Introduction
This chapter will center around the managerial(管理的) and leadership(领导) skills important to today's construction professionals, especially to project manager. Employees, materials, and equipment must all be organized, supervised, and brought to bear on(对...产生影响) the project in a timely and cost-efficient manner.
Leading a significant construction project can be compared to going into a battle. Whether the battle a failure or a triumphant(胜利), it depends on the commander. In construction project, the commander is the project manager(项目经理).
The project manager must be self-confident and get the respect of all members of the project team. Due to the time, cost and organizational pressure a project manager faces, his or her looks, stature (身材身高height) and personality may be just as important as his or her understanding of theoretical managerial principles. Project manager need integrity(正直), vision(远见) and confidence to direct and lead their project teams through the entire design/build process.To a project manager, dialogue and discussion are nice, but timely decisions are a necessity, which is difficult without precedent(先前的) or imperfect knowledge, so project manager is a demanding(要求高的) position to most people.
To survive(生存), and prosper(繁荣、发展), construction companies need well-thought (深思熟虑的)policies and procedures, training, work condition, and communication. Project manager must provide aggressive management, discipline, and motivation to the project team.
★What's a project ?(什么是项目)
More and more work is being classified as projects, Individuals are being assigned responsibility to achieve a specific objective within a given budget and by a specified deadline(最后期限). Project management, with its triple(三角) focus on time, cost, and performance, is proving to be an efficient, flexible way to get things done.

----A project is a unique venture (独特的冒险)with a beginning and end, conducted by people to meet established goals within parameters(参数) of cost, schedule, and quality.
---A project can be considered to be any series of activities or tasks that:–Have a specific objective to be completed within certain specifications(规范、说明书) –Have defined start and end date –Have funding limits –Consume human and nonhuman resources.
☛A deeper look at project:
---Projects are complex, one-time process: a project arises for a specific purpose or to meet a stated goal; they are complex because they typically require the coordinated inputs of numerous members of the organization
---Projects are limited by budget, schedule, and resources: project work requires that members work with limited financial and human resources for a specified time period; project are resource-constrained activities
---Projects are developed to resolve a clear goal or set of goals: its goals or deliverables(可交付成果), define the nature of the project and that of its team
---Projects are customer-oriented(以客户为导向的): the underlying purpose of any project is to satisfy customer needs either internal or external customers(内部或者外部的客户)
Projects are the "building blocks" of corporate strategy because they serve as the most basic tools by which firms can implement previously formulated(执行先前制定的) objectives and strategies.
★Difference between operation and project(项目与运营的区别)
Operation refers to ongoing, day-to-day activities in which an organization engages while producing goods or services; operation uses existing system, properties(不动产、房屋), and capabilities in a continuous, fairly repetitive(重复的) manner. Projects take place outside the normal, operation-oriented world of the firm.
★Determinants of Project Success(项目成功的判定因素)
Project success must take into consideration the elements that define the very nature of a project
Time: (工期目标实现)projects are constrained by a specified time frame during which they must be completed
Cost: (成本管控目标实现)all project have budget limitation. they must meet budget and schedule expectations.
Performance(quality): (质量目标实现)all projects are developed in order to adhere to some initially determined technical specifications ( the CTQ is closely related to project efficiency)
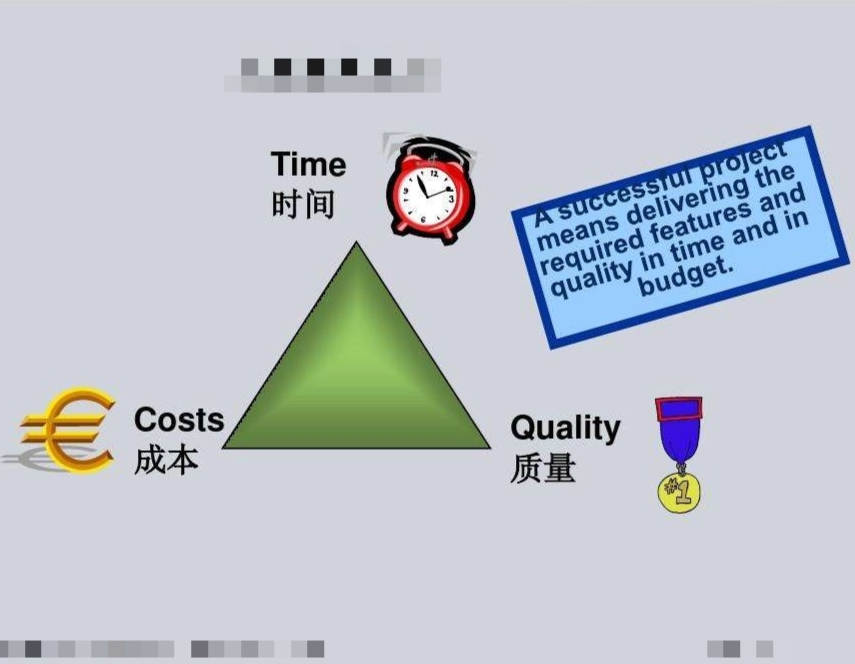
Client acceptance: (顾客满意目标实现)the principle of client acceptance argues that projects are developed with customers, or clients, in mind, and their purpose is to satisfy customers’ needs.(this is closely related to business or commercial success)
Future opportunity generation :(未来机会创造目标实现) Future potential. determining whether the project opened new markets or new product lines or helped to develop new technology ( this is closely related to future success)
![D]_ACSBJCL1M]QHR$B0P%[8.png](https://p.ananas.chaoxing.com/star3/origin/d38c7c031d02230a7caff9f69bb9225f.png)
★What is Project Management?(什么是项目管理)
问:What is management?
