-
1.1前 言
-
1.2目录
-
1.3Chapter 1 Introduction to New Energy Vehicles
-
1.3.11.1 Environmental Impact
-
1.3.1.11.1.1 Air Pollution
-
1.3.1.21.1.2 Global Warming
-
1.3.1.31.1.3 Petroleum Resources
-
1.3.21.2 Sustainable Transportation
-
1.3.31.3 EV History
-
1.3.3.11.3.1 The Early Years
-
1.3.3.21.3.2 1970s
-
1.3.3.31.3.3 1980s and 1990s
-
1.3.3.41.3.4 EV Market
-
1.3.41.4 History of HEVs
-
1.3.51.5 History of Fuel Cell Vehicles
-
1.4Chapter 2 New Energy Vehicle Types
-
1.4.12.1 Electric Vehicles
-
1.4.1.12.1.1 Configuration of Electric Vehicles
-
1.4.1.22.1.2 Conceptual Illustration of a General EV Conf...
-
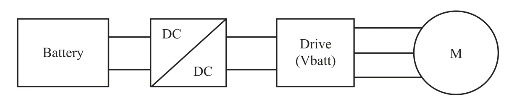
1.4.1.32.1.3 System Level Diagram of an EV
-
1.4.22.2 Hybrid Electric Vehicles
-
1.4.2.12.2.1 Parallel Hybrid
-
1.4.2.22.2.2 Series Hybrid
-
1.4.2.32.2.3 Series-parallel Hybrid
-
1.4.2.42.2.4 Complex Hybrid
-
1.4.32.3 Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle(PHEV)
-
1.4.3.12.3.1 Why PHEV
-
1.4.3.22.3.2 Constituents of a PHEV
-
1.4.42.4 Fuel Cell Vehicles(FCVs)
-
1.5Chapter 3 Energy Storages
-
1.5.13.1 Electrochemical Batteries
-
1.5.23.2 Battery Characterization
-
1.5.33.3 Battery Technologies
-
1.5.3.13.3.1 Lead-Acid Battery
-
1.5.3.23.3.2 Nickel-Based Batteries
-
1.5.3.33.3.3 Lithium-Based Batteries
-
1.5.43.4 Supercapacitors and Ultracapacitors
-
1.5.53.5 Flywheels
-
1.5.63.6 Fuel Cells
-
1.5.6.13.6.1 Operating Principles of Fuel Cells
-
1.5.6.23.6.2 Fuel Cell Technologies
-
1.6Chapter 4 Management of Energy Storage Systems
-
1.6.14.1 Introduction
-
1.6.24.2 Battery Management
-
1.6.2.14.2.1 Parameter Monitoring
-
1.6.2.24.2.2 Calculation of SOC
-
1.6.2.34.2.3 Fault and Safety Protection
-
1.6.2.44.2.4 Charge Management
-
1.6.34.3 Battery Cell Balancing
-
1.7Chapter 5 Electric Propulsion Systems
-
1.7.15.1 Electric Motors
-
1.7.1.15.1.1 Advantage of Electric Motors
-
1.7.1.25.1.2 Classification of Electric Motors
-
1.7.25.2 Electronic Structure
-
1.7.35.3 Electronic Converters
-
1.7.3.15.3.1 Components of Electronic Converters
-
1.7.3.25.3.2 Rectifiers
-
1.7.3.35.3.3 Choppers
-
1.7.3.45.3.4 Inverters
-
1.8Chapter 6 Recharging Systems for Electric Vehicles
-
1.8.16.1 What Is Battery Charging
-
1.8.26.2 The Various Types of Chargers
-
1.8.36.3 Recharging Efficiency
-
1.8.46.4 Recharging in Complete Safety
-
1.8.56.5 Charging Methods
-
1.8.5.16.5.1 Constant Voltage Charge
-
1.8.5.26.5.2 Constant Current Charge
-
1.8.5.36.5.3 Taper Current Charge
-
1.8.5.46.5.4 Pulse Charge
-
1.8.5.56.5.5 Reflex Charge
-
1.8.5.66.5.6 Float Charge
-
1.8.66.6 Termination Methods
-
1.8.6.16.6.1 Time
-
1.8.6.26.6.2 Voltage
-
1.8.6.36.6.3 Voltage Drop(dV/dT)
-
1.8.6.46.6.4 Current
-
1.8.6.56.6.5 Temperature
-
1.9第1章 新能源汽车概述
-
1.9.11.1 环境影响
-
1.9.1.11.1.1 大气污染
-
1.9.1.21.1.2 全球变暖
-
1.9.1.31.1.3 石油资源
-
1.9.21.2 可持续发展的交通运输
-
1.9.31.3 电动汽车的发展史
-
1.9.3.11.3.1 早期
-
1.9.3.21.3.2 20世纪70年代
-
1.9.3.31.3.3 20世纪80年代和90年代
-
1.9.3.41.3.4 电动汽车的市场前景
-
1.9.41.4 混合动力电动汽车的历史
-
1.9.51.5 燃料电池电动汽车的历史
-
1.10第2章 新能源汽车类型
-
1.10.12.1 纯电动汽车
-
1.10.1.12.1.1 纯电动汽车结构
-
1.10.1.22.1.2 EV结构的概念性图示
-
1.10.1.32.1.3 EV系统级原理图
-
1.10.22.2 混合动力电动汽车
-
1.10.2.12.2.1 并联式混合
-
1.10.2.22.2.2 串联式混合
-
1.10.2.32.2.3 混联式混合
-
1.10.2.42.2.4 复联式混合
-
1.10.32.3 插电式混合动力电动汽车
-
1.10.3.12.3.1 为什么需要插电式混合动力电动汽车
-
1.10.3.22.3.2 插电式混合动力电动汽车的结构
-
1.10.42.4 燃料电池电动汽车
-
1.11第3章 能量储存装置
-
1.11.13.1 电化学蓄电池组
-
1.11.23.2 电池特性参数
-
1.11.33.3 蓄电池技术
-
1.11.3.13.3.1 铅酸蓄电池
-
1.11.3.23.3.2 镍基蓄电池
-
1.11.3.33.3.3 锂基蓄电池
-
1.11.43.4 超大容量电容器和超级电容器
-
1.11.53.5 飞 轮
-
1.11.63.6 燃料电池
-
1.11.6.13.6.1 燃料电池的工作原理
-
1.11.6.23.6.2 燃料电池技术
-
1.12第4章 储能系统的管理
-
1.12.14.1 简 介
-
1.12.24.2 电池管理
-
1.12.2.14.2.1 参数监测
-
1.12.2.24.2.2 SOC的计算
-
1.12.2.34.2.3 故障和安全保护
-
1.12.2.44.2.4 充电管理
-
1.12.34.3 电池单体均衡
-
1.13第5章 电驱动系统
-
1.13.15.1 电动机
-
1.13.1.15.1.1 电动机应用优势
-
1.13.1.25.1.2 电动机的分类
-
1.13.25.2 电气结构
-
1.13.35.3 功率电子变换器
-
1.13.3.15.3.1 功率电子元件
-
1.13.3.25.3.2 整流器
-
1.13.3.35.3.3 斩波器
-
1.13.3.45.3.4 逆变器
-
1.14第6章 电动汽车的充电系统
-
1.14.16.1 什么是电池的充电
-
1.14.26.2 不同类型的充电器
-
1.14.36.3 充电效率
-
1.14.46.4 充电的安全问题
-
1.14.56.5 电池的充电方式
-
1.14.5.16.5.1 恒压充电
-
1.14.5.26.5.2 恒流充电
-
1.14.5.36.5.3 锥电流充电
-
1.14.5.46.5.4 脉冲充电
-
1.14.5.56.5.5 反射充电
-
1.14.5.66.5.6 浮压充电
-
1.14.66.6 充电的终止方式
-
1.14.6.16.6.1 时间
-
1.14.6.26.6.2 电压
-
1.14.6.36.6.3 电压降(dV/dT)
-
1.14.6.46.6.4 电流
-
1.14.6.56.6.5 温度
-
1.15参考文献
1
新能源汽车专业英语