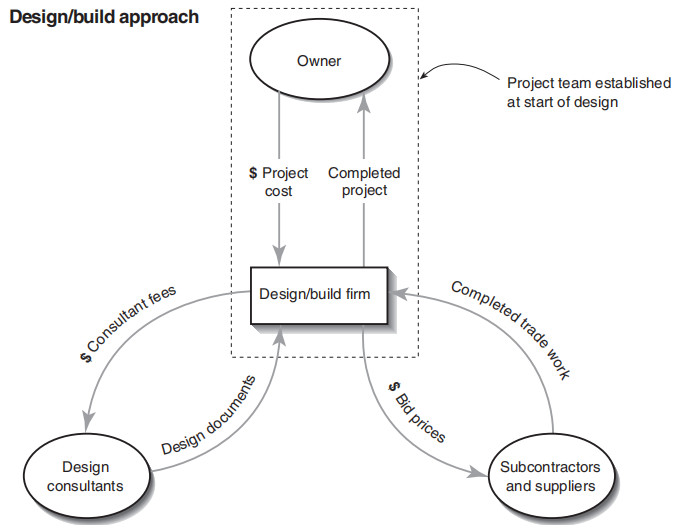
The firm hired by the owner will perform both design and construction. Firms offering such service are usually called design/build firms. They have in-house employees or joint venture firms that come together contractually to perform a single project. The design/ build firms can hire subcontractors to perform the actual construction in the field.
Advantages:
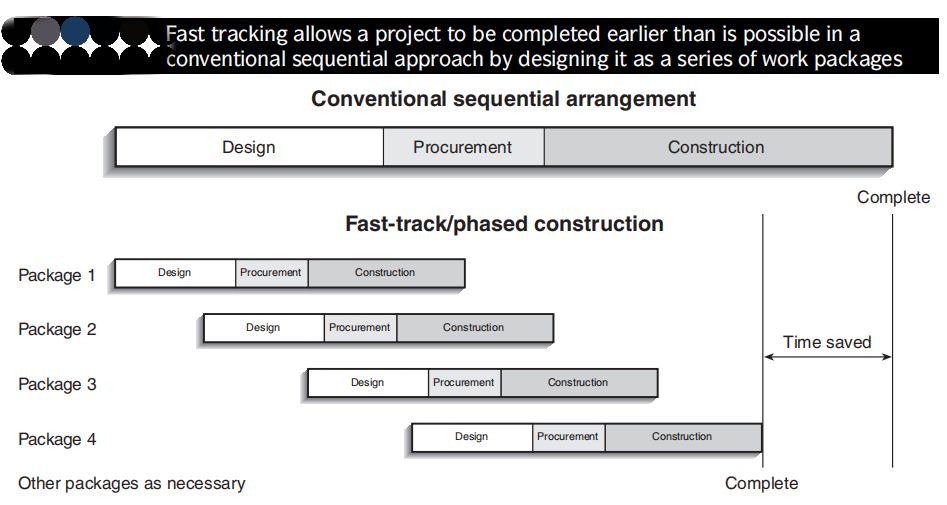
☝ Good communication between the design team and the construction team. Many large design/build firms specialize in particular areas, such as oil refineries and power plants offshore oil drilling platforms. They can guarantee the collaboration between the design and construction phases.The collaboration allows the project to be easily fast-tracked, cutting down on overall schedule for the project.
☝ The owner is less involved and can sit outside of the direct day-to-day communication between designer and constructor.
Disadvantages:
☟ No guarantee of a firm price.The firm is hired before the design has started, so the owner may not have a good idea about the final price.
☟ No guarantee of a firm price.The firm is hired before the design has started, so the owner may not have a good idea about the final price.
☟ Lack of checks and balances. the product could be less than the owner had hoped for. In the traditional arrangement, the designer prepares a complete set of documents, which is used to measure and evaluate the performance of the contractor in the filed. But in the design/build arrangement, the designer and build works for the same company. So the owner can only rely on the ethics of the firm.
