Economic growth and dEvElopmEnt of social undErtakings
The decade since 1950 was an extraordinary period. In order to accomplish the arduous tasks of reform and development in a complicated and volatile situation, the Party led Dulan people of all ethnic groups in holding high the great banner of unity of nationalities, overcoming difficulties, creating a new situation in modernization construction. In order to implement the guiding principles of Reform and Open Up and focus on strengthening economy, county government of Dulan made decisions on and arrangements for major issues of overall significance such as deepening industrial restructuring, improving the market economy, and building a harmonious society. All these helped the county score great new achievements.
Flourishing industry and economy: The establishment of Dulan’s modern industry comes from a humble origin of handicraft industry. Established in 1950s, the development of such early industry was greatly impeded by county’s poor infrastructure, and the rough situation put the economic development in difficult position in the following two decades. For the picture to get better, Dulan’s industrial development was boosted by the Reform and Open up policy; during late 1970s, and collective industrial enterprises grow out of the handicraft sector. Yet, collective industrial enterprises are not outstanding at all in terms of productivity and profitability, the county thus decided to reorient itself toward more economic-rationality and reemphasize on efficiency and cost-benefit considerations. During the 8th Five-Year Plan period (1991-1995), the government reorganized the industrial enterprises in the county, and adjusted their structure of production, to urge technological transformation. By the end of 8th plan, the number of county’s industrial enterprises reached 224, 19 of them are state-owned, gross output value of industry reached 26 million Yuan by 1995. During the 9th Five-Year Plan (1996-2000), the central government adopted the strategy of west development. Seized this historical opportunity, county’s industry had been developing by leaps and bounds, industries with different types of ownership started to flourish, while the policies were made to facilitate industrial entities of non-public sector, by 2000, county’s total value of industrial output had reached 42 million.
To ensure continuous development of industry, the government gave full play to county’s resource advantages and looked to step up investment in industrial facility construction. During the 10th Five Year Plan period (2000-2005), 58 million Yuan was allocated to local industrial facility construction; in return, county’s value of industrial output increased drastically and reached 264 million Yuan. With industry development fully accelerated during the 11th Five Year Plan (2006-2010) period, Dulan’s industrial strength was further enhanced. Series of product lines were put into production; main product categories included iron powder, copper powder, lead oxide, gold ore, raw coal, and potash fertilizer. Meanwhile, Dulan County’s value of industrial output started to take larger portion in provincial GNP. In 2009, county’s gross value of industrial output hit 576 million Yuan, while industrial added value and sales value of industry reached 256 million Yuan and 416 million Yuan respectively. Remarkable development of county’s industry during the period also gave an impetus to fiscal income growth. In 2009, county’s fiscal income reached 47.5 million Yuan, which is 15 times as much as the figure of 1990.
Endeavors in attracting investment: During the decades between 1996 and 2010, the value of fixed assets investment projects being developed rose to a record. Until 2009, county’s total investment in fixed assets exceeded 413 million Yuan. During the same period, the county created measures to attract foreign money, contracts with a total value of 660 million Yuan had been made with foreign traders by 2009.
Development of agriculture and animal science: The agricultural history of Dulan dates back to 280 years ago. Earliest pioneers arrived at this region in 1727. These pioneers were Han people, who were exiled by Qing government, they were forced to leave inland area and open up barren land in Qaidam Basin. The wasteland was reclaimed by the joint force of army and civilian at that time, villages were built in current Nuomuhong region of Dulan County, as their living place. However, owning to the hostile environment and inappropriate farming method, the reclamation activity was a failure, and most of pioneers died of starving. The second largescale reclamation activity in this area was carried out in 1942. To supply the military force and expand westward, Kuomintang Government of Qinghai sent Ma Cheng-xiang, the commander of 5th Division, to station his troops and open up wasteland in this area, 2 bureaus of reclamation and 4 subordinate reclamation groups were founded later on. Between 1945 and 1949, large waves of refugees flood into Dulan from Haidong, small-scale agricultural regions started to occur in Chahanwusu, Xiangride, Xiariha and Nuomuhong regions accordingly. Despite the sprout of small-scale agricultural regions around Dulan region, the refugees still lived a pathetic life upon the barren land, with slash and burn as the main technique applied to agricultural production; crop yield was extremely low.
Situation started to change at 1950’s, the land reform won millions of supporters among the poor peasantry, and agricultural output increased moderately during this period. By 1950, the total area of farmland in the county was 13.5 thousand acres, while the grain yield reached 920 thousand kilograms. However, constrained by the hostile environment and under-developed agricultural techniques, the low agriculture productivity remained unchanged. To cope with such issues, extensive farming system was adopted, and the county’s grain planting area continued to rise. Although the total area of farmland had increased to 73.3 thousand acres by 1961, farmers still had just barely enough food to maintain a self-sufficient life style.
The introduction of household contract responsibility system provided an unprecedented opportunity for Dulan’s agricultural development between 1978 and 1990, and the situation started to turn for the better. This system greatly inspired farmers’ production initiative and helped elevate farmers from self-sufficient petty producers to commodity producers and managers. Moreover, it transformed production mode in rural areas, efforts were directed toward careful agricultural planning and the development of market-oriented, intensive agricultural operations. In addition to these structural changes, the county government and the newly established departments and institutions of agricultural technology also engaged in irrigation projects, ran large farms, and encouraged mechanization and fertilizer use. The practice of household contract responsibility not only released rural productive forces but also enhanced the comprehensive agricultural production capacity. By 1990, the estimated area of county’s farmland was 118 thousand acres, with grain production reaching 22 million kilograms. The planting area for oil-bearing crops was 2200 acres, with the crop yield of 0.28 million kilograms. Dulan County earned recognition for such achievement in agricultural development and was honored ‘National advanced county for commodity grain production and trading’ by Ministry of Commerce in 1989.
Step into 21st century, agricultural development in Dulan was confronted with new challenges. To cope with the change on supply and demand of agricultural products, planting of vegetables and forage crops were advocated by the government. In response to government’s policy, farmers altered planting structure, planting area of cereal crops decreased by 26% in 2003, while planting area of field mustard increased by 69.7%. In 2009, planting area of cereal crops further decreased by 24 thousand acres, while planting area of potatoes, forage crops and wolfberries reached 27.7, 7.7 and 73.6 thousand acres respectively. Farmers benefited from planting structure adjustment and their living standards have been improved markedly, in 2009, the average income of farmers was 4371 Yuan, while agricultural output value of the county peaked at 230 million Yuan. By 2010, the planting area of commercial wolfberry has reached 120 thousand acres, with annual fruit production of 600 thousand kilograms, which provides an additional annual income of 700 million Yuan for the county.
Dulan is also famous for its long history of animal husbandry; ancient people in this area began to keep livestock 2800 years ago. However, the development of animal husbandry had long been suffered from ceaseless war and followed epidemic diseases. Until 1949, the population of livestock in the county is still under 100 thousand.
Not until the establishment of PRC, animal husbandry production in Dulan was recovered: With epidemic control network built up among the villages and townships in the county; deratization operations and livestock breed improvement programmes carried out under the guidance of the People’s Government, the number of livestock increased rapidly to 570 thousand. The practical application of reform and open-up policy led to further development of county’s animal husbandry between 1978 and 1990; the number of livestock increased continuously during the decade, 1990 population of livestock was 668 thousand. With the reform deepened in pastoral area, more budget and man power were allocated to the project of livestock infrastructure construction, epidemic prevention and livestock breed improvement. Local goat breed improvement programme was launched in 1985, cashmere goats of fine breed, which originated in Liaoning Province, were introduced into Dulan County. The husbandry of hybrid goat was popularized in Xiangride, Xiangjia and Barlong, and produced a marked increase in wool yield. By 1986, average wool yields of improved goat breed reached 400 grams, which was four times as much as the average wool yield before 1985. Major breakthrough was also achieved in epidemic control and prevention programmes, by 1990, 33 types of epidemic diseases had been brought under control, and county’s overall value of livestock output had reached 10.4 million Yuan.
More endeavors are directed toward developing high-quality, high-productivity and high-efficiency animal husbandry industry in the following decade. Moreover, West Development policy brought unprecedented development of county’s animal husbandry after 2000, livestock population continues growth, and the number reached 1 million in 2009.

