-
1.1出版说明
-
1.2前 言
-
1.3目录
-
1.4Chapter I Pre-career Stage
-
1.4.1Unit 1 Structure and Styles of Letters
-
1.4.1.1Part I Introduction
-
1.4.1.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.4.1.2.1Sample 1
-
1.4.1.2.2Sample 2
-
1.4.1.2.3Sample 3 Block Style
-
1.4.1.2.4Sample 4 Indented Style
-
1.4.1.3Part III Writing Tips
-
1.4.1.4Part IV Practice
-
1.4.1.4.1Task 1
-
1.4.1.4.2Task 2
-
1.4.1.4.3Task 3
-
1.4.1.4.4Task 4
-
1.4.2Unit 2 E-mails
-
1.4.2.1Part I Introduction
-
1.4.2.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.4.2.2.1Sample 1
-
1.4.2.2.2Sample 2
-
1.4.2.2.3Sample 3
-
1.4.2.2.4Sample 4
-
1.4.2.3Part III Useful Expressions
-
1.4.2.4Part IV Writing Tips
-
1.4.2.5Part V Practice
-
1.4.2.5.1Task 1
-
1.4.2.5.2Task 2
-
1.4.2.5.3Task 3
-
1.4.2.5.4Task 4
-
1.4.2.5.5Task 5
-
1.4.2.5.6Task 6
-
1.4.3Unit 3 Résumés
-
1.4.3.1Part I Introduction
-
1.4.3.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.4.3.2.1Sample 1
-
1.4.3.2.2Sample 2
-
1.4.3.3Part III Useful Expressions
-
1.4.3.4Part IV Writing Tips
-
1.4.3.5Part V Practice
-
1.4.3.5.1Task 1
-
1.4.3.5.2Task 2
-
1.4.3.5.3Task 3
-
1.4.3.5.4Task 4
-
1.4.3.5.5Task 5
-
1.4.4Unit 4 Job Application Cover Letters
-
1.4.4.1Part I Introduction
-
1.4.4.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.4.4.2.1Sample 1
-
1.4.4.2.2Sample 2
-
1.4.4.3Part III Useful Expressions
-
1.4.4.4Part IV Writing Tips
-
1.4.4.5Part V Practice
-
1.4.4.5.1Task 1
-
1.4.4.5.2Task 2
-
1.4.4.5.3Task 3
-
1.4.4.5.4Task 4
-
1.5Chapter II Career Stage (Social Letters)
-
1.5.1Unit 5 Office Correspondence
-
1.5.1.1Part I Introduction
-
1.5.1.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.5.1.2.1Sample 1
-
1.5.1.2.2Sample 2
-
1.5.1.2.3Sample 3
-
1.5.1.2.4Sample 4
-
1.5.1.2.5Sample 5
-
1.5.1.2.6Sample 6
-
1.5.1.2.7Sample 7
-
1.5.1.3Part III Useful Expressions
-
1.5.1.4Part IV Writing Tips
-
1.5.1.5Part V Practice
-
1.5.1.5.1Task 1
-
1.5.1.5.2Task 2
-
1.5.1.5.3Task 3
-
1.5.1.5.4Task 4
-
1.5.1.5.5Task 5
-
1.5.1.5.6Task 6
-
1.5.2Unit 6 Invitations
-
1.5.2.1Part I Introduction
-
1.5.2.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.5.2.2.1Sample 1
-
1.5.2.2.2Sample 2
-
1.5.2.2.3Sample 3
-
1.5.2.2.4Sample 4
-
1.5.2.2.5Sample 5
-
1.5.2.2.6Sample 6
-
1.5.2.2.7Sample 7
-
1.5.2.2.8Sample 8
-
1.5.2.2.9Sample 9
-
1.5.2.2.10Sample 10
-
1.5.2.3Part III Useful Expressions
-
1.5.2.4Part IV Writing Tips
-
1.5.2.5Part V Practice
-
1.5.2.5.1Task 1
-
1.5.2.5.2Task 2
-
1.5.2.5.3Task 3
-
1.5.2.5.4Task 4
-
1.5.2.5.5Task 5
-
1.5.2.5.6Task 6
-
1.5.3Unit 7 Letters of Congratulations
-
1.5.3.1Part I Introduction
-
1.5.3.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.5.3.2.1Sample 1
-
1.5.3.2.2Sample 2
-
1.5.3.2.3Sample 3
-
1.5.3.2.4Sample 4
-
1.5.3.2.5Sample 5
-
1.5.3.3Part III Useful Expressions
-
1.5.3.4Part IV Writing Tips
-
1.5.3.5Part V Practice
-
1.5.3.5.1Task 1
-
1.5.3.5.2Task 2
-
1.5.3.5.3Task 3
-
1.5.3.5.4Task 4
-
1.5.4Unit 8 Thank-you Letters
-
1.5.4.1Part I Introduction
-
1.5.4.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.5.4.2.1Sample 1
-
1.5.4.2.2Sample 2
-
1.5.4.2.3Sample 3
-
1.5.4.2.4Sample 4
-
1.5.4.3Part III Useful Expressions
-
1.5.4.4Part IV Writing Tips
-
1.5.4.5Part V Practice
-
1.5.4.5.1Task 1
-
1.5.4.5.2Task 2
-
1.5.4.5.3Task 3
-
1.5.4.5.4Task 4
-
1.5.5Unit 9 Letters of Apology
-
1.5.5.1Part I Introduction
-
1.5.5.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.5.5.2.1Sample 1
-
1.5.5.2.2Sample 2
-
1.5.5.2.3Sample 3
-
1.5.5.3Part III Useful Expressions
-
1.5.5.4Part IV Writing Tips
-
1.5.5.5Part V Practice
-
1.5.5.5.1Task 1
-
1.5.5.5.2Task 2
-
1.5.5.5.3Task 3
-
1.5.5.5.4Task 4
-
1.5.6Unit 10 Letters of Complaint and Reply
-
1.5.6.1Part I Introduction
-
1.5.6.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.5.6.2.1Sample 1
-
1.5.6.2.2Sample 2
-
1.5.6.2.3Sample 3
-
1.5.6.2.4Sample 4
-
1.5.6.2.5Sample 5
-
1.5.6.2.6Sample 6
-
1.5.6.3Part III Useful Expressions
-
1.5.6.4Part IV Writing Tips
-
1.5.6.5Part V Practice
-
1.5.6.5.1Task 1
-
1.5.6.5.2Task 2
-
1.5.6.5.3Task 3
-
1.5.6.5.4Task 4
-
1.5.6.5.5Task 5
-
1.5.6.5.6Task 6
-
1.5.6.5.7Task 7
-
1.6Chapter III Career Stage (Business Letters)
-
1.6.1Unit 11 Establishing Business Relations
-
1.6.1.1Part I Introduction
-
1.6.1.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.6.1.2.1Sample 1 The exporter writes to a trade dealer
-
1.6.1.2.2Sample 2 Reply to the exporter from the trade deal...
-
1.6.1.2.3Sample 3 The importer wants to set up relations wi...
-
1.6.1.2.4Sample 4 Reply to the importer
-
1.6.1.3Part III Extra Tips
-
1.6.1.4Part IV Basic Words & Phrases
-
1.6.1.5Part V Useful Expressions
-
1.6.1.6Part VI Practice
-
1.6.1.6.1Task 1
-
1.6.1.6.2Task 2
-
1.6.1.6.3Task 3
-
1.6.1.6.4Task 4
-
1.6.1.6.5Task 5
-
1.6.1.6.6Task 6
-
1.6.2Unit 12 Inquiries and Responses
-
1.6.2.1Part I Introduction
-
1.6.2.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.6.2.2.1Sample 1 General inquiry
-
1.6.2.2.2Sample 2 Response to general inquiry
-
1.6.2.2.3Sample 3 Specific inquiry
-
1.6.2.2.4Sample 4 Response to specific inquiry
-
1.6.2.3Part III Extra Tips
-
1.6.2.4Part IV Basic Words & Phrases
-
1.6.2.5Part V Useful Expressions
-
1.6.2.6Part VI Practice
-
1.6.2.6.1Task 1
-
1.6.2.6.2Task 2
-
1.6.2.6.3Task 3
-
1.6.2.6.4Task 4
-
1.6.2.6.5Task 5
-
1.6.2.6.6Task 6
-
1.6.3Unit 13 Offers and Counter-offers
-
1.6.3.1Part I Introduction
-
1.6.3.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.6.3.2.1Sample 1 Firm offer
-
1.6.3.2.2Sample 2 Counter-offer to the above
-
1.6.3.2.3Sample 3 Another counter-offer (Reply to the above...
-
1.6.3.2.4Sample 4 Non-firm offer
-
1.6.3.2.5Sample 5 Counter-offer to the above
-
1.6.3.3Part III Extra Tips
-
1.6.3.4Part IV Basic Words & Phrases
-
1.6.3.5Part V Useful Expressions
-
1.6.3.6Part VI Practice
-
1.6.3.6.1Task 1
-
1.6.3.6.2Task 2
-
1.6.3.6.3Task 3
-
1.6.3.6.4Task 4
-
1.6.3.6.5Task 5
-
1.6.4Unit 14 Order Letters
-
1.6.4.1Part I Introduction
-
1.6.4.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.6.4.2.1Sample 1
-
1.6.4.2.2Sample 2
-
1.6.4.2.3Sample 3
-
1.6.4.2.4Sample 4
-
1.6.4.3Part III Useful Expressions
-
1.6.4.4Part IV Writing Tips
-
1.6.4.5Part V Practice
-
1.6.4.5.1Task 1
-
1.6.4.5.2Task 2
-
1.6.4.5.3Task 3
-
1.6.4.5.4Task 4
-
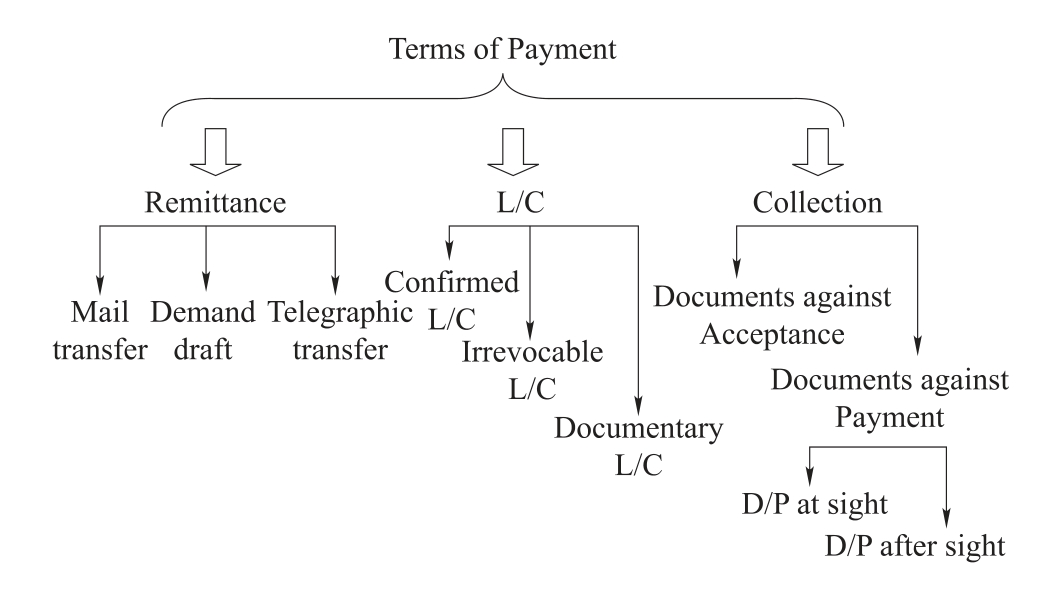
1.6.5Unit 15 Terms of Payment
-
1.6.5.1Part I Introduction
-
1.6.5.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.6.5.2.1Sample 1 Buyer asking for other terms of payment
-
1.6.5.2.2Sample 2 Seller insisting on payment by L/C
-
1.6.5.2.3Sample 3 Seller agreeing to other terms of payment
-
1.6.5.2.4Sample 4 Seller asking for extension of L/C
-
1.6.5.3Part III Extra Tips
-
1.6.5.4Part IV Basic Words & Phrases
-
1.6.5.5Part V Useful Expressions
-
1.6.5.6Part VI Practice
-
1.6.5.6.1Task 1
-
1.6.5.6.2Task 2
-
1.6.5.6.3Task 3
-
1.6.5.6.4Task 4
-
1.6.5.6.5Task 5
-
1.6.6Unit 16 Packing and Shipment
-
1.6.6.1Part I Introduction
-
1.6.6.2Part II Sample Analysis
-
1.6.6.2.1Sample 1 Buyer informing the packing and shipping ...
-
1.6.6.2.2Sample 2 Seller replying the packing and shipping ...
-
1.6.6.2.3Sample 3 Buyer urging shipment
-
1.6.6.2.4Sample 4 Shipping Advice
-
1.6.6.3Part III Extra Tips
-
1.6.6.4Part IV Basic Words & Phrases
-
1.6.6.5Part V Useful Expressions
-
1.6.6.6Part VI Practice
-
1.6.6.6.1Task 1
-
1.6.6.6.2Task 2
-
1.6.6.6.3Task 3
-
1.6.6.6.4Task 4
-
1.6.6.6.5Task 5
-
1.6.7Keys for Reference
-
1.6.7.1Unit 1 Structure and Styles of Letters
-
1.6.7.1.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.1.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.1.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.1.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.2Unit 2 E-mails
-
1.6.7.2.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.2.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.2.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.2.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.2.5Task 5
-
1.6.7.2.6Task 6
-
1.6.7.3Unit 3 Résumés
-
1.6.7.3.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.3.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.3.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.3.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.3.5Task 5
-
1.6.7.4Unit 4 Job Application Cover Letters
-
1.6.7.4.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.4.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.4.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.4.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.5Unit 5 Office Correspondence
-
1.6.7.5.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.5.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.5.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.5.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.5.5Task 5
-
1.6.7.5.6Task 6
-
1.6.7.6Unit 6 Invitations
-
1.6.7.6.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.6.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.6.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.6.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.6.5Task 5
-
1.6.7.6.6Task 6
-
1.6.7.7Unit 7 Letters of Congratulations
-
1.6.7.7.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.7.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.7.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.7.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.8Unit 8 Thank-you Letters
-
1.6.7.8.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.8.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.8.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.8.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.9Unit 9 Letters of Apology
-
1.6.7.9.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.9.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.9.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.9.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.10Unit 10 Letters of Complaint and Reply
-
1.6.7.10.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.10.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.10.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.10.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.10.5Task 5
-
1.6.7.10.6Task 6
-
1.6.7.10.7Task 7
-
1.6.7.11Unit 11 Establishing Business Relations
-
1.6.7.11.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.11.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.11.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.11.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.11.5Task 5
-
1.6.7.11.6Task 6
-
1.6.7.12Unit 12 Inquiries and Responses
-
1.6.7.12.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.12.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.12.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.12.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.12.5Task 5
-
1.6.7.12.6Task 6
-
1.6.7.13Unit 13 Offers and Counter-offers
-
1.6.7.13.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.13.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.13.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.13.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.13.5Task 5
-
1.6.7.14Unit 14 Order Letters
-
1.6.7.14.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.14.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.14.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.14.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.15Unit 15 Terms of Payment
-
1.6.7.15.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.15.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.15.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.15.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.15.5Task 5
-
1.6.7.16Unit 16 Packing and Shipment
-
1.6.7.16.1Task 1
-
1.6.7.16.2Task 2
-
1.6.7.16.3Task 3
-
1.6.7.16.4Task 4
-
1.6.7.16.5Task 5
-
1.7参考文献
1
新编商务英语应用文写作