Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) is a broad concept referring to the incorporation of valid and relevant external evidence during the decision making process.
In the health sciences, such evidence is most commonly found in high-quality research studies that can be applied to the specific patient or population being considered.
什么是循证实践?
The most common definition of Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) is from Dr. David Sackett. EBP is “the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of the individual patient. It means integrating individual clinical expertise with the best available external clinical evidence from systematic research.” (Sackett D, 1996)EBP is the integration of clinical expertise, patient values, and the best research evidence into the decision making process for patient care. Clinical expertise refers to the clinician’s cumulated experience, education and clinical skills. The patient brings to the encounter his or her own personal preferences and unique concerns, expectations, and values. The best research evidence is usually found in clinically relevant research that has been conducted using sound methodology. (Sackett D, 2002)

The evidence, by itself, does not make the decision, but it can help support the patient care process. The full integration of these three components into clinical decisions enhances the opportunity for optimal clinical outcomes and quality of life. The practice of EBP is usually triggered by patient encounters which generate questions about the effects of therapy, the utility of diagnostic tests, the prognosis of diseases, and/or the etiology of disorders.
Evidence-Based Practice requires new skills of the clinician, including efficient literature searching, and the application of formal rules of evidence in evaluating the clinical literature.
循证实践模式
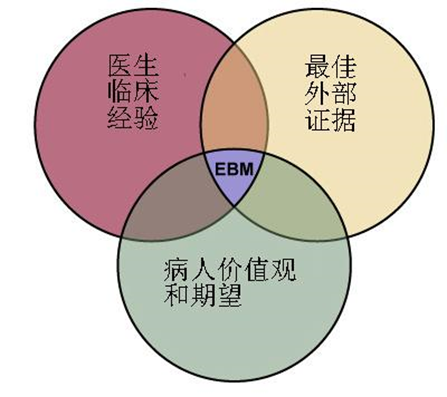
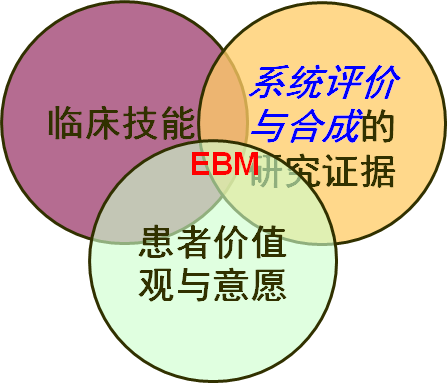
1992年提出的循证医学模式概念 2014年更新后的循证医学概念
循证实践的步骤:
ASSESS | 1. Start with the patient -- a clinical problem or question arises from the care of the patient |
ASK | 2. Construct a well built clinical question derived from the case |
ACQUIRE | 3. Select the appropriate resource(s) and conduct a search |
APPRAISE | 4. Appraise that evidence for its validity (closeness to the truth) and applicability (usefulness in clinical practice) |
APPLY: | 5. Return to the patient -- integrate that evidence with clinical expertise, patient preferences and apply it to practice |
Self-evaluation | 6. Evaluate your performance with this patient |
拓展学习
1.循证医学在中国的起源与发展
2.循证实践重要理念的提出
"Evidence-Based Medicine: A New Approach to Teaching the Practice of Medicine"
Centre for Health Evidence
"Evidence-Based Medicine: What it is and what it isn`t"
D. L. Sackett, W. M. Rosenberg, J. A. Gray, R. B. Haynes, and W. S. Richardson

Introduction to Evidence-Based Medicine
Duke University Medical Center Library Tutorial
Accessing preappraised evidence: fine-tuning the 5S model into a 6S model
Alba DiCenso, Liz Bayley, and R B Haynes. "ACP Journal Club. Editorial." Annals of Internal Medicine 151.6 (2009): JC3-2, JC3.

3.重要检索资源
Check out these helpful HSL tutorials for tips on conducting an effective and efficient search!
A primer on the foundations of database searching
Searching the biomedical database Medline, using the OVID search interface
Searching the biomedical database Medline, using the PubMed interface
Searching for systematic reviews and more on the Cochrane Library (requires Flash)
Searching the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health (CINAHL) database
4.循证实践工具箱
工具包
Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Oxford University
指南
AGREE II: Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation
Downloadable instrument for evaluating clinical practice guidelines.
McMaster guide to inclusion criteria for systematic reviews.
Critical Appraisal of Evidence
Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine
Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine
CATWalk: A Guide to Critically Appraised Topics
University of Alberta
Software for creating critically-appraised topics.
From Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Oxford UniversityGuide to searching the grey literature from CADTH
书籍与文献
Users' Guide to the Medical Literature - 3rd Edition
Available through JAMA Evidence
JAMA Rational Clinical Examination Series
Journal of the American Medical Association
BMJ series on evaluating research articles
Evidence-Based Surgery Article Series
Surgical Outcomes Research Centre (SOURCE) at McMaster
参考资讯
"Making Sense of Diagnostic Tests Likelihood Ratios"

Perera R. & Heneghan C.
Standards for the Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies


