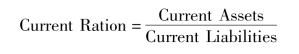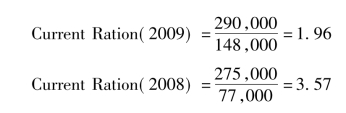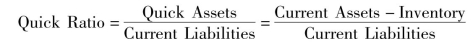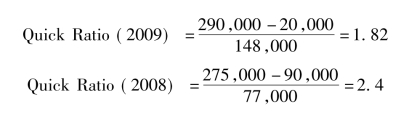11.4 Ratio Analysis
The Ratio Analysis is used to evaluate the financial success of a company by computing a series of financial ratio indicators.It is the most useful and important approach.With these ratio indicators,we can find the information of operating activities such as liquidity,solvency and profitability,and make relative decisions.
When using financial ratios,we should make a comparison with certain set standard ratios.There are three main types of comparisons used to evaluate financial ratios:(1)with a company's own historical ratios,(2)with general rules of thumb or bench marks,and(3)with ratios of other companies or with industry averages.
In general,financial ratios are classified into four types:(1)Solvency Ratios,(2)Profitability Ratios,(3)Activity Ratios,and(4)Stability Ratios.
11.4.1Solvency Ratios
Solvency Ratios are used to evaluate a company's liquidity and short-term debtpaying ability.The liquidity is the ability to convert the company's assets into cash.Most companies seek to keep a good liquidity to meet a series of demands.
In general,some popular solvency ratios are used for evaluating liquidity and short-term debt-paying ability,they are shown as follows:
1.Current Ratio.The Current Ratio is probably the most commonly used indicator of a company's short-term solvency.It expresses the relationship of current assets to current liabilities.It can be computed as follows:
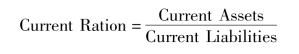
In general,the higher the current ratio,the more assurance creditors have about being paid in full and on time.Conversely,a current ratio that is too high may indicate excessive holdings of cash,accounts receivable,or inventories.Excessive holdings of these resources are bad for a company because it ties up money that could be more effectively used elsewhere.We will compare a company's current ratio with those of past years and with those of similar companies to make judgments about the company's solvency.In general,a current ratio of 2 is considered good in most industries.
Using data from Table 11-1,we can compute STE Company's current ratio as follows:
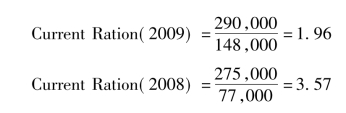
The above figures show that the current ratio has fast decreased from 2008 to 2009.But it is still an acceptable ratio.
2.Quick Ratio.The Quick Ratio or Acid Test Ratio is a more severe test of a company's short-term debt-paying abilities.In this ratio only the current assets that may be easily converted into cash are used in the calculation.These assets are referred to as quick assets,and they generally consist of cash,short-term investment,and accounts receivable,and short-term notes receivable.Inventory is excluded because it is frequently sold on credit and it can't be quickly converted into cash.It can be computed as:
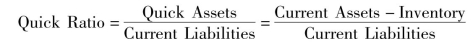
The quick ratio highlights potential solvency problems resulting from a poor mix of current assets.For instance,the use of this ratio usually shows the lower liquidity of a company with a high investment in inventory that would not be revealed in the current ratio.In general,a quick ratio of 1 is considered good in most industries.
Using data from Table 11-1,we can compute STE Company's quick ratio as follows:
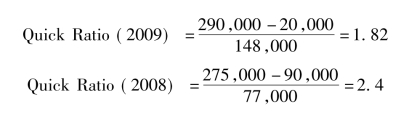
The above figures show that the quick ratio of 2009 and 2008 is all above the standard.
11.4.2Profitability Ratios
Profitability is the ability of a company to provide its investors with a particular rate of return on their investment.It is reflected by the performance in the form of net income earned.Profitability measures are useful decision-making tools for company managers.Managers are often faced with a decision to buy another company,a division of a company,or a machine that makes a new product.In every such case,the manager will evaluate the profitability of the project as part of making the decision.Investors use profitability measures to distinguish between different opportunities they are considering.
The common ratios used in analysis of profitability are through some popular ratios as follows.
1.Rate of Return on Sales.The Rate of Return on Sales'or simply Return on Sales shows the relationship of net income to sales revenue,indicates how much net income is produced by each revenue dollar.The rate can be computed as follows:
Rate of Return on Sales=Net Income/Sales
We all are willing to see the rate of return on net sales higher.Because the higher rate means that the company can earn more profit,and correspondingly reflects well profitability.
Using data from Table 11-2,we can compute STE Company's current ratio as follows(amounts in thousands):
Rate of Return on Sales(2009)=72,000/1,000,000=7.2%
Rate of Return on Sales(2008)=60,000/800,000=7.5%
The above figures show that the rate has decreased a little from 2008 to 2009.
2.Gross Profit Percentage.Gross Profit Percentage is particularly useful to a retailer in choosing a price strategy and in judging its results.It's defined as gross profit(sales revenues minus cost)divided by sales,or it can be computed as follows:
Gross Profit Percentage=Gross Profit/Sales
The gross profit percentage expresses the relationship of gross profit to the sales.It varies greatly by industry.Usually retail companies have higher gross profit percentage than wholesale companies.
Using data from Table 11-2,we can compute STE Company's gross profit percentage as follows(amounts in thousands):
Gross Profit Percentage(2009)=600,000/1,000,000=60%
Gross Profit Percentage(2008)=450,000/800,000=56.25%
The above figures show that the rate has increased a little from 2008 to 2009.Investors is glad to see this point.
3.Return on Stockholders'Equity.Return on Stockholders'Equity is the most important indicator in evaluating the profitability.It's widely regarded as the ultimate measure of overall accomplishment.This ratio expresses the relationship of net income to stockholders'equity,and indicates how much is earned for each dollar invested by owners.To determine the numerator of the ratio preferred dividends are subtracted from net income to obtain net income available for common stock.The ratio can be computed as follows:
Return on Stockholders'Equity=(Net Income-Preferred Dividends)/Average Common Stockholders'Equity
Using data from Tables 11-1 and 11-2,we can compute STE Company's Return on Stockholders'Equity as follows(amounts in thousands):
Return on Stockholders'Equity(2009)=72,000/(310,000+298,000)/2 =23.68%
Return on Stockholders'Equity(2008)=60,000/(298,000+288,000)/2 =20.47%
The above figures show that the rate has increased a little from 2008 to 2009,and the company's profitability has improved slightly.
4.Return on Total Assets.The Return on Total Assets is the best overall measure of the earning power of a corporation.The amount of net income earned in relation to total assets is an indicator of a company's efficiency in the use of its economic resources.We all want to see higher rate of return on total assets.The formulary is computed as follows:
Return on Total Assets=Net Income/Average Total Assets
Using data from Tables 11-1 and 11-2,we can compute STE Company's Return on total assets as follows:
Return on Total Assets(2009)=72,000/(498,000+455,000)/2 =15.13%
Return on Total Assets(2008)=60,000/(455,000+465,000)/2 =13.04%
The above figures show that the rate has increased a little from 2008 to 2009;it is a good trend of development.
11.4.3Activity Ratios
Activity Ratios are used to give a general idea of the length of the segments of a company's operating cycle so that the liquidity of selected current assets may be evaluated.A company's operating cycle is the length of time it takes to invest in inventory,make credit sales,and convert the receivables into cash.The ratio also indicates the efficiency with which the company uses its short-term economic resources.The two common ratios are shown as follows:
1.Inventory Turnover.Inventory Turnover,which is defined as cost of goods sold divided by the average inventory,held during a given period,shows the number of times the inventory is turned over or sold during that period.The formula is as follows:
Inventory Turnover=Cost of Goods Sold/Average Inventory
As a general rule,the higher the inventory turnover,the more efficient the company is in its operations and the lesser the amount of investment that must be tied up in inventory.A company with a higher turnover is usually using its purchasing,receiving,and sales department more efficiently.It's also minimizing the chance of having obsolete inventory.Too high an inventory turnover,however,may indicate lost sales because there were not enough inventories on hand.
Using data from Tables 11-1 and 11-2,we can compute STE Company's inventory turnover as follows:
Inventory Turnover(2009)=400,000/(20,000+90,000)/2=7.3
Inventory Turnover(2008)=350,000/(90,000+45,000)/2=5.2
The above figures show that the rate has increased a little from 2008 to 2009.It indicates the speed of inventory turnover faster.
2.Accounts Receivable Turnover.Once inventory has been sold on credit,the company must collect the receivables to compute its operating cycle.The accounts receivable turnover reflects the efficiency with which the company collects its receivables and converts them back into cash.The formula is as follows:
Accounts Receivable Turnover=Net Credit Sales(or Total Sales)/Average Net Receivables
As a general rule,the higher the turnover the better,because the company has less resources tied up in receivables,collects these resources at a faster pace,and usually has fewer uncollectible accounts.The amount of net credit sales is the appropriate figure to use in the accounts receivable turnover.Most companies report only total sales without giving a breakdown of credit and cash sales,however.
Using data from Tables 11-1 and 11-2,we can compute STE Company's accounts receivable turnover as follows:
Accounts Receivable Turnover(2009)=1,000,000/(95,000+70,000)/2= 12.2
Accounts Receive Turnover(2008)=800,000/(70,000+60,000)/2=12.2
From the above figures,we can see that the accounts receivable turnover in 2009 is 12.2,which is as same as the figure of 2008.
11.4.4Stability Ratios
The Stability Ratios are used to indicate the long-term solvency and stability of the company.They provide evidence of the safety of the investments in the company by long-term bondholders and stockholders.Several stability ratios are shown as follows:
1.Debt Ratio.The debt ratio shows the percentage of total assets contributed by creditors.It helps us to determine how well creditors are protected in case of insolvency.The debt ratio can be computed as follows:
Debt Ratio=Total Liabilities/Total Assets
The different figures of debt ratio express different meanings.In general,creditors prefer to see a lower debt ratio because if business decline it is more likely that the company will be able to pay its interest costs.Up to a point,stockholders prefer a higher debt ratio when the company borrows money from creditors at interest rate that is lower than the return the company can earn in its operations.A very high debt ratio,however,is usually a disadvantage when a company wants to attract additional capital.
Using data from Table 11-l,we can compute STE Company's Debt Ratio as follows:
Debt Ratio(2009)=188,000/498,000=37.7%
Debt Ratio(2008)=157,000/455,000=34.5%
From the above figures,we can see that debt ratio has increased slightly in 2009 compared to 2008.
2.Debt-to-equity Ratio.The debt-to-equity ratio is another indicator that reflects a company's long-term debt-paying ability.It reflects the percentage of what part of the resources is obtained by borrows and what part the owners invest.The ratio can be computed as follows:
Debt-to-equity Ratio=Total Liabilities/Total Stockholders'Equity
From the formula,we can see that the more the borrowing,and the less the equity,the riskier it is to lend money to the company.From the perspective of longterm solvency,the lower the ratio is the better the company's financial positions.
Using data from Table 11-1,we can compute STE Company's debt-to-equity ratio as follows:
Debt-to-equity Ratio(2009)=188,000/310,000=60.6%
Debt-to-equity Ratio(2008)=157,000/298,000=52.7%
From the above figures,we can see that debt-to-equity ratio has increased slightly in 2009 compared to 2008.
3.Time-interest Earned Ratio.The time-interest earned ratio(sometimes called the interest coverage ratio)is used to show the ability of a company to meet its interest obligation.It is a measure of the safety of creditors'investments in the company.The formula is shown as follows:
Time-interest Earned Ratio=(Pretax Income+Interest Expense)/Interest Expense
The numerator of the time-interest earned ratio is usually pretax operating income;that is,income before income taxes,to which interest expense is added back.As general rule,the higher the ratio,the better able is the company to meet its interest obligations.
Using data from Table 11-2,we can compute STE Company's time-interest earned ratio as follows:
Time-interest Earned Ratio(2009)=(120,000+100,000)/100,000=2.2
Time-interest Earned Ratio(2008)=(100,000+80,000)/80,000=2.25
From the above figures,we can see that the ratio has slowed slightly in 2009 compared to 2008.
Words&Expressions
11.1
assess评估
internal内部的
analyst分析人员
external外部的
evaluate评价
objective目标,目的
dividend股息
profitability赢利能力
assessment评价
profitability可赢利性
security安全;证券
creditor债权人
receive接受
principal本金
liquidity资产流动性
solvency偿债能力
current当前的
potentialities可能性;潜力
associated with与……相关
primarily主要地
annual每年的
annual reports年度报告
explanatory解释的
independent独立的
auditor审计员
corporate公司的
11.2
trend analysis趋势分析
horizontal analysis横向分析
amount数量
base year基准年份
formula公式
liability债务
equity权益
exceed超过
gross大体的
11.3
common-size analysis结构分析
vertical垂直的
vertical analysis纵向分析
computation计算
dividing拆分;除以
shift变迁
composition构成
decline减少;下降
pretax税前的
slightly轻微地
11.4
ratio analysis比率分析
approach方法
standard ratios标准比率
comparison比较
historical历史的
thumb大拇指
bench marks单凭经验的规则
average平均数
profitability ratio获利比率
current ratio流动比率
assurance保险
conversely相反地
excessive过度的,过量的
tie up占用
quick ratio速动比率
acid test ratio酸性测试比率
be converted into被转变成
quick assets速动资产
sold on credit赊销
decision-making tools作出决策的工具
division分支,分部
distinguish区分
rate of return on sales销售报酬率
correspondingly相应地
gross profit percentage毛利率
retailer零售商
strategy策略
wholesale批发