素有西北“枸杞王”之称的都兰诺木洪枸杞


高原粮仓——香日德
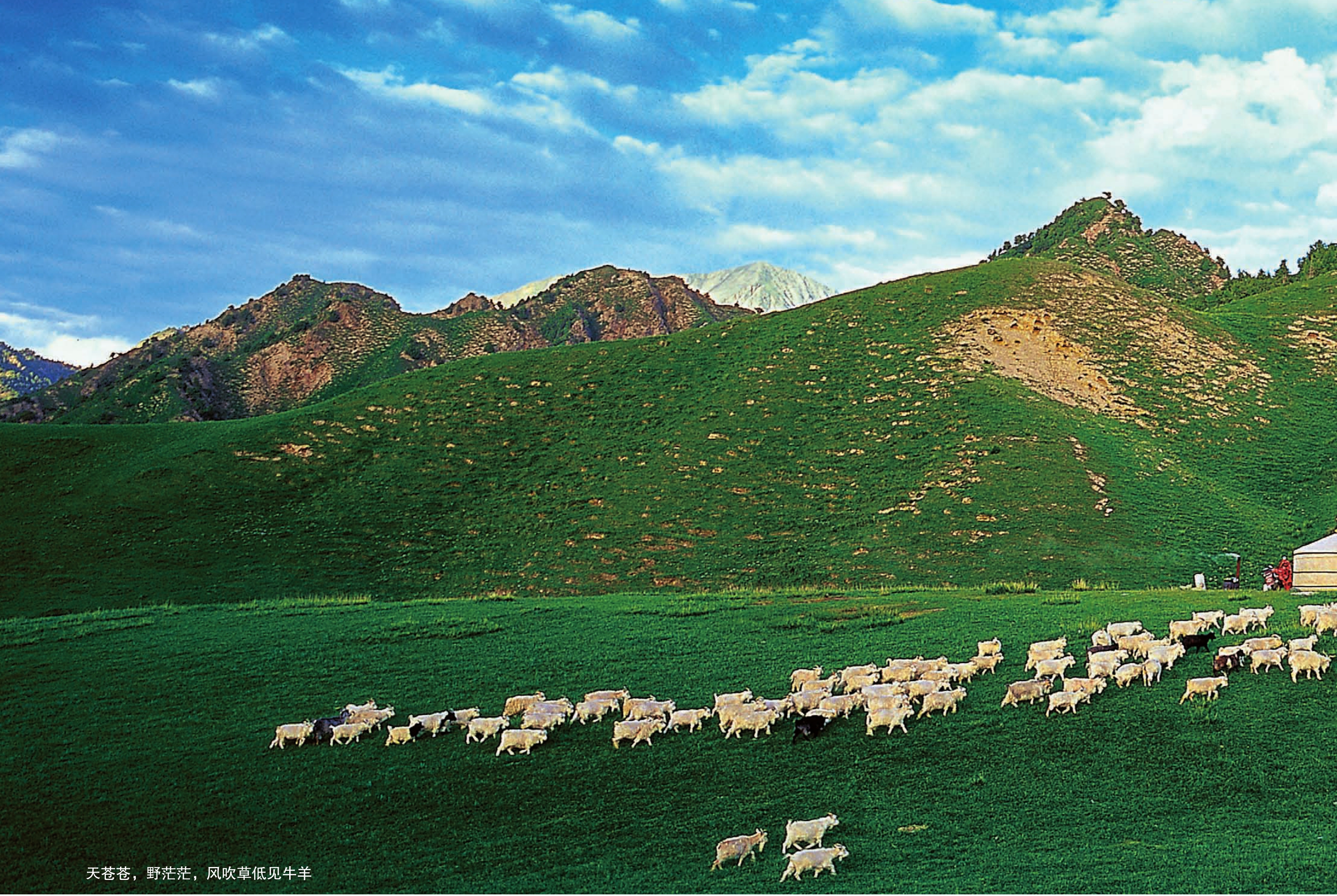


天苍苍,野茫茫,风吹草低见牛羊
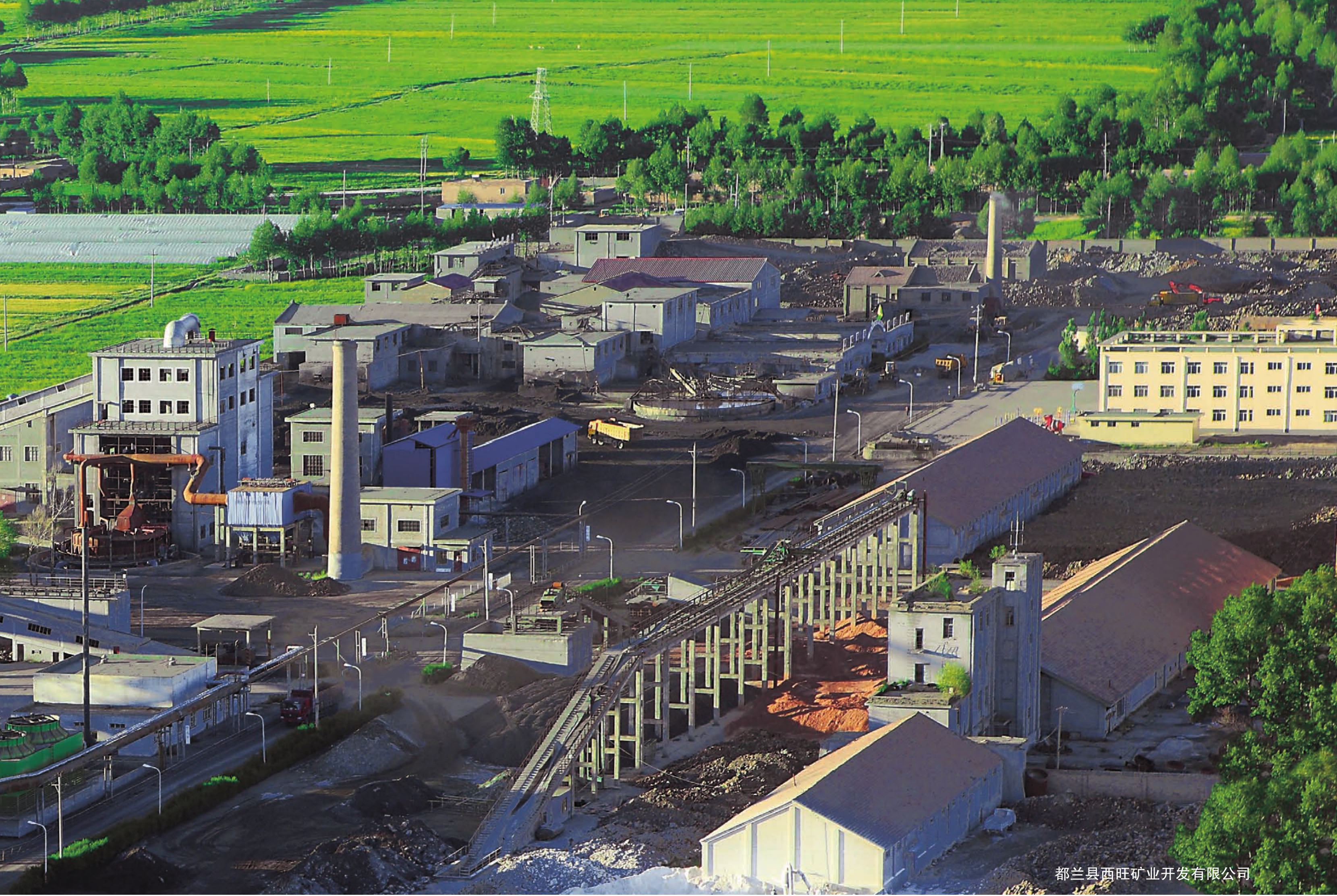



都兰县西旺矿业开发有限公司

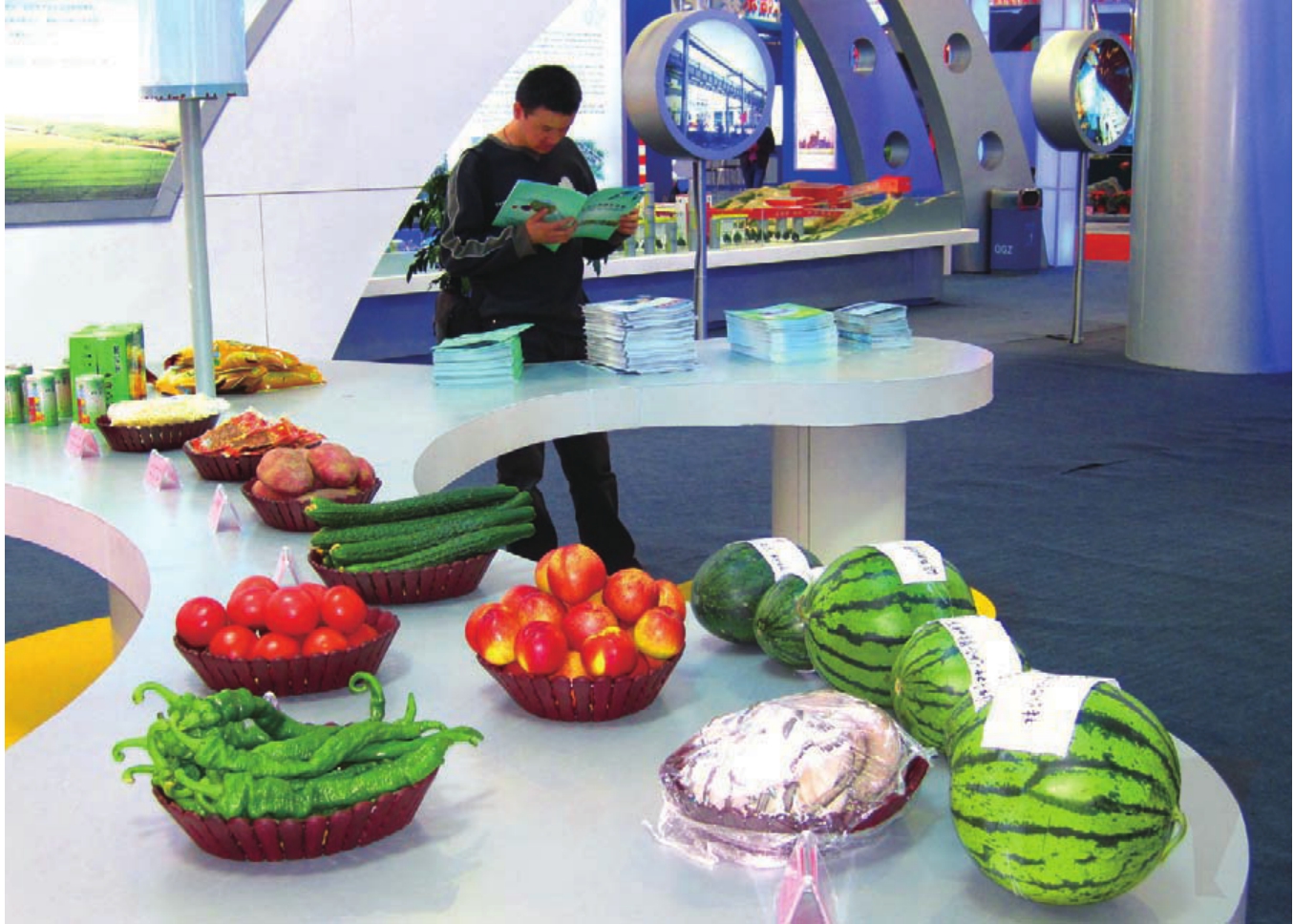
特色农业
素有柴达木盆地“绿洲”之称的都兰是一块待开发的宝地,地理条件优越,气候温润,资源丰富。
近年来,县委、县政府按照“一红一黄一绿一制种”和“一白一黑一草业”的农牧业结构调整思路,继续加大农牧业结构调整力度,对已经形成规模的枸杞、马铃薯种植加强引导规范,进一步扩大产业规模和效益,至“十二五”末,全县枸杞和马铃薯种植面积分别达到30万亩和10万亩。
都兰县共有耕地30余万亩,盛产小麦、青稞、油菜。春小麦单产曾达到1013.3公斤,创全国乃至世界最高记录,1989年进入了全国粮食生产交售百强县行列,号称“柴达木粮仓”。
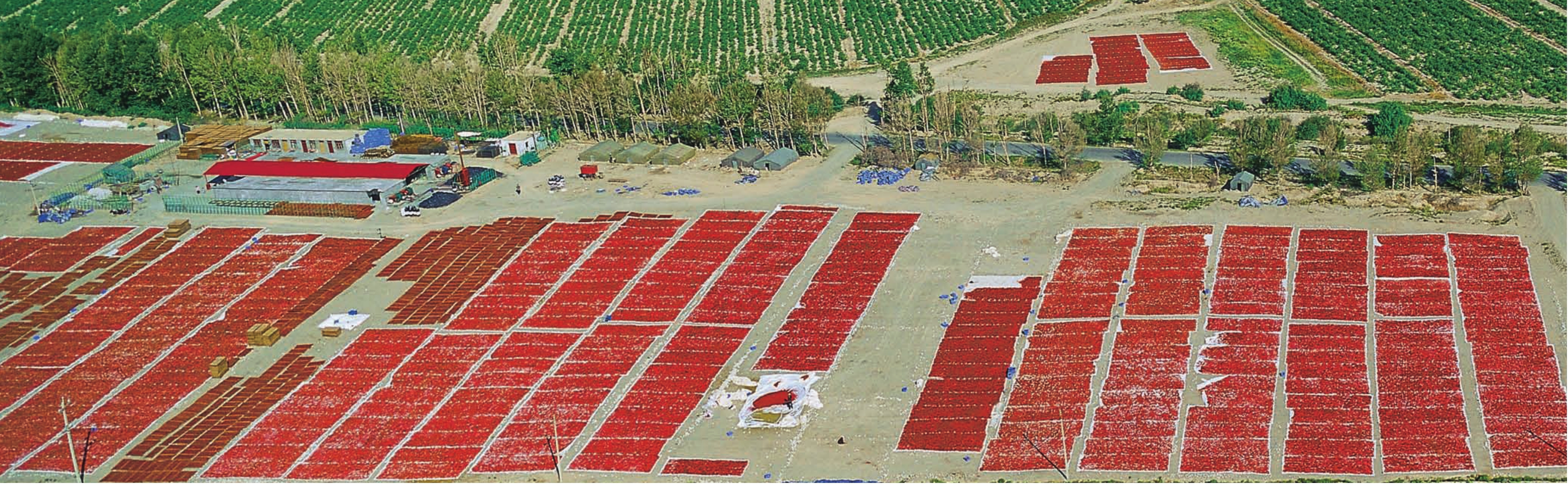
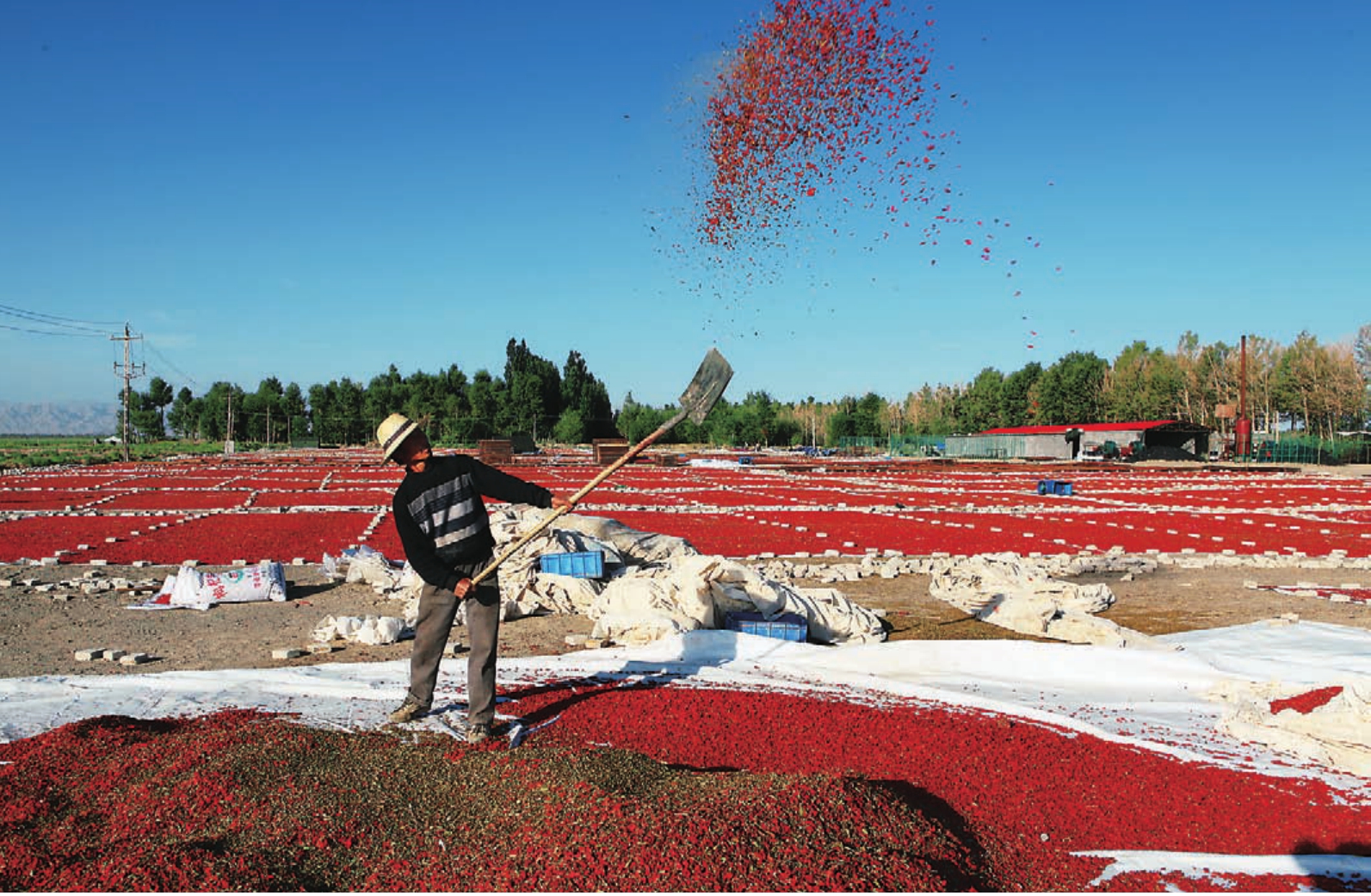
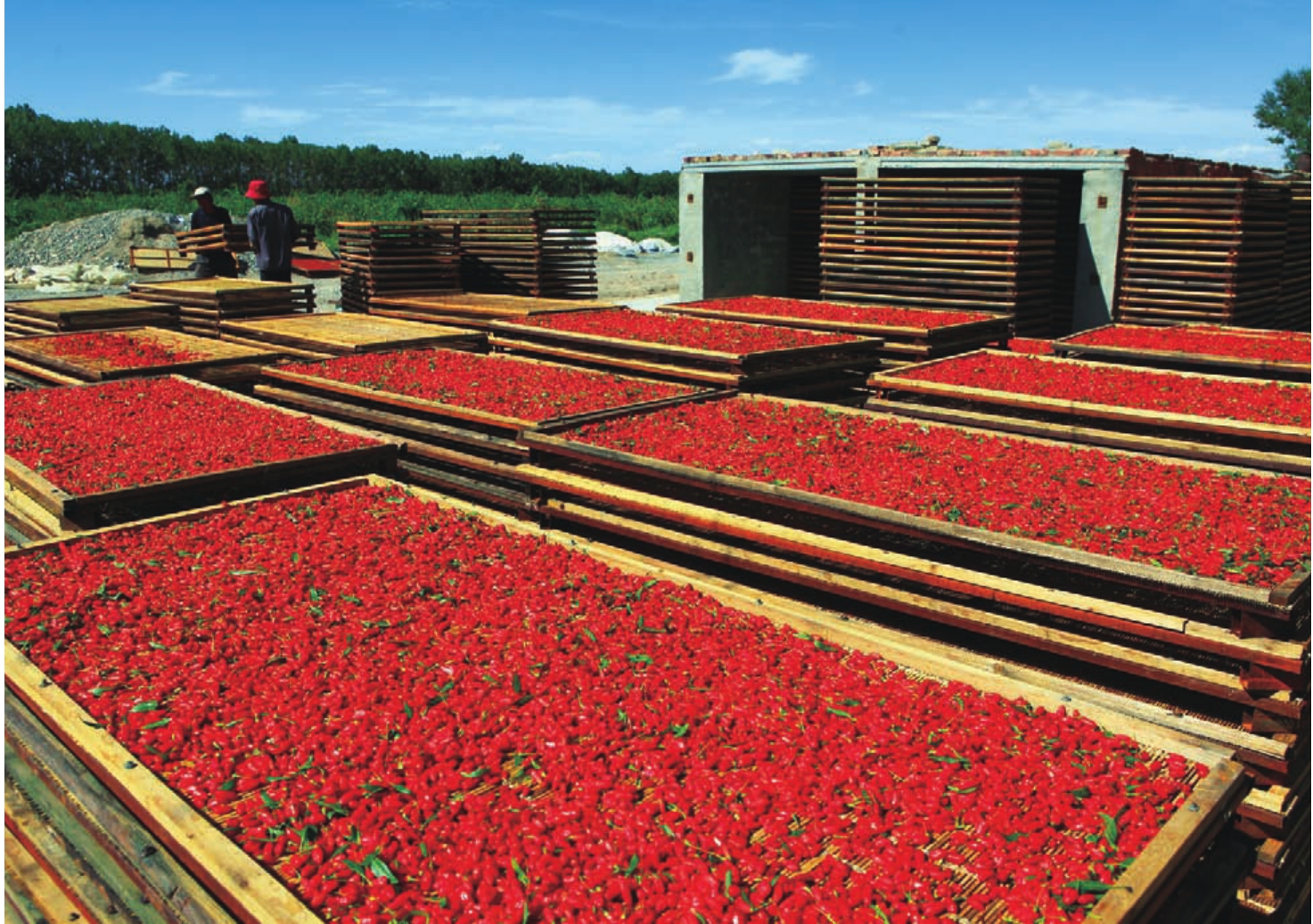