★Construction management(工程管理模式)
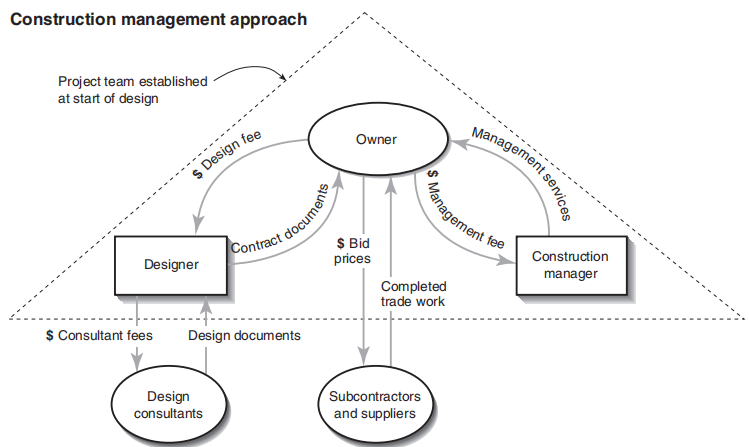
In this delivery method the owner hires both a design firm and a construction project management firm before the construction. The responsibility of the hired firm varies, depending on the owner’s involvement. This delivery method has many variations, including program management, professional management, construction management, and professional construction management. The differences among these arrangements reflect the expertise of the management team. In a construction management delivery method the owner does much of the programming and designer selection.
Advantages:
☝ Good communication among the owner, the designer, and the constructor throughout the project (from beginning to the end) the designer has a say in selecting the contractor and reviewing the work in the field. Problems are solved collaboratively because they share the same goal- to produce the best product for the owner. Both architect and the contractor are paid by their professional expertise through the entire project.
☝ It allows fast tracking and time saving because the design and construction people work together early enough to develop the necessary schedules.
☝ The owner receives the cost benefit of the competition among the subcontractor bids.
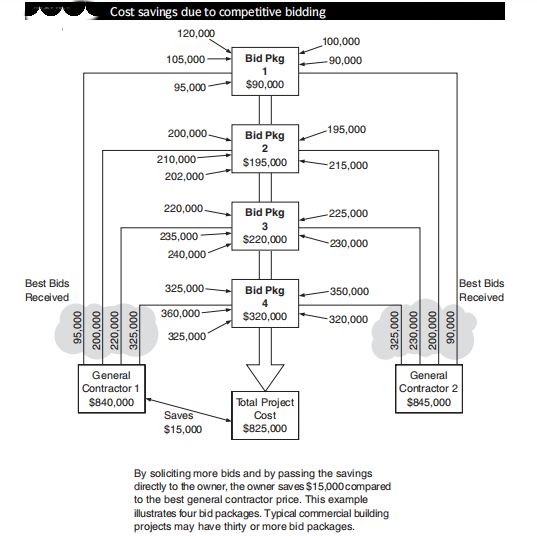
☝ Easy implementation of changes during the course of construction because of the close communication between the designer and construction manager.
Disadvantages:
☟ This arrangement requires a more sophisticated owner than the other two delivery methods.
☟ If the good communication and cooperation among owner, designer and construction manager is gone, all the advantages will became disadvantages.
★IPD(综合交付模式)
Integrated project delivery (IPD) is a project delivery approach that assembles a team and aligns interests between the critical particpants early in the construction process to achieve project success. The project owner, designer, constructor, and critical subcontractors and design consultants may all be included. The model can be applied to a variety of contract types.(综合项目交付是一种项目交付方法,为了项目成功,它在施工过程的早期组建团队并协调关键参与者之间的利益。项目业主、设计师、建造商、关键分包商和设计顾问可能都包括在内。该方式可应用于各种合同类型。)
IPD seeks to streamline processes and information sharing with the early involvement of important project participants. Key trade contractors such as a mechanical, electrical, or curtain wall subcontractor may be brought into the design process as a “stakeholder” sharing in goal setting and profit sharing as appropriate. The basis of the model is collaboration and a shared information platform such Building Information Model (BIM) is a critical tool to the IPD delivery approach.(IPD寻求通过项目重要参与方的早期参与来简化流程、实现信息共享。关键贸易承包商,如机械、电气或幕墙分包商都可作为“利益相关者”参与设计过程、分享目标设定和利润分享。该模型的基础是协作和共享信息平台,如建筑信息模型BIM是IPD交付方法的关键工具。)
☛Summary:
In some cases the three basic delivery methods are used together. Take the real estate development project as an example. Sometimes the project starts with a construction project management arrangement. Then as the design nears completion, the construction manager negotiates a fixed price with the owner, and the project becomes a design/bid/build arrangement.
Discussion


