-
1.1前 言
-
1.2第一章 跨文化交际概论
-
1.2.11.跨文化交际的定义
-
1.2.22.跨文化交际的分类
-
1.2.33.学习跨文化交际的意义
-
1.3第二章 文化休克
-
1.3.11.文化休克的定义和特征
-
1.3.22.文化休克产生的原因
-
1.4第三章 跨文化交际的失误
-
1.4.11.言语交际失误
-
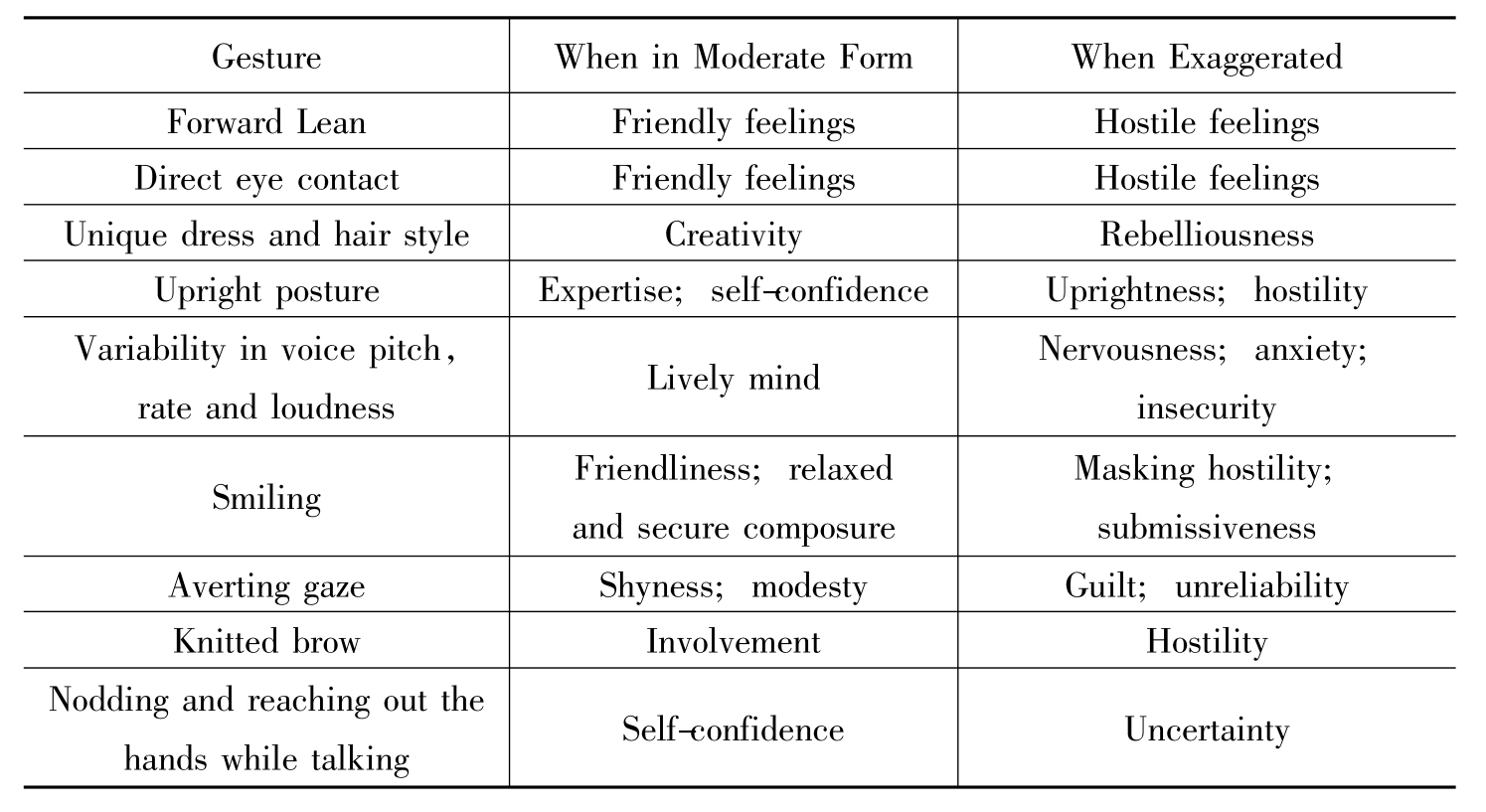
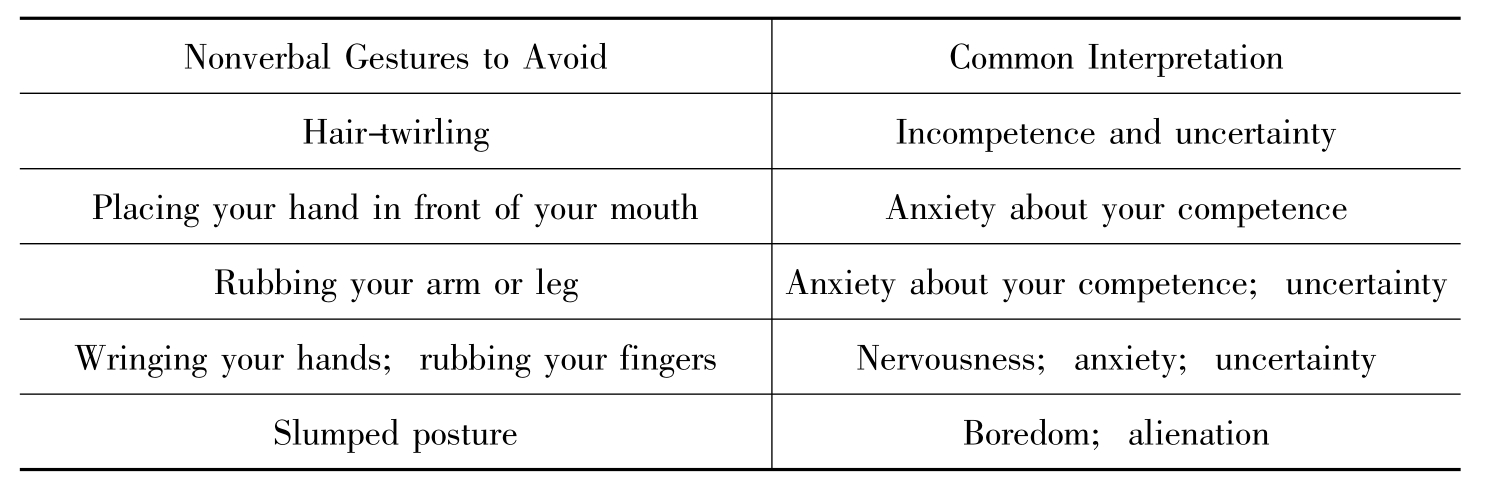
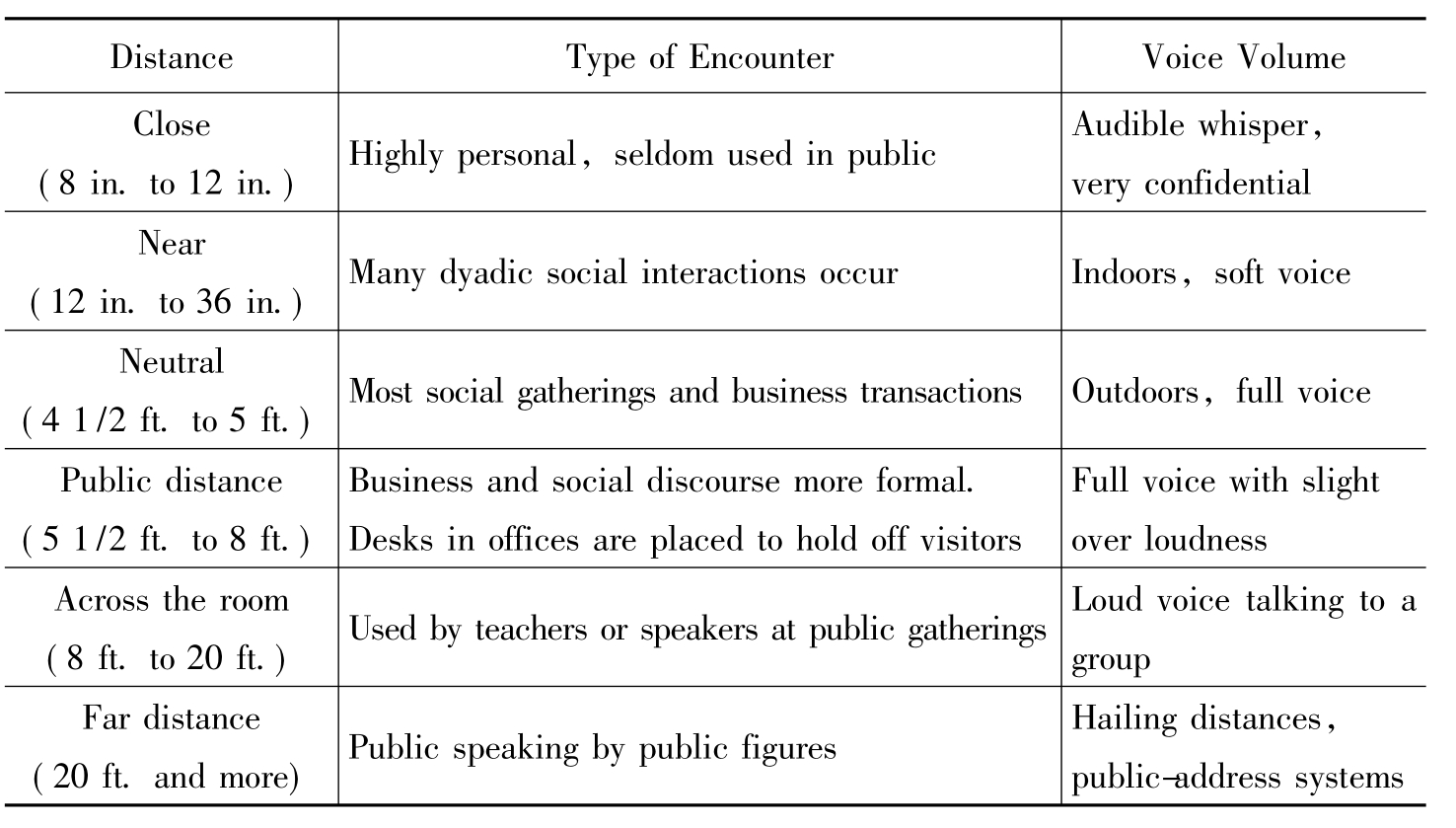
1.4.22.非言语交际失误
-
1.5第四章 交际
-
1.5.11.交际的概念
-
1.5.22.影响交际的因素
-
1.5.33.交际的过程
-
1.5.44.交际的模式
-
1.6第五章 交际符号
-
1.6.11.符号的类型
-
1.6.22.符号与含义
-
1.7第六章 跨文化的言语交际
-
1.7.11.语言是文化的产物与载体
-
1.7.22.言语符号的交际功能
-
1.7.33.言语符号的交际局限性
-
1.7.44.言语符号的交际失误
-
1.8第七章 跨文化非言语交际
-
1.9第八章 文化
-
1.9.11.文化的组成
-
1.9.22.文化的分类
-
1.9.33.文化的功能
-
1.9.44.文化的特点
-
1.10第九章 中西文化的渊源及其影响下形成的文化差异
-
1.10.11.中国文化的渊源及其影响
-
1.10.22.西方文化的渊源及其影响
-
1.10.33.中西文化的差异性特点
-
1.11第十章 观念对跨文化交际的影响
-
1.11.11.观念差异
-
1.11.22.观念对交际的影响
-
1.12第十一章 环境对跨文化交际的影响
-
1.12.11.圈内环境和圈外环境
-
1.12.22.自然环境、社会环境和人物个性环境
-
1.12.33.高环境与低环境
-
1.13第十二章 跨文化交际与规范
-
1.13.11.规范
-
1.13.22.规范对跨文化交际的影响
-
1.14第十三章 跨文化交际中的习俗与禁忌
-
1.14.11.习俗
-
1.14.22.禁忌
-
1.15第十四章 跨文化交际中的礼仪
-
1.15.11.礼仪
-
1.15.22.交际中的礼仪
-
1.16第十五章 跨文化交际的原则
-
1.16.11.质量原则
-
1.16.22.礼貌原则
-
1.16.33.得体与适应原则
-
1.16.44.机敏原则
-
1.16.55.尊重习俗的原则
-
1.16.66.民族中心原则
-
1.17Reading Material 1 Intercultural Communication
-
1.18Reading Material 2 Communication
-
1.19Reading Material 3 Verbal Communication (VC)
-
1.20Reading Material 4 Nonverbal Communication (NVC)
-
1.21Reading Material 5 Culture
-
1.22Reading Material 6 Perception
-
1.23Reading Material 7 Social Groupings and Relationsh...
-
1.24Reading Material 8 Customary or Social Conventions
-
1.25Reading Material 9 Social Norms
-
1.26Reading Material 10 Bridal Customs and Traditions
-
1.27Reading Material 11 Swedish Folklore
-
1.28Reading Material 12 Intercultural Communication Pr...
-
1.29Reading Material 13 Perception Can Be Linked to Cu...
-
1.30Reading Material 14 Perception Can Be Linked to Cu...
-
1.31Reading Material 15 Marriage Culture of Naxi Peopl...
-
1.32参考书目
1
跨文化交际