目前,全县枸杞种植面积已达到12万亩,今后三至五年内,将大幅度增加枸杞种植面积,逐步使诺木洪地区成为海西州最大的枸杞产业化种植基地。
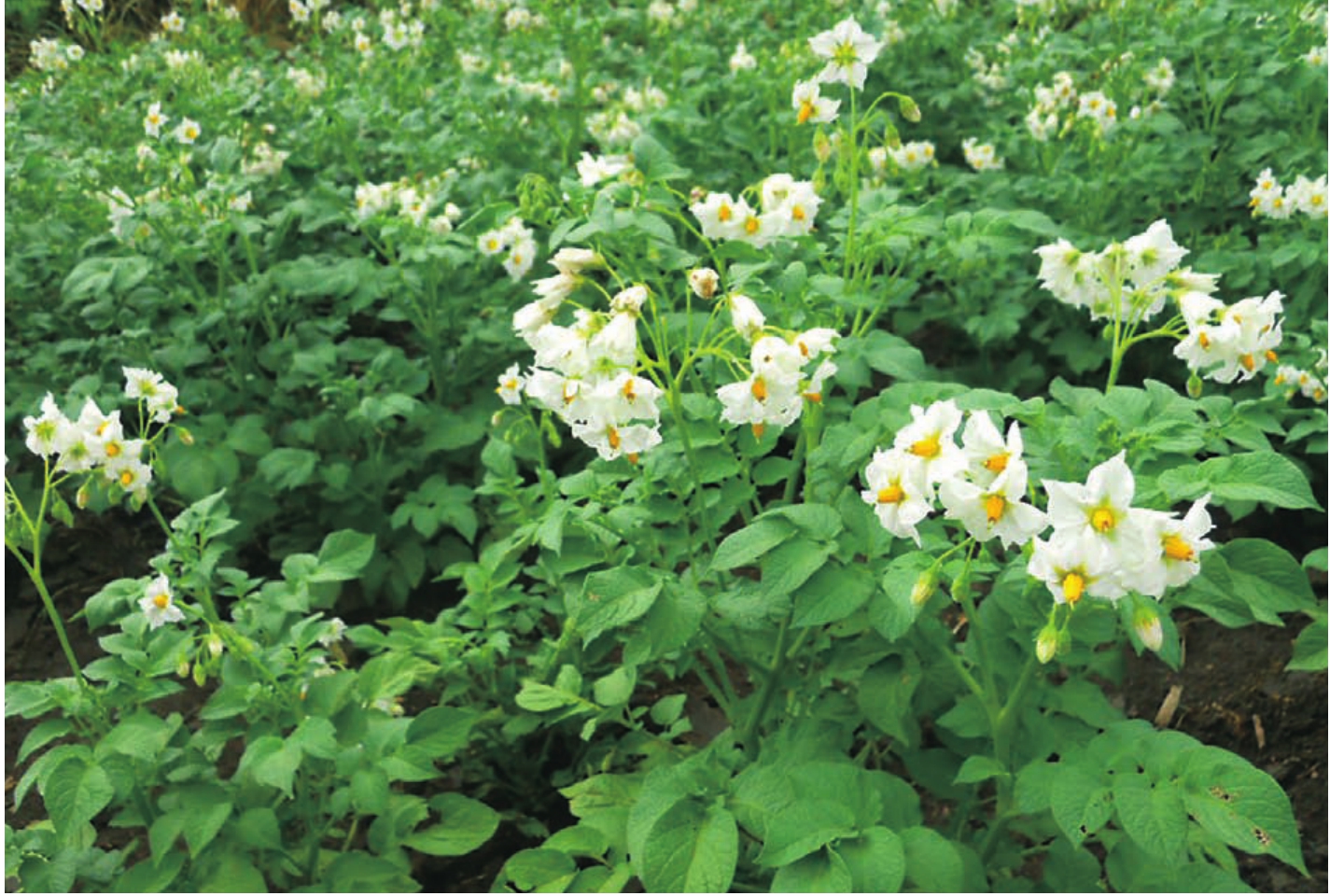
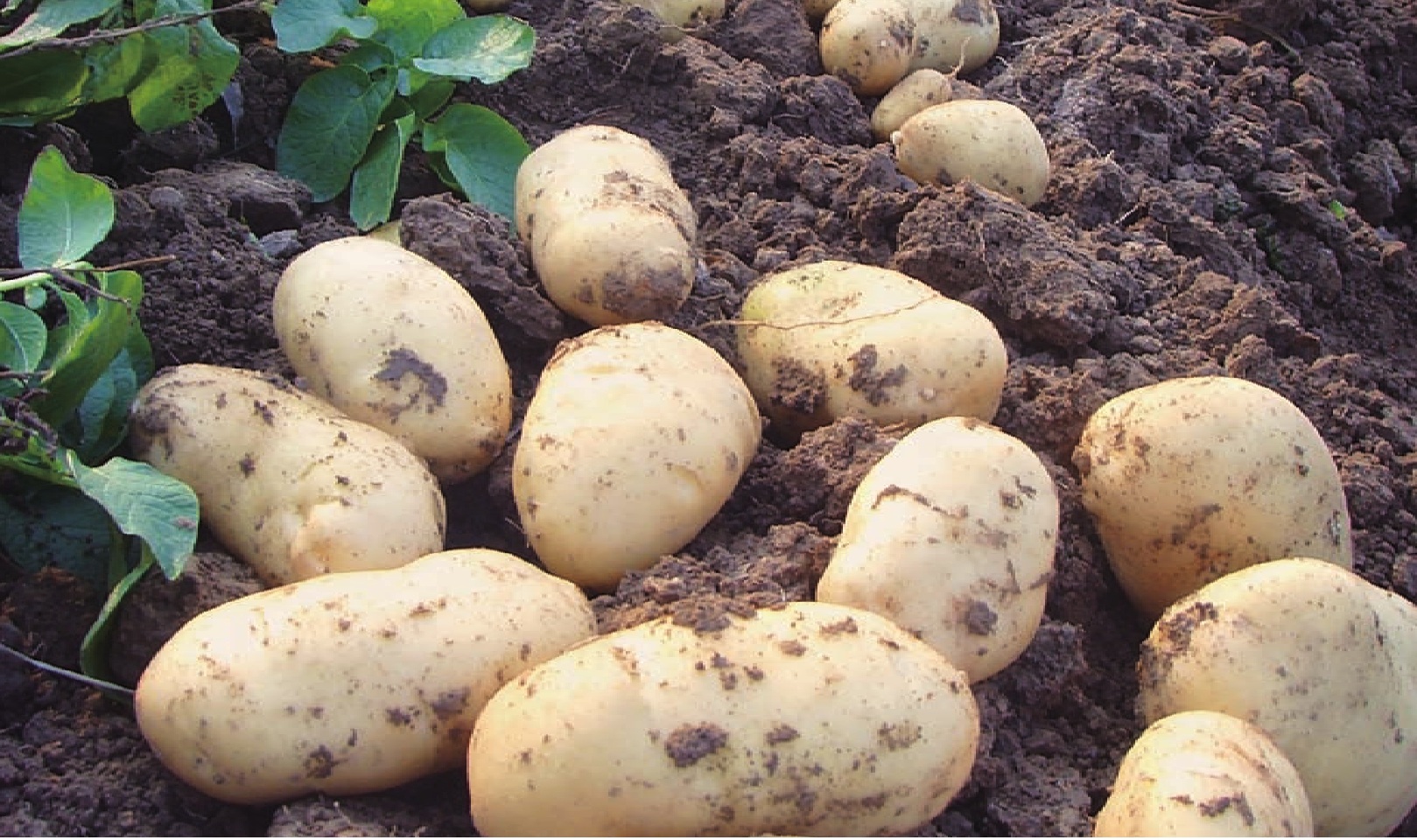



“都兰马铃薯”是都兰在农牧业发展中重点推出的特色品牌。都兰县巴隆乡耕地属于沙壤土壤,是马铃薯种植的最佳土壤,出产的脱毒马铃薯富含淀粉、糖类、蛋白质、矿物质、盐类和维生素B等营养物质,具有早熟、高产、味香、耐贮运等特点。应用在食品、纺织、石油化工、医药等各个领域,市场前景极为广阔。
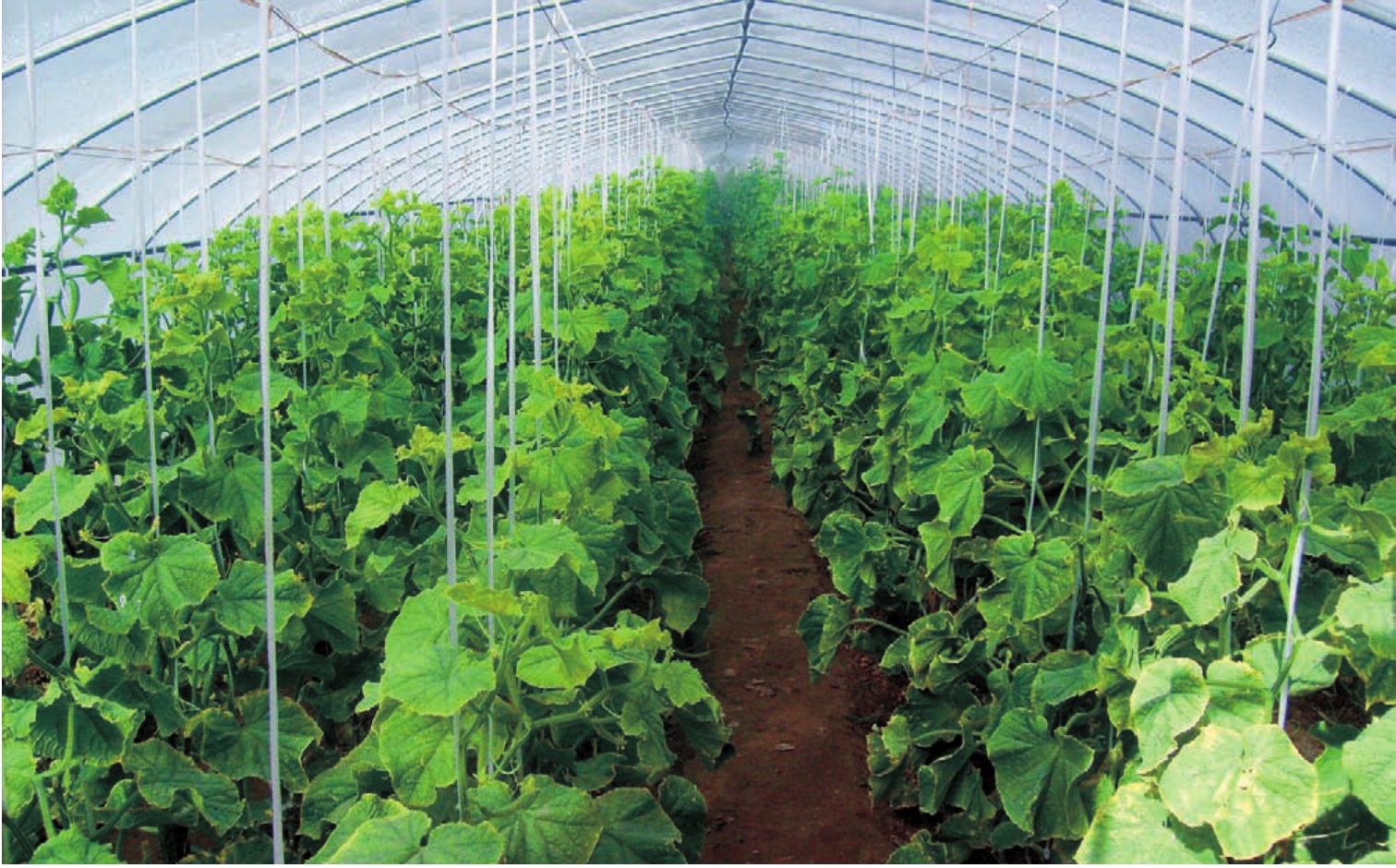
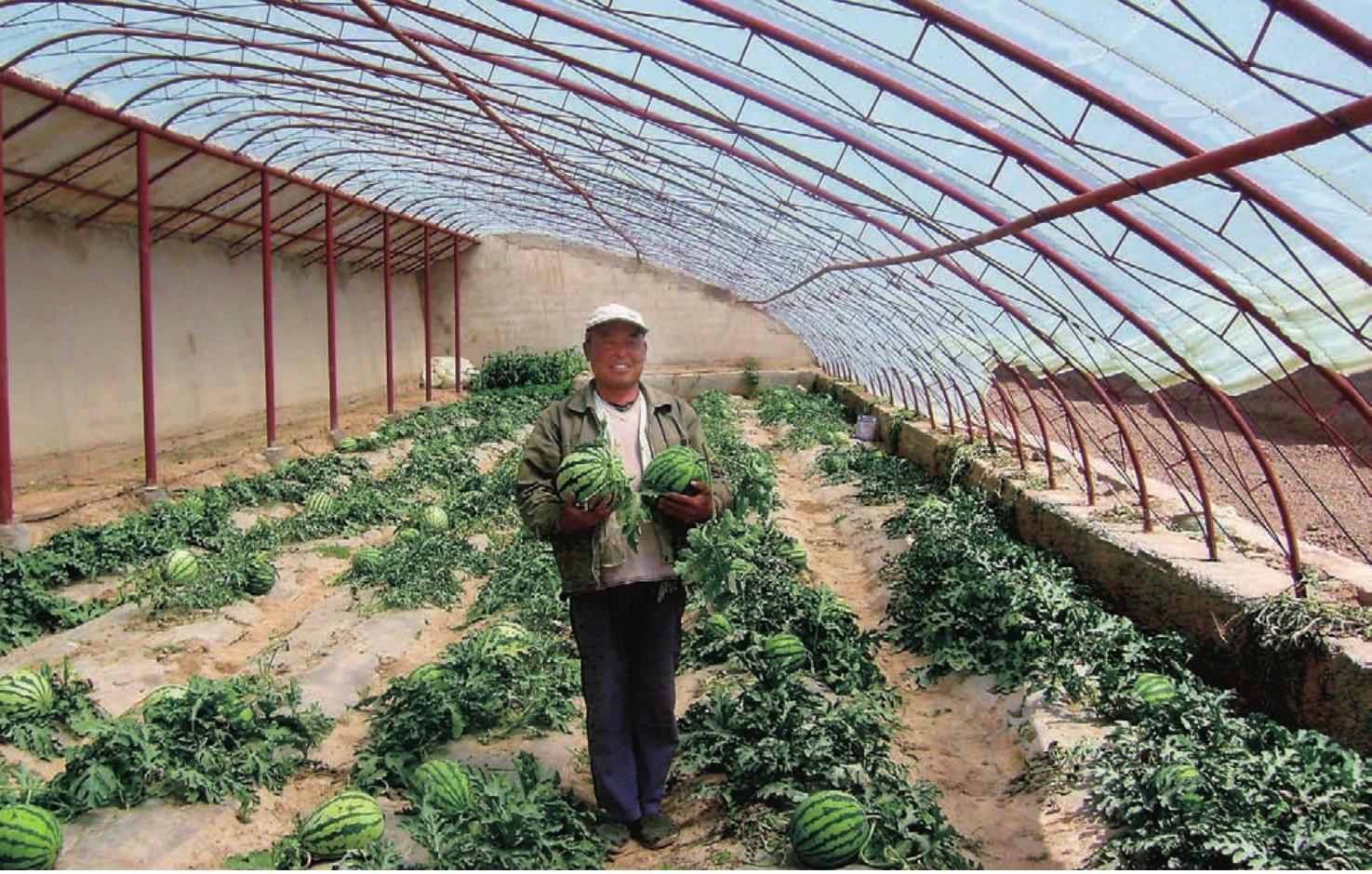
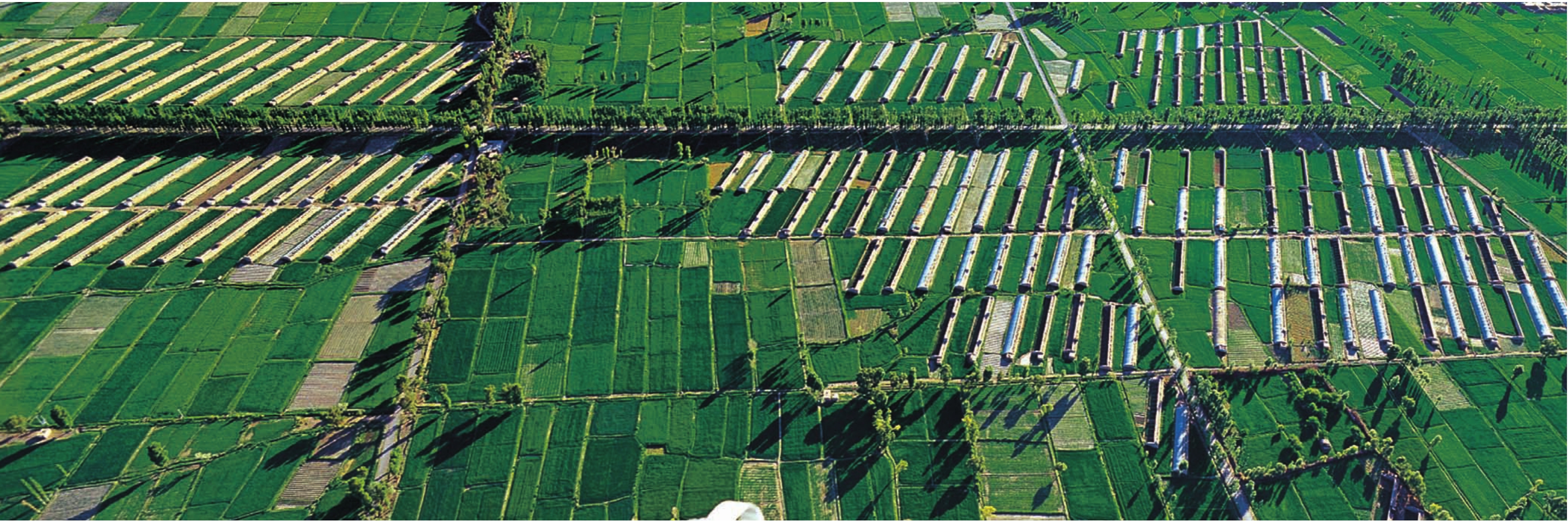



都兰县委、县政府瞄准周边地区市场需求,大力发展果蔬种植,努力把都兰打造成海西州重要的果蔬生产基地。与此同时,塑料大棚蔬菜种植、农区养殖、花卉种植、蘑菇栽培等新兴产业犹如百花园中竞相吐艳的鲜花,与粮油、药材、林业、草业比肩并行,形成了多姿多彩的都兰特色农业经济。
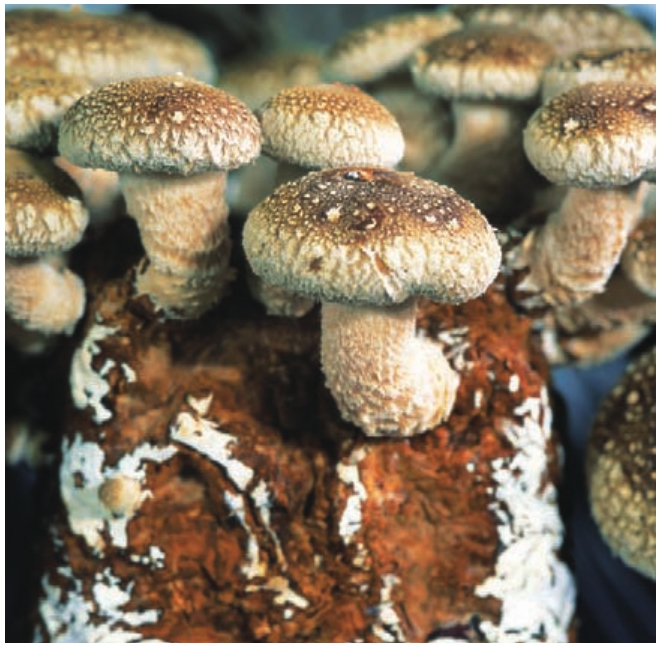
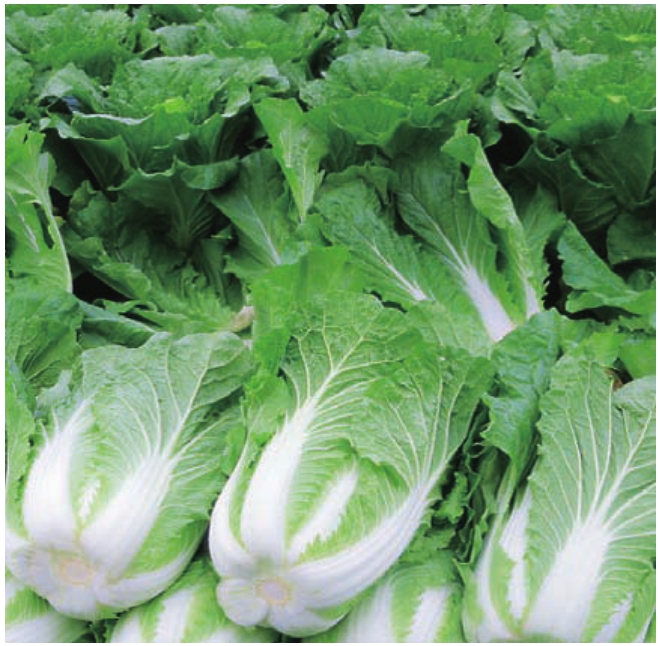
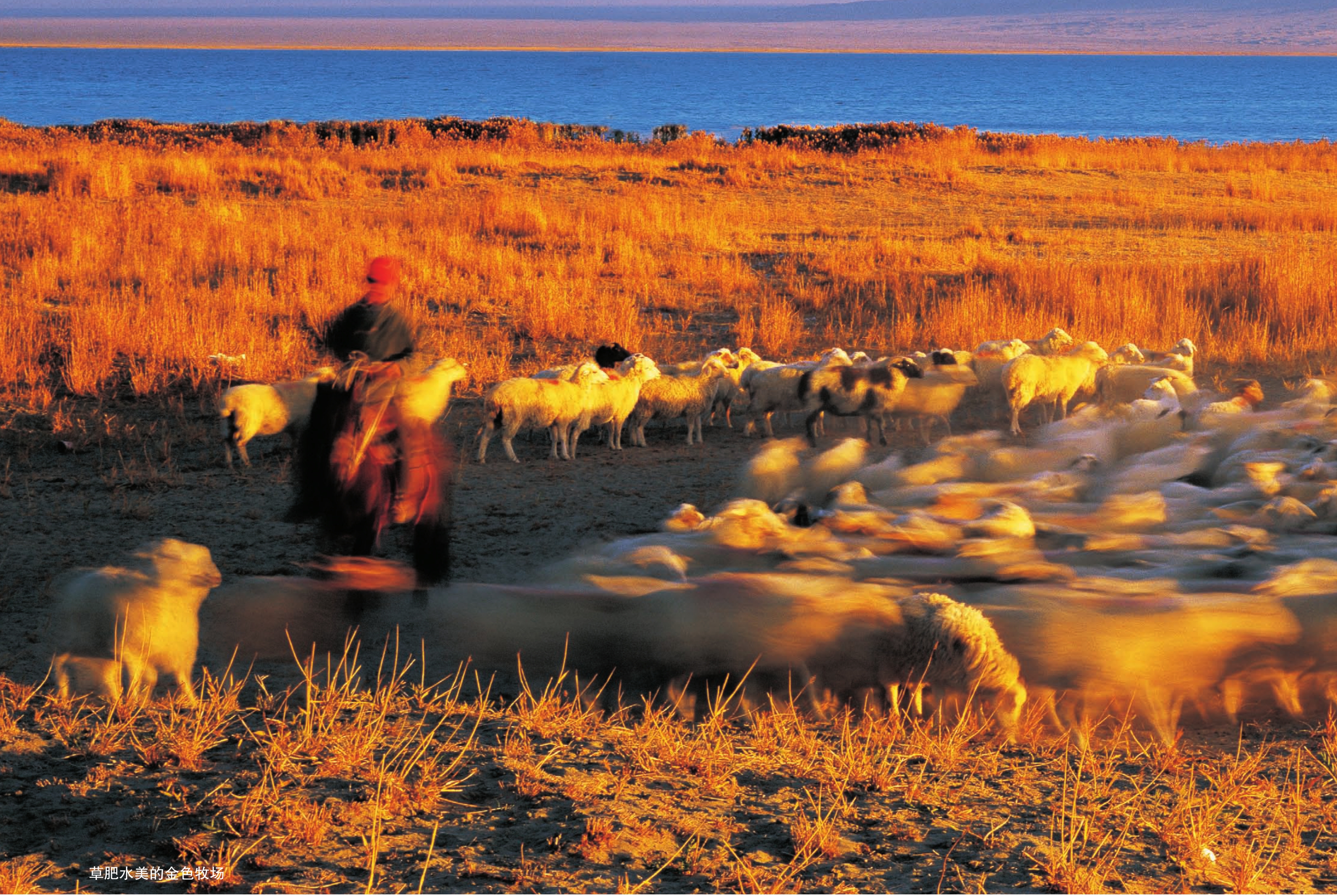









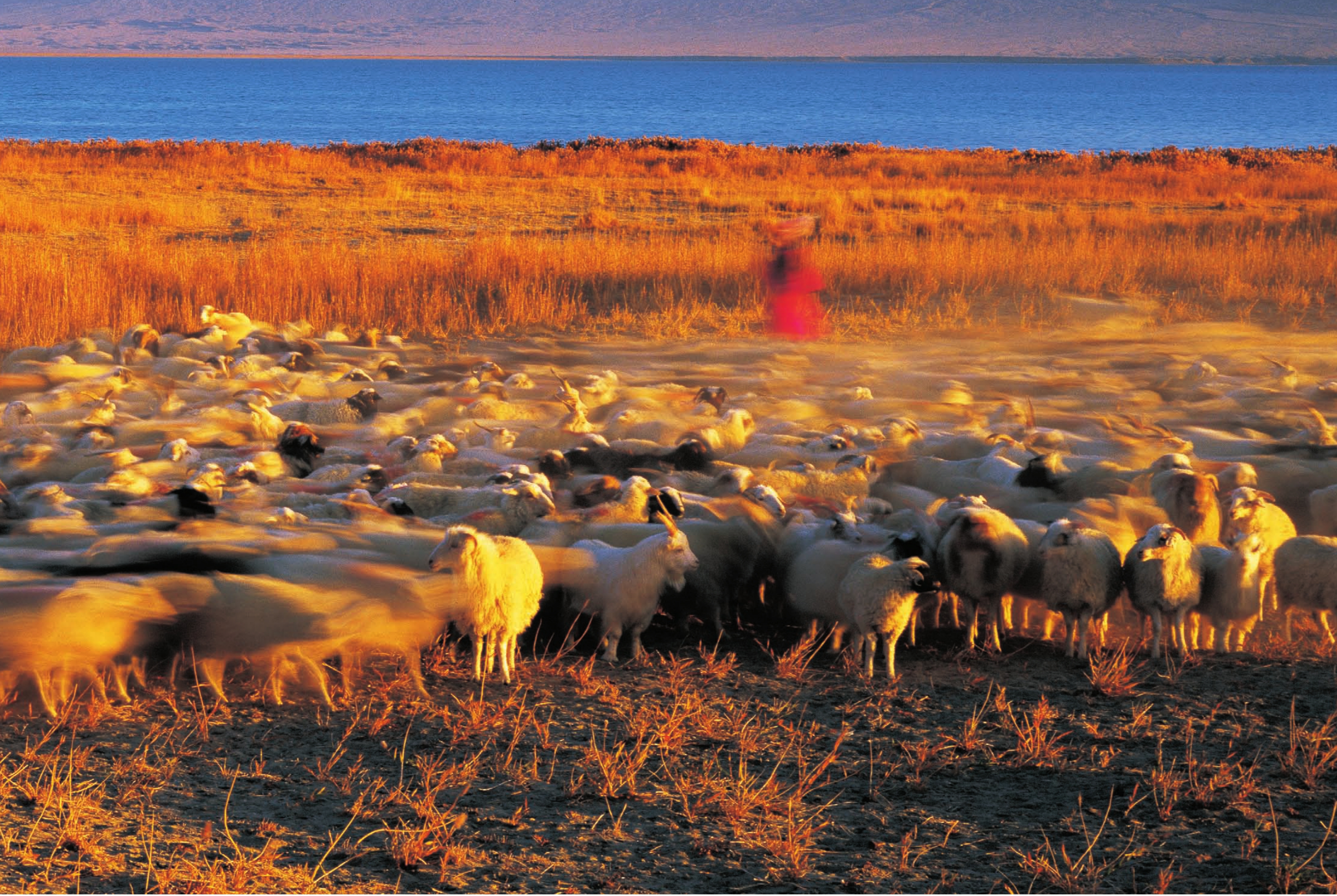
草肥水美的金色牧场
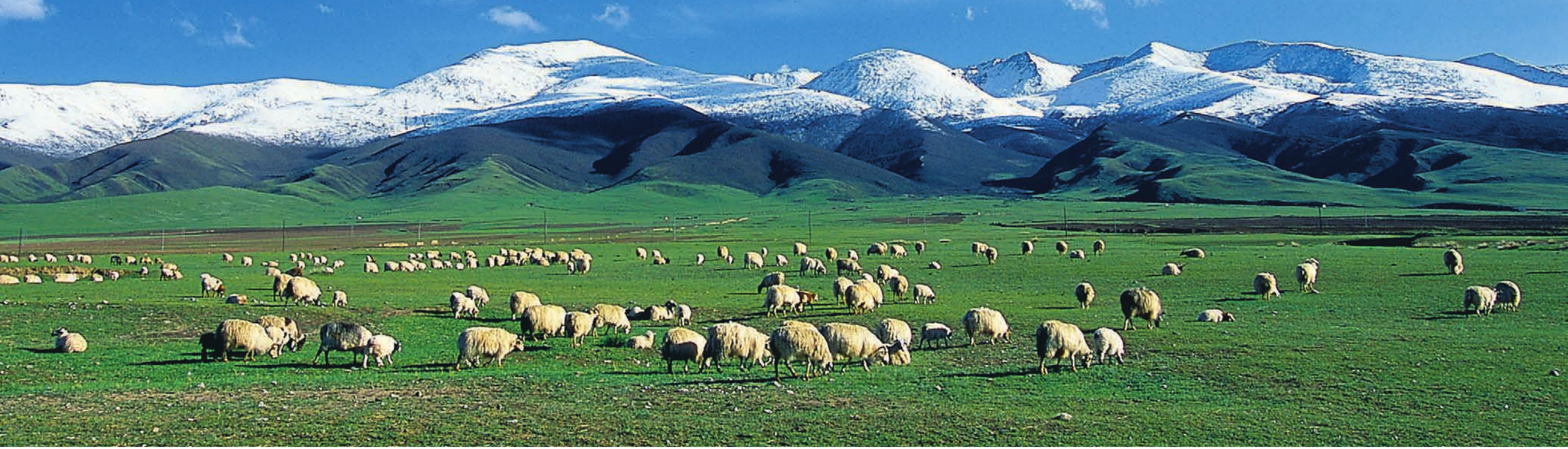
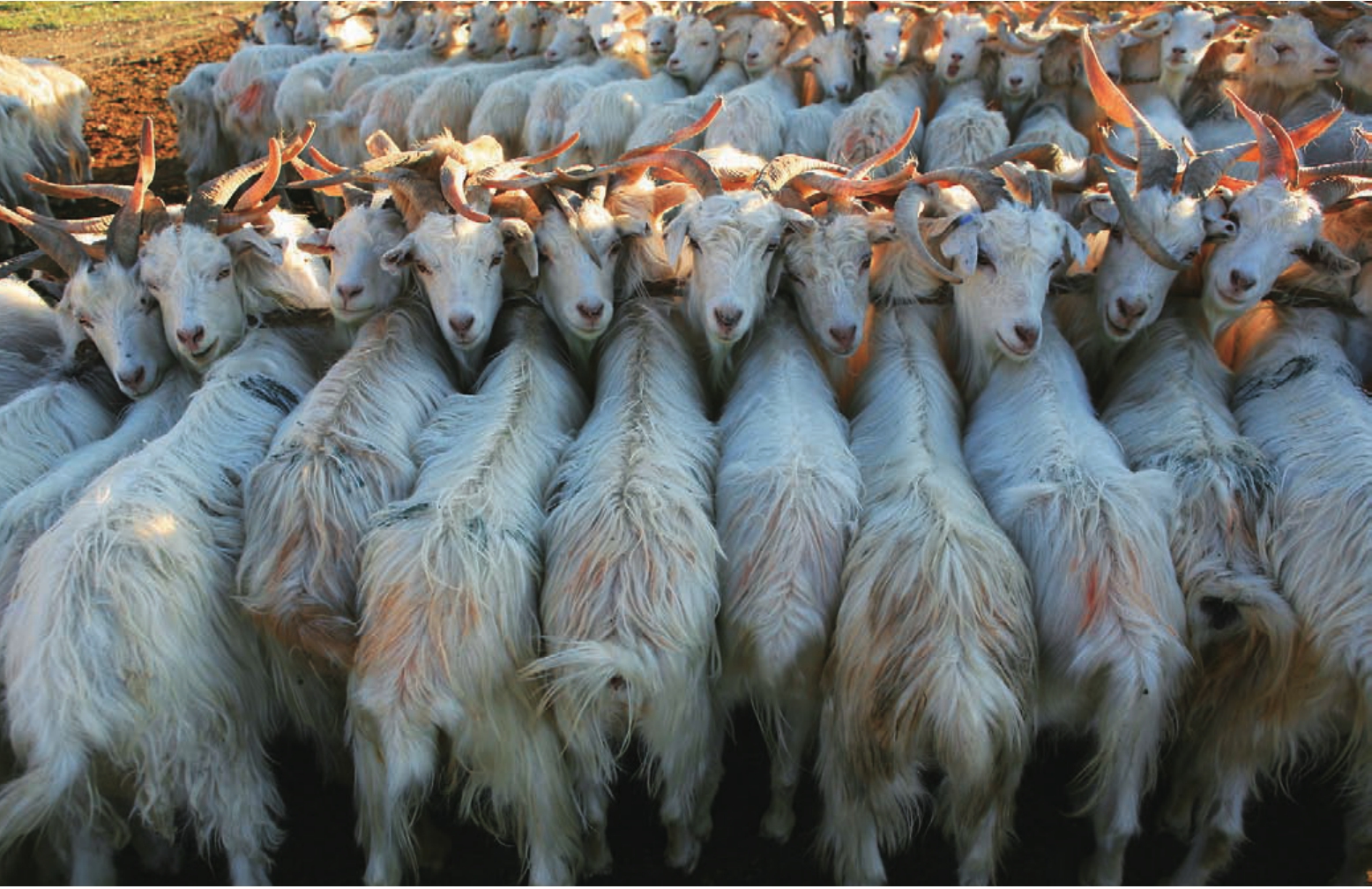
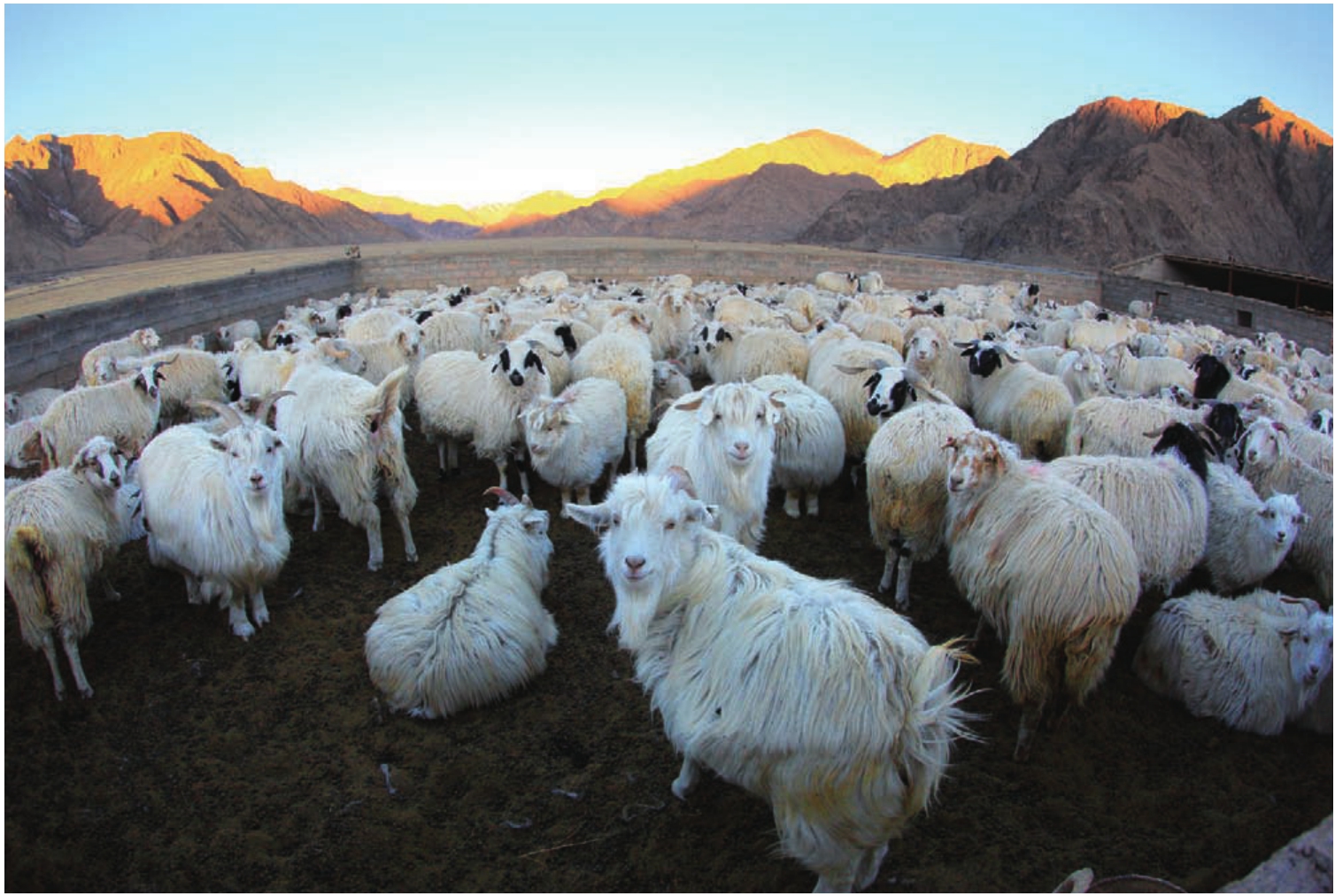