答:Management is the process of getting activities completed efficiently and effectively with and through people.”It includes 4 major functions:planning, organizing, leading and controlling.
(Efficiency:效率 (做事情要正确)“Doing things right Getting the most output for the least inputs ”)
(Effectiveness :效果 (做正确的事情)“Doing the right things”Attaining organizational goals)
(It’s more important to do right things than to do things right “做正确的事要比正确地做事重要得多 ")
Project management is a comprehensive and exciting undertaking(综合性的激动人心的事业). It requires us to understand aspects of management science in building schedules, assigning(分配) resources, monitoring and controlling our projects and so forth(等等). At the same time, successful project managers also must integrate(整合,融合) fundamental issues of behavioral science, involing knowledge of human beings, leadership practices, motivation and team development, conflict resolution, and negotiation skills. In a nutshell, project management is an exciting and challenging blend(混合) of the science and art of management. It always focuses on the following tasks:
▶Selecting a team: team building, conflict management, leadership, and motivation are the first challenges that PMs face
▶Developing project objectives and execution plan: identifying project requirements and a logical plan to develop the project are crucial
▶Performing risk management activities: projects are not developed without a clear sense of the risks involved in their planning and implementation
▶Cost estimating and budgeting: because projects are resource-constrained activities, careful budgeting and cost estimation are critical
▶Scheduling: the heart of project planning revolves around the process of creating clear, aggressive, yet reasonable schedules that chart the most efficient course to project completion
▶Managing resources: the final step in project planning is the careful management of project resources, including project team personnel, to most efficiently perform tasks
PM is often divided into 9 Distinct Areas (9个专项管理领域) These nine areas form the basis of the Project Management Institute’s certification program for project managers in any industry.
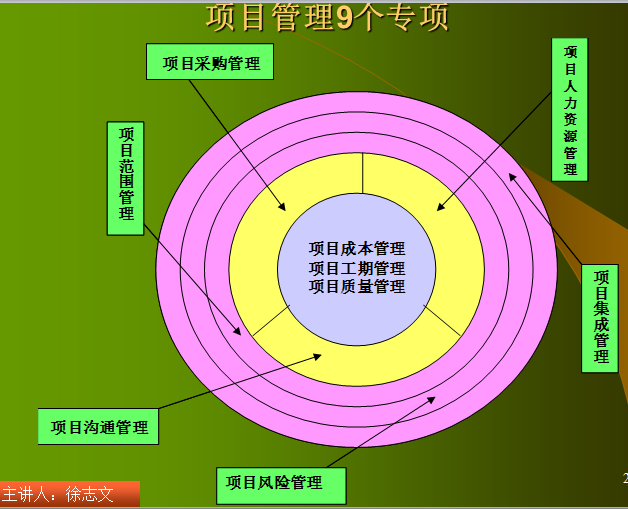
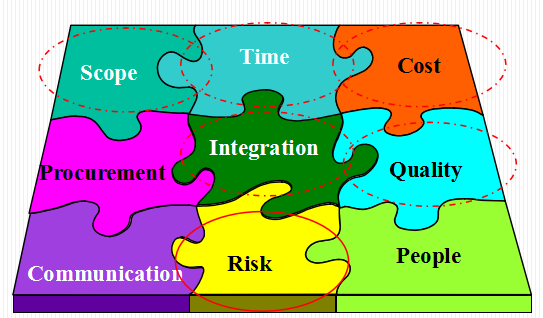
1.Project integration management(项目集成管理) to ensure that the various project elements are effectively coordinated.
2.Project scope management(项目范围管理) to ensure that all the work required (and only the required work) is included.
3.Project time management(项目工期管理) to provide an effective project schedule. 4.Project cost management(项目成本管理) to identify needed resources and maintain budget control.
5.Project quality management(项目质量管理) to ensure functional requirements are met.
6.Project human resource management(项目人力资源管理) to development and effectively employ project personnel.
7.Project communications management(项目沟通管理) to ensure effective internal and external communications.
8.Project risk management(项目风险管理) to analyze and mitigate potential risks.
9.Project procurement management(项目采购管理) to obtain necessary resources from external sources.
视频:What’ s project management?
视频:Project planning for beginner
★ The traits of Project manager:
Poject managers represent the new corporate elite(企业精英): a corps(一群人) of skilled individuals who routinely(常规的,例行的) make order out of chaos(拨乱反正), improving a firm's bottom line and burnishing(磨光,打磨) their own value in the process. Successful PM(projet manager) must possess both behavioral(行为的) and science knowledge:


