-
1.1前言
-
1.2目录
-
1.3Unit 1 PracticaI Writing
-
1.3.1BUSINESS ENGLISH WRITING STYLE商务英语写作风格
-
1.3.1.11.Principles of Good Business Writing商务英语写作的原则
-
1.3.1.22.Organization组织
-
1.3.1.33.Electronic Mail电子邮件
-
1.3.2Language Review
-
1.3.3NOUNS名词
-
1.3.3.11.Plurals复数
-
1.3.3.22.Possessives所有格
-
1.4Unit 2 PracticaI Writing
-
1.4.1LETTER FORMAT信函格式
-
1.4.1.11.Introduction简介
-
1.4.1.22.Parts of a Business Letter商业信函的组成部分
-
1.4.1.33.Letter Styles书信格式
-
1.4.1.44.Punctuation Styles标点格式
-
1.4.1.55.Envelope Addressing信封格式
-
1.4.2Language Review
-
1.4.3PRONOUNS代词
-
1.4.3.11.Personal Pronouns人称代词
-
1.4.3.22.Relative Pronouns关系代词
-
1.4.3.33.Indefinite Pronouns不定代词
-
1.4.3.44.Some Writing Problems Concerning Pronouns写作中牵涉到的...
-
1.5Unit 3 PracticaI Writing
-
1.5.1ESTABLISHING BUSINESS RELATIONS建立商业合作关系
-
1.5.2Language Review
-
1.5.3ADJECTIVES形容词
-
1.5.3.11.Degree Forms形容词的比较等级
-
1.5.3.22.Placement of Adjectives形容词的位置
-
1.5.3.33.Articles冠词
-
1.5.3.44.Adjectives That Cannot Be Compared不可比较的形容词
-
1.5.3.55.Prepositional Phrases介词短语
-
1.6Unit 4 PracticaI Writin
-
1.6.1REQUEST LETTERS询价信函
-
1.6.1.11.Inquiries询价
-
1.6.1.22.Inquiry Reply
-
1.6.2Language Review
-
1.6.3ADVERBS副词
-
1.6.3.11.Adjective and Adverb Form Changes形容词和副词的词形变化
-
1.6.3.22.Placement of Adjectives and Adverbs in Sentences...
-
1.6.3.33.Prepositional Phrases介词短语
-
1.7Unit 5 PracticaI Writing
-
1.7.1QUOTATION,OFFER AND COUNTER-OFFER报价、报盘和还盘
-
1.7.2Language Review
-
1.7.3PREPOSITIONS介词
-
1.7.3.11.Prepositional Phrases介词词组
-
1.7.3.22.Prepositional Combinations介词短语
-
1.7.3.33.Phrasal Prepositions复杂介词(成语介词)
-
1.7.3.44.Ending Sentences with Prepositions句末介词
-
1.7.3.55.Unnecessary Prepositions不必要的介词
-
1.8Unit 6 PracticaI Writing
-
1.8.1ORDER AND CONTRACT订单与合同
-
1.8.1.11.Place an Order
-
1.8.1.22.Covering Letter with an Order
-
1.8.1.33.Order Acknowledgment9订单回执
-
1.8.1.44.Covering Letter with a Sales Confirmation
-
1.8.2Language Review
-
1.8.3VERBS动词
-
1.8.3.11.Tenses of Verbs动词时态
-
1.8.3.22.Moods of Verbs动词的语气
-
1.8.3.33.Voices of Verbs动词的语态
-
1.8.3.44.Infinitives,Gerunds,and Participles不定式、动名词和分词
-
1.9Unit 7 PracticaI Writing
-
1.9.1PAYMENT AND COLLECTION LETTERS1付款与催款
-
1.9.1.11.Payment付款
-
1.9.1.22.Collection Letters催款函
-
1.9.1.33.A Sample L/C 信用证范例
-
1.9.1.44.Insurance保险
-
1.9.2Language Review
-
1.9.3CONJUNCTIONS连词
-
1.9.3.11.Coordinate Conjunctions并列连词
-
1.9.3.22.Subordinate Conjunctions从属连词
-
1.9.3.33.Correlative Conjunctions相关连接词
-
1.9.3.44.Conjunctive Adverbs连接副词
-
1.10Unit 8 PracticaI Writing
-
1.10.1COMPLAINTS,CLAIMS AND ADJUSTMENTS投诉、索赔和理算
-
1.10.1.11.Complaints投诉
-
1.10.1.22.Claims索赔
-
1.10.1.33.Adjustments13理算
-
1.10.2Language Review
-
1.10.3SENTENCES句子
-
1.10.3.11.Sentence Structure句子结构
-
1.10.3.22.Kinds of Sentences句子类型
-
1.10.3.33.Run-on Sentences乱加从句的冗句
-
1.10.3.44.Sentence Length句子长度
-
1.11Unit 9 PracticaI Writing
-
1.11.1SALES LETTERS推销信
-
1.11.2Language Review
-
1.11.3CLAUSES AND PHRASES分句和词组
-
1.11.3.11.Independent Clauses独立分句
-
1.11.3.22.Dependent Clauses从属分句
-
1.11.3.33.Prepositional Phrases介词词组
-
1.11.3.44.Infinitive Phrases不定式结构
-
1.11.3.55.Gerund Phrases动名词结构
-
1.11.3.66.Verb Phrases动词词组
-
1.12Unit 10 PracticaI Writing
-
1.12.1JOB APPLICATION AND RESUME求职信和履历表
-
1.12.1.11.Application Letters求职信
-
1.12.1.22.Resume简历
-
1.12.1.33.Letters of Reference and Recommendation证明与推荐信
-
1.12.1.44.Letters Declining a Job Offer拒绝求职的信函
-
1.12.1.55.Letters of Application for Studying Abroad出国留学申请...
-
1.12.1.66.Letters of Recommendation for Studying Abroad出国留...
-
1.12.1.77.Letters of Supporting担保信
-
1.12.2Language Review
-
1.12.3PARAGRAPHS段落
-
1.12.3.11.Qualities of Paragraphs段落的特性
-
1.12.3.22.Related Paragraphs相关的段落
-
1.12.3.33.Kinds of Paragraphs段落的种类
-
1.13Unit 11 PracticaI Writin
-
1.13.1SOCIAL BUSINESS LETTERS商务社交信函
-
1.13.1.11.Letters of Thanks致谢信
-
1.13.1.22.Letters of Congratulations贺信
-
1.13.1.33.Invitations邀请函
-
1.13.1.44.Announcements公告
-
1.13.1.55.Letters of Condolence11 or Sympathy吊唁或慰问信
-
1.13.1.66.Letters of Resignation辞职信
-
1.13.1.77.Applications for Leave请假条
-
1.13.2Language Review
-
1.13.3PUNCTUATION(Ⅰ)标点符号
-
1.13.3.11.The Period句号
-
1.13.3.22.The Question Mark问号
-
1.13.3.33.The Exclamation Point感叹号
-
1.14Unit 12 PracticaI Writing
-
1.14.1MEMOS AND MINUTES备忘录和会议记录
-
1.14.1.11.Interoffice Memos1备忘录
-
1.14.1.22.Minutes10
-
1.14.2Language Review
-
1.14.3PUNCTUATION(Ⅱ)标点符号
-
1.14.3.11.The Comma逗号
-
1.14.3.22.The Semicolon分号
-
1.14.3.33.The Quotation Marks引号
-
1.14.3.44.The Colon冒号
-
1.14.3.55.The Dash破折号
-
1.14.3.66.The Parentheses括号
-
1.15Unit 13 PracticaI Writin
-
1.15.1BUSINESS REPORTS商业报告
-
1.15.1.11.The Parts of a Report报告的组成部分
-
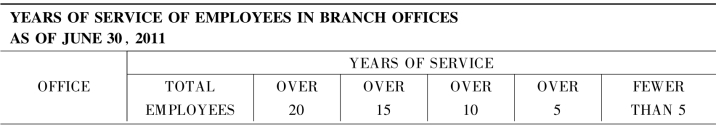
1.15.1.2c.List of tables and illustrations表格和插图
-
1.15.1.32.Kinds of Reports报告的种类
-
1.15.1.43.Formats of Reports报告的形式
-
1.15.1.54.Writing Suggestions
-
1.15.2Language Review
-
1.15.3CAPITALIZATION,ABBREVIATION AND NUMBER大写、缩略语和数字
-
1.15.3.11.Capitalization大写
-
1.15.3.22.Abbreviations缩略语
-
1.15.3.33.Numbers数字
-
1.16KEYS TO EXERCISES
1
新编实用商务英语写作