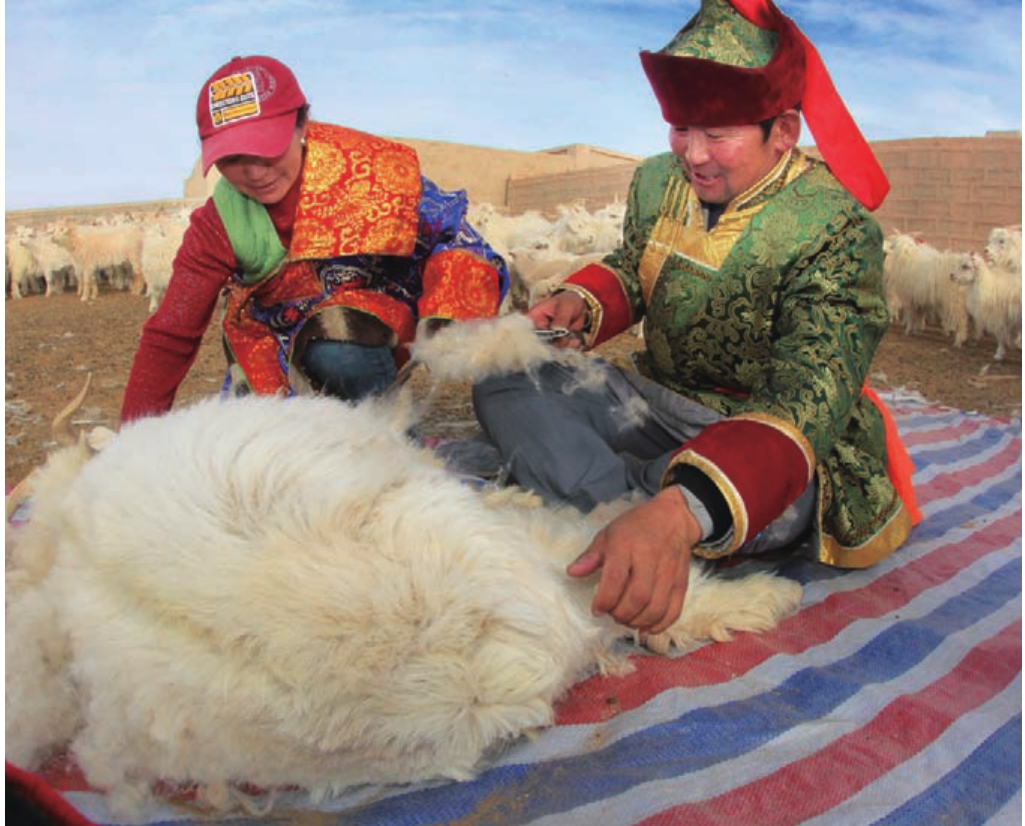
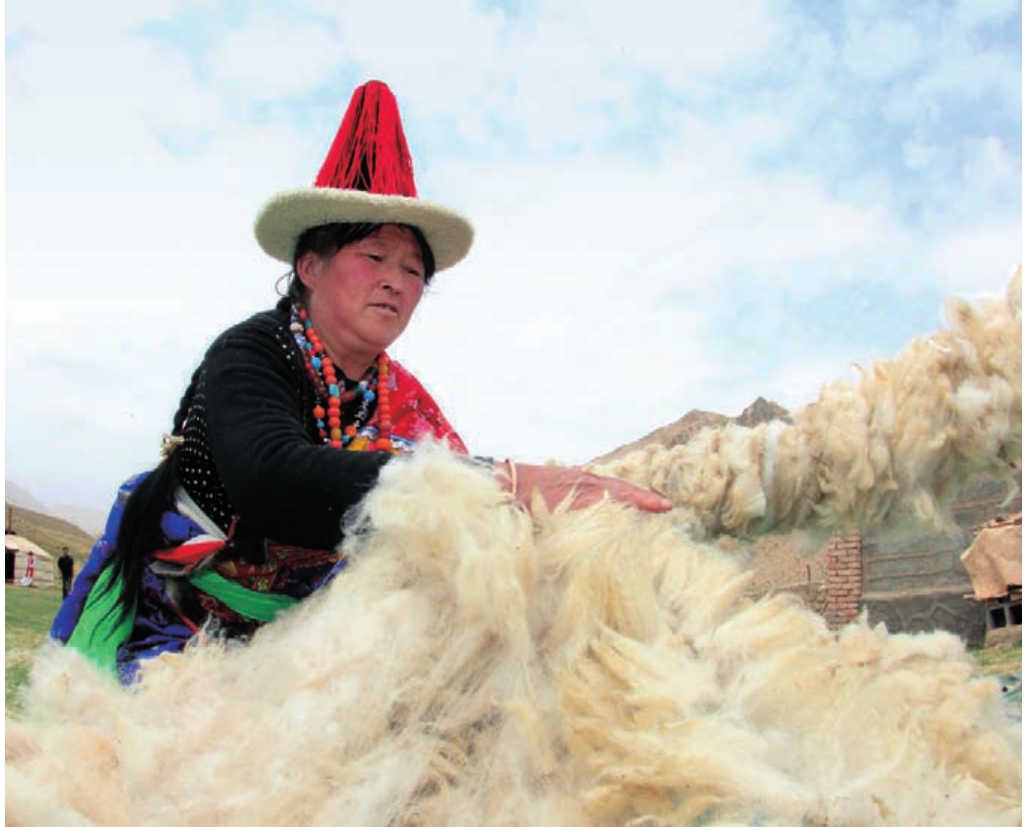
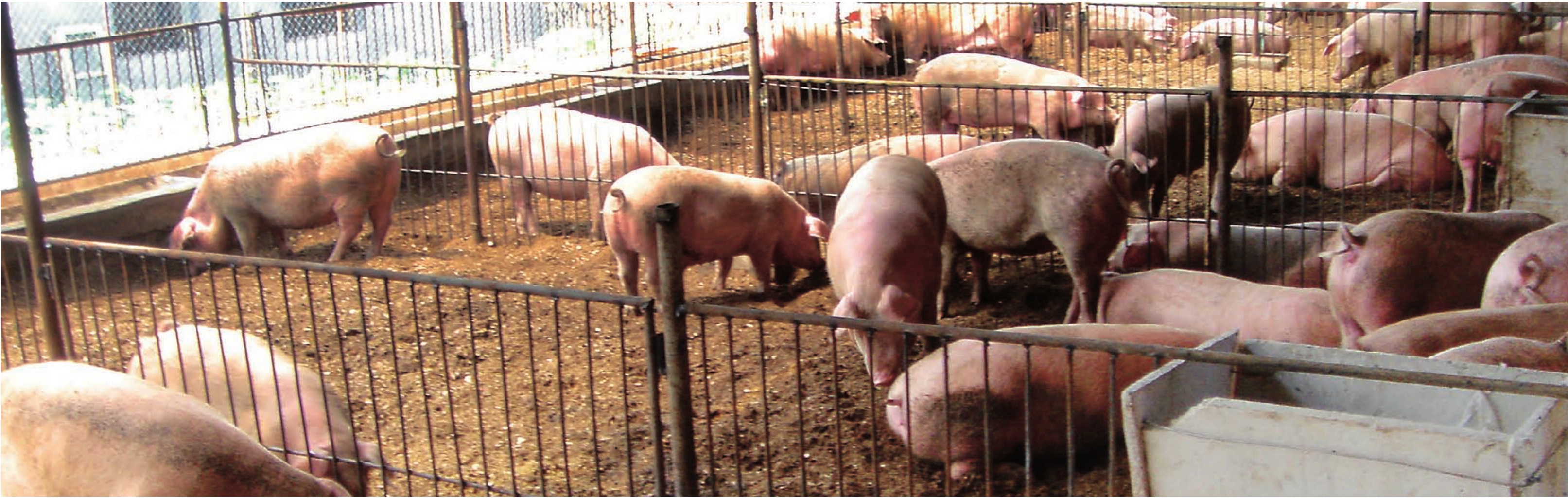
畜牧业是都兰农牧业经济持续发展的另一重头产业。在各级政府的资金扶持下,随着牧民生产经营方式的科学改变,草地生态环境得到了持续改善,草畜动态平衡基本实现,具有高原特色专业化、集约化的高效畜牧业发展方向已经明确。目前,全县共成立农牧民专业合作社82个,其中畜牧业43个。2010年末,全县牲畜存栏110万头(只),其中适龄母畜65.45万头(只),占牲畜总数的 59.5%。
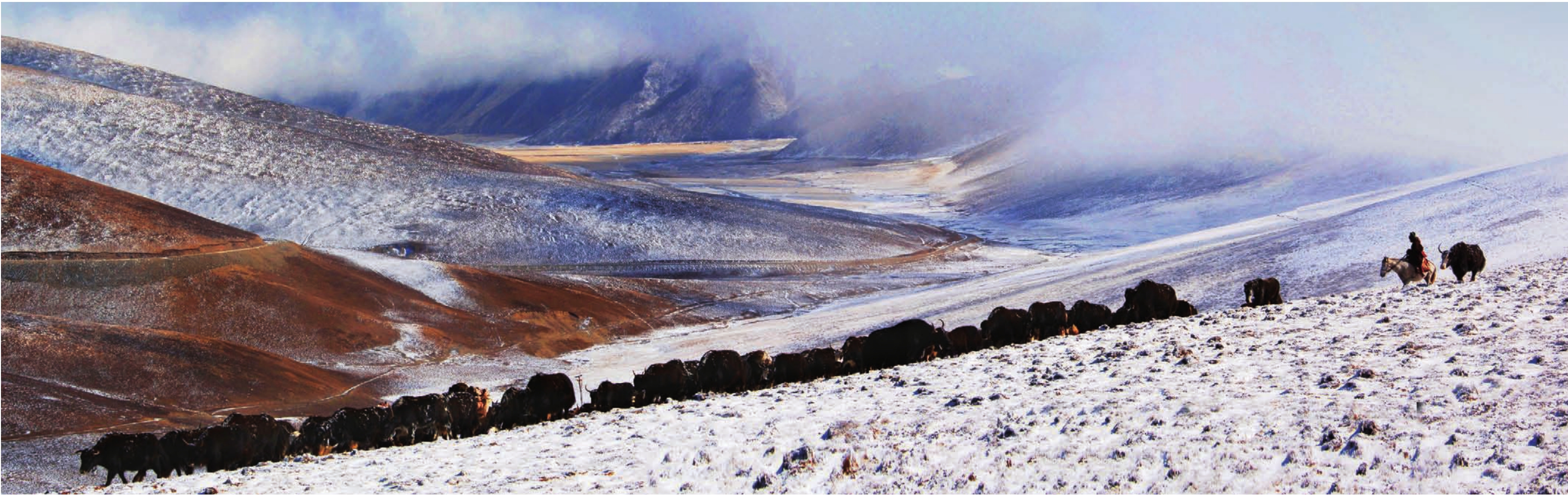
“十二五”时期,都兰县委、县政府按照“一白一黑一草业”特色牧业发展思路,加快构建宗加、巴隆、香加等西部乡镇青海半细毛羊、柴达木绒山羊产业带和沟里、热水、夏日哈等南部山区牦牛、藏羊产业带,将完成全县38个牧业村的生态畜牧业建设项目,通过划区轮牧等基础设施建设,合理调整畜群结构,大幅提高适龄母畜比例,运用新技术加快畜群周转周期,建立牧业合作社经济组织,发展适度规模经营和管理,依托牛羊优势资源,发展牛羊育肥,着力发展第三产业,转变畜牧业生产经营方式,改善草地生态环境,确保草畜动态平衡,走畜牧业发展的科学之路。





青海骢

绒山羊

半细毛羊
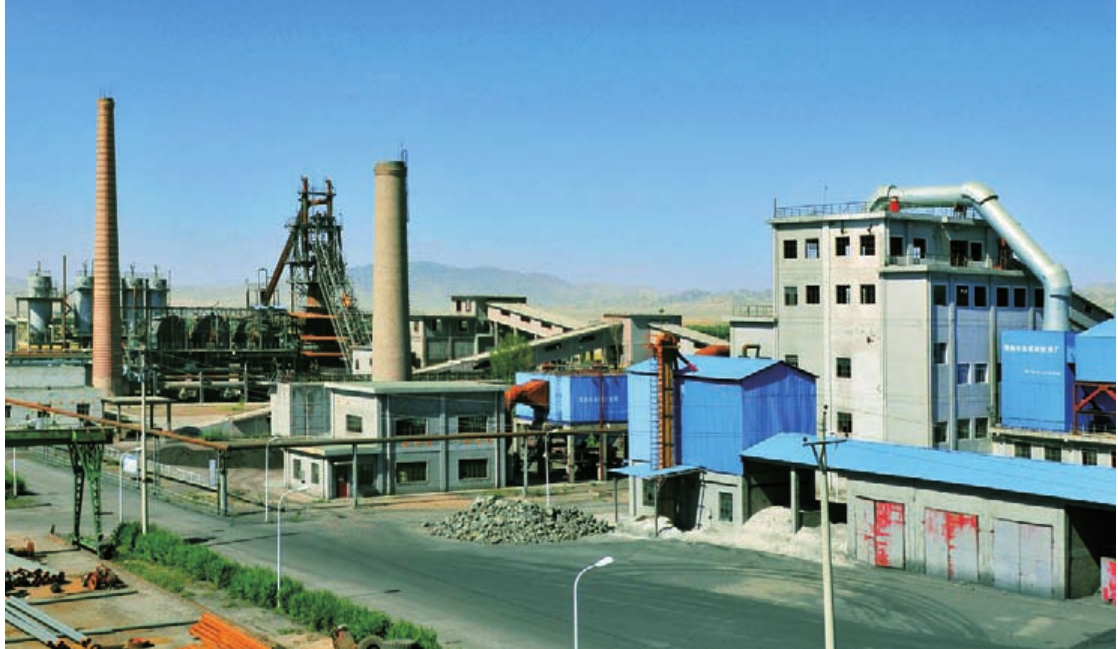
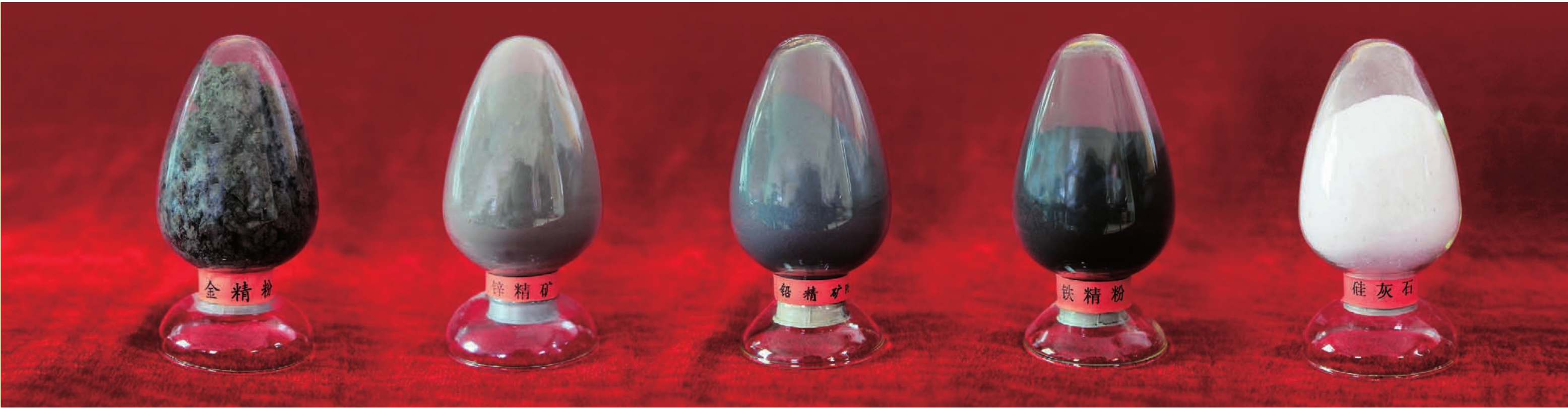












工矿企业
都兰县现有各类规模较大的工矿企业30余家,分别从事铁精粉、黄金、铅锌精粉、氯化钾和铜精粉的加工。2010年,全县工业系统全面落实省、州经济工作会议精神,切实加强工业经济运行工作,全县工业经济保持了平稳快速发展的良好势头。“十二五”期间,都兰县将大力发展循环经济,按照“布局合理、产业聚集、循环发展、基础配套”的思路,建设都兰工业园:包括黄金产业园、国际石材工业园、多金属工业园、生物产业科技园、枸杞产业园、盐湖工业园和新能源工业园等7个园区。
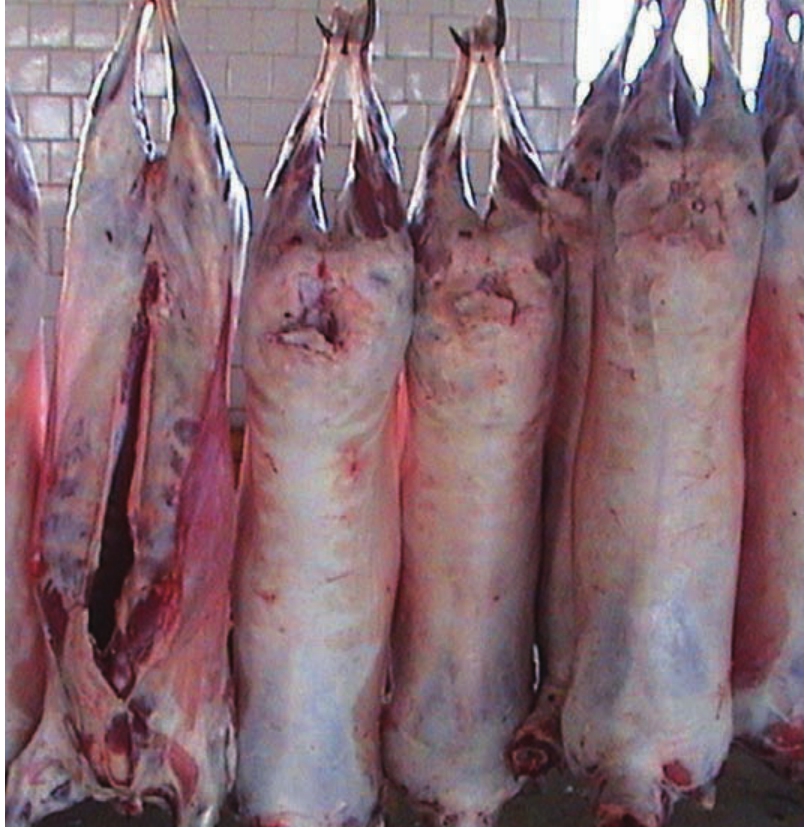
今后,都兰县将充分利用现有资源,扩大特色资源产业,积极发展具有高原特色的高效生态农牧业。重点开发枸杞、马铃薯、绿色蔬菜等深加工产品及相关的有机绿色食品。畜牧产品加工业以牦牛、藏系绵羊等为重点,建设标准化、无公害畜产品生产及加工基地,形成饲养、育肥、成品肉分类处理生产系统。鼓励具有地方特色和民族特色肉制品加工技术的研究与开发,生产方便安全的肉类制品。



2010年以来,通过招商引资,许多大项目纷纷落户都兰。
都兰县国际石材工业园区主要以丰富的花岗岩、大理石、蛇纹岩、橄榄石等石材为原料,建立以装饰型石材加工为主的都兰县国际建材工业园区。以龙鑫矿业为基础引进150-200家集开发加工销售一条龙的企业,力争将其打造成义乌模式。
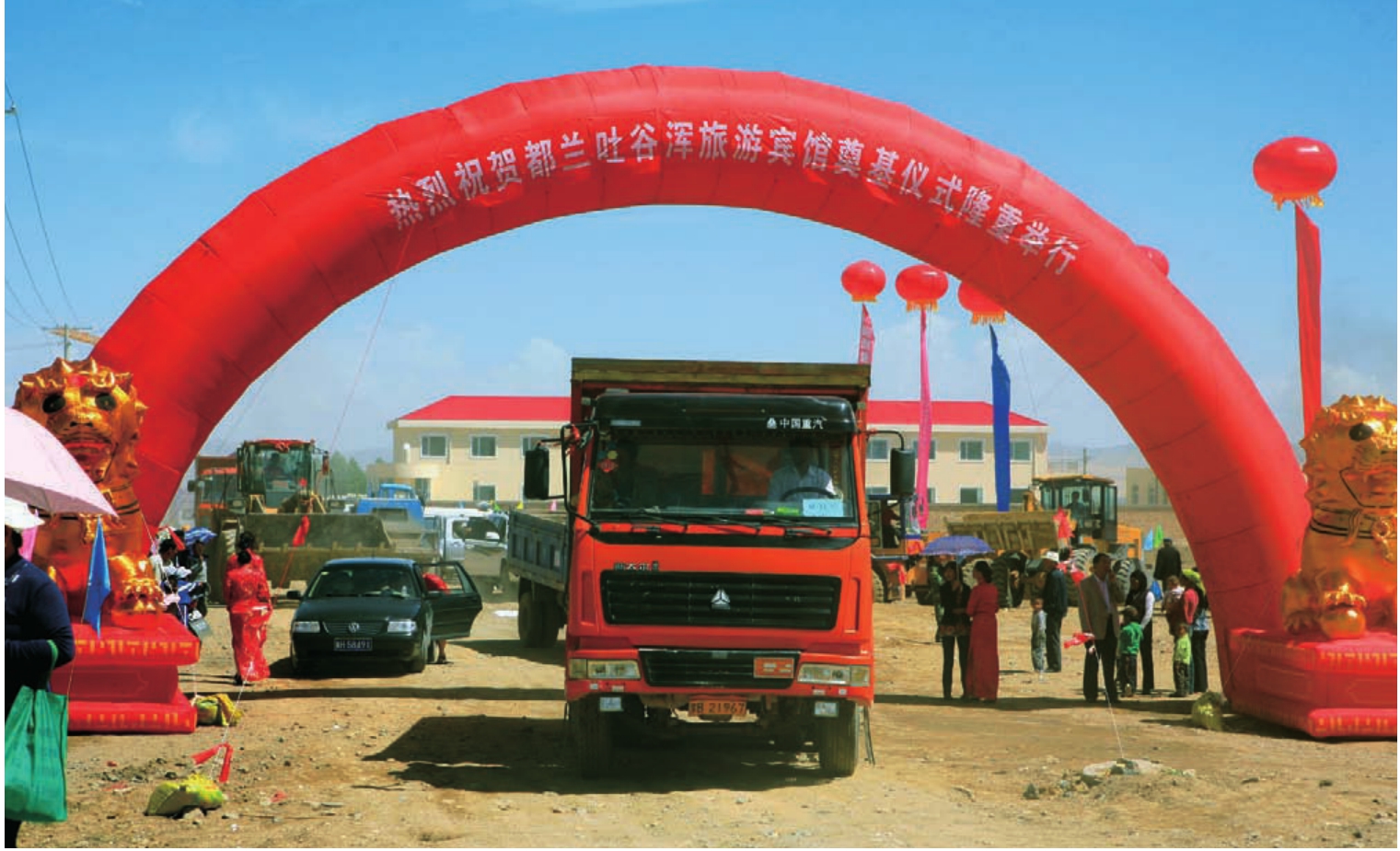


大项目“都兰吐谷浑旅游宾馆”于2010年开工建设。
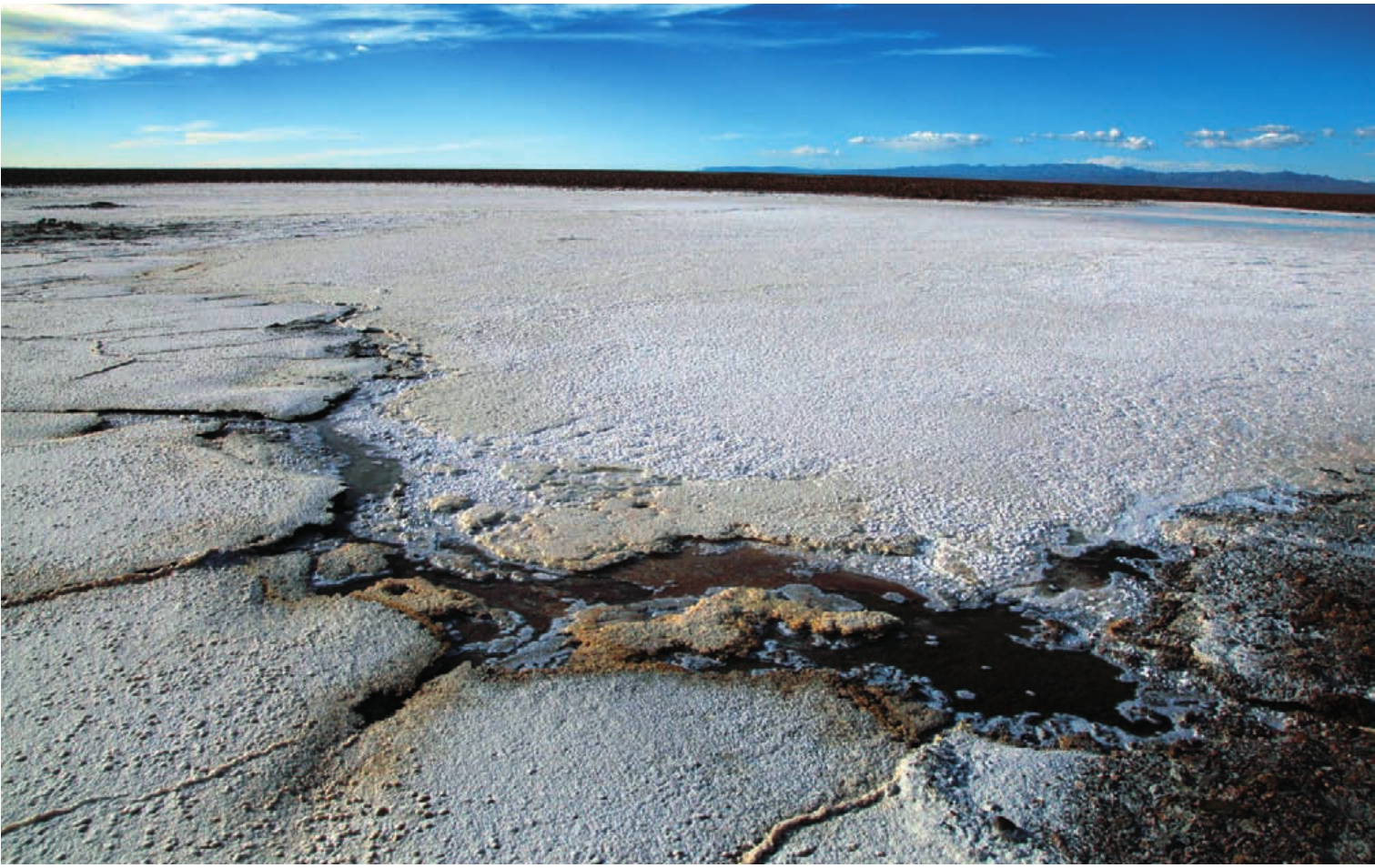

都兰县幅员辽阔,氯化钾储量丰富。规划建设中的盐湖工业园将着力发展钾肥产业。
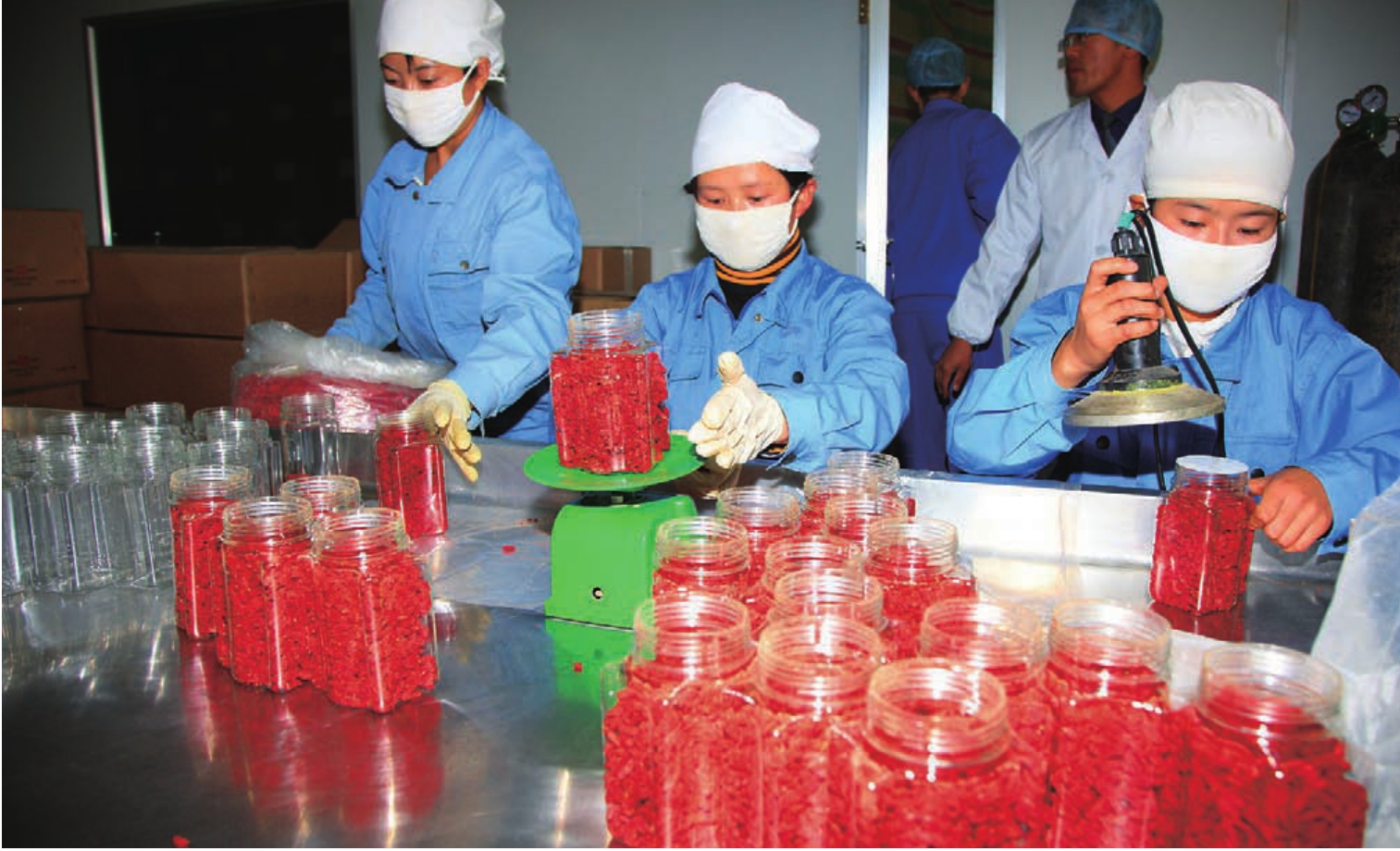

枸杞,俗称“明目子”,是中药里的珍品。诺木洪枸杞皮薄肉厚,单果颗粒体积属国内枸杞之冠。

截至2010年底,都兰县注册登记的私营企业152户,注册资金达54568多万元,从业人员4455人;注册登记的个体工商户1567户,注册资金达5144万多元,从业人员2176人。
前景广阔的新能源产业
新能源(风能、太阳能)由于具有储量大、可再生性强、清洁环保等突出优势,是都兰县大力发展的新兴产业。为加快推进都兰县新能源产业的发展,优化产业和能源结构,推动节能减排,促进经济平稳较快和可持续发展,根据新能源产业发展趋势,对照新能源发展的特点,都兰县紧紧围绕州委、州政府的中心工作,积极开发再生能源,准备于近年在县域诺木洪、巴隆地区大力发展风能、太阳能光伏产业。诺木洪、巴隆地区日照充足、风力资源丰富,充分利用风能、光能等优势资源,有计划地推进新能源开发利用,坚持以光伏电力为中心,积极推进风电项目、光电项目建设,大力发展风电等产品的加工循环链,积极推进风、光并网发电项目建设进程。目前已有800兆瓦的风能项目和300兆瓦的太阳能项目落地。

































































