-
1.1序
-
1.2前 言
-
1.3Chapter 1 Internet and World Wide Web
-
1.3.1Section A E-Business Essentials
-
1.3.1.1The ABC of Internet and World Wide Web
-
1.3.2Section B Online Reading Material
-
1.3.2.1The Internet and Business
-
1.3.3Section C Online Surfing
-
1.3.3.1What We Will Need to Get Started
-
1.3.4Section D Supplementary Reading
-
1.3.4.1E-English Rules the Waves
-
1.4Chapter 2 Electronic Business Basics
-
1.4.1Section A E-Business Essentials
-
1.4.1.1Defining E-Business
-
1.4.2Section B Online Reading Material
-
1.4.2.1Power at Last
-
1.4.3Section C Online Surfing
-
1.4.3.1An E-mail Account
-
1.4.4Section D Supplementary Reading
-
1.4.4.1What's the Meaning of@in the E-mail Address
-
1.5Chapter 3 Business-to-Business E-Business
-
1.5.1Section A E-Business Essentials
-
1.5.1.1Defining Business-to-Business E-Business
-
1.5.2Section B Online Reading Material
-
1.5.2.1How Business-to-Business Works
-
1.5.3Section C Online Surfing
-
1.5.3.1Search Engines and Directories
-
1.5.4Section D Supplementary Reading
-
1.5.4.1Google Is Adding Major Libraries to Its Database
-
1.6Chapter 4 Business-to-Consumer E-Business
-
1.6.1Section A E-Business Essentials
-
1.6.1.1Defining Business-to-Consumer E-Business
-
1.6.2Section B Online Reading Material
-
1.6.2.1Understanding B2C E-Business
-
1.6.3Section C Online Surfing
-
1.6.3.1Web Address and Domain Names
-
1.6.4Section D Supplementary Reading
-
1.6.4.1From a Librarian to America's Richest Man
-
1.7Chapter 5 E-Business Web Site
-
1.7.1Section A E-Business Essentials
-
1.7.1.1Reviewing Web Hosting Vocabulary
-
1.7.2Section B Online Reading Material
-
1.7.2.1Usability of the E-Business Web Site
-
1.7.3Section C Online Surfing
-
1.7.3.1Visiting Online Stores
-
1.7.4Section D Supplementary Reading
-
1.7.4.1Big Media,Little Blogosphere
-
1.8Chapter 6 Marketing Strategy for E-Business(Ⅰ)
-
1.8.1Section A E-Business Essentials
-
1.8.1.1Identifying Marketing Issues
-
1.8.2Section B Online Reading Material
-
1.8.2.1E-Marketing Planning
-
1.8.3Section C Online Surfing
-
1.8.3.1Online Advertising:Banner Ads
-
1.8.4Section D Supplementary Reading
-
1.8.4.1China Promises Internet Bounty
-
1.9Chapter 7 Marketing Strategy for E-Business(Ⅱ)
-
1.9.1Section A E-Business Essentials
-
1.9.1.1Market Research for E-Business
-
1.9.2Section B Online Reading Material
-
1.9.2.1Applying the Marketing Mix to E-Business
-
1.9.3Section C Online Surfing
-
1.9.3.1Online Forms
-
1.9.4Section D Supplementary Reading
-
1.9.4.1How Auction Sites Work Online
-
1.10Chapter 8 Electronic Payments
-
1.10.1Section A E-Business Essentials
-
1.10.1.1Electronic Payments
-
1.10.2Section B Online Reading Material
-
1.10.2.1E-payment on the World Wide Web
-
1.10.3Section C Online Surfing
-
1.10.3.1E-Bank
-
1.10.4Section D Supplementary Reading
-
1.10.4.1Gates:China Will Become Biggest User of Broadband
-
1.11Chapter 9 Security Issues
-
1.11.1Section A E-Business Essentials
-
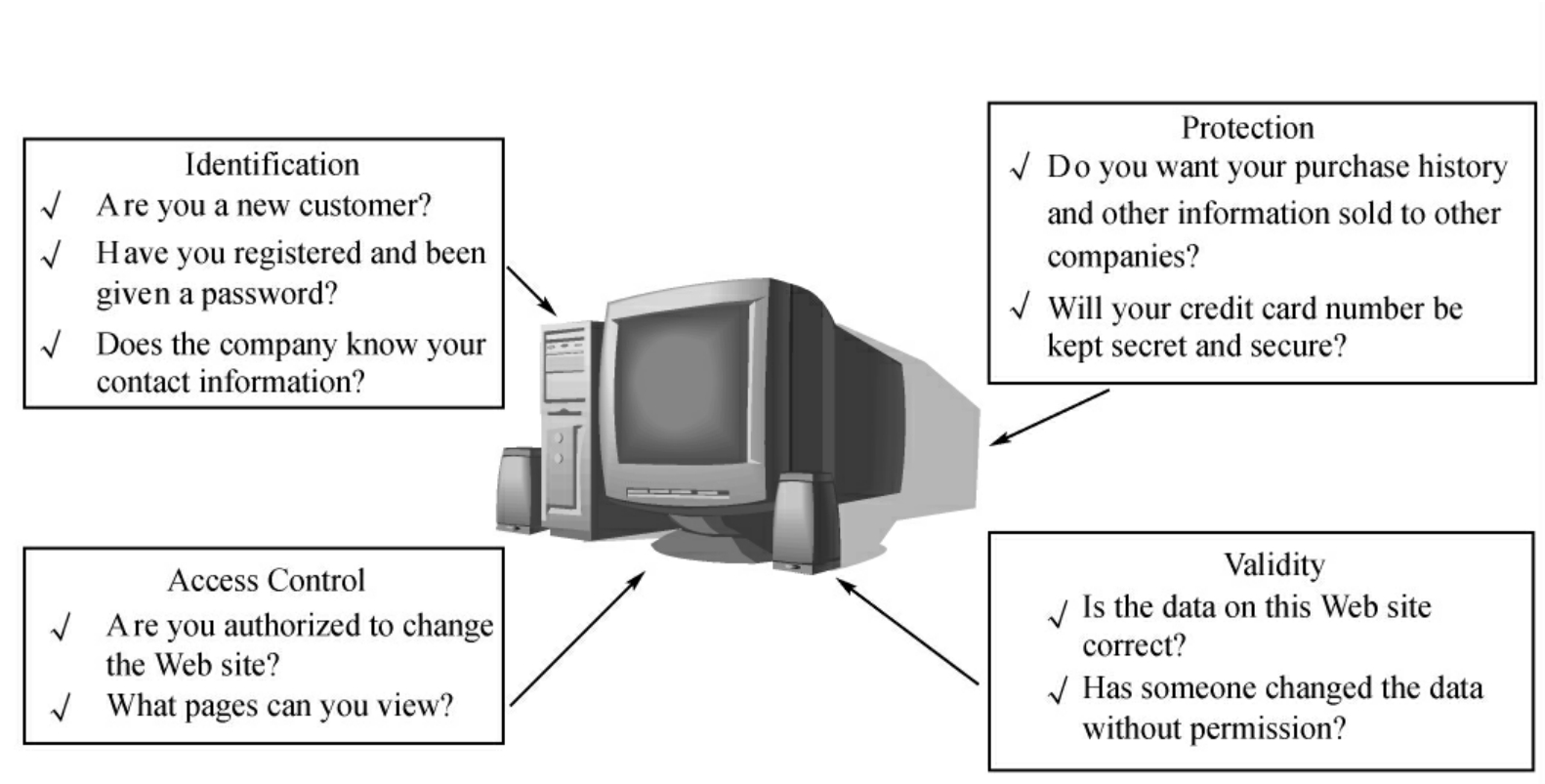
1.11.1.1Security Requirements and Threats
-
1.11.2Section B Online Reading Material
-
1.11.2.1A Security Plan for E-Business
-
1.11.3Section C Online Surfing
-
1.11.3.1Upgrade Security Guard
-
1.11.4Section D Supplementary Reading
-
1.11.4.1Why eBay Is Buying Skype
-
1.12Chapter 10 Customer Service Strategies
-
1.12.1Section A E-Business Essentials
-
1.12.1.1Customer Service
-
1.12.2Section B Online Reading Material
-
1.12.2.1Supporting Customers Online
-
1.12.3Section C Online Surfing
-
1.12.3.1Discussion Forums and Chat Rooms
-
1.12.4Section D Supplementary Reading
-
1.12.4.1The Finer Points of E-mail Etiquette
-
1.13阅读材料参考译文
-
1.14参考书目
1
电子商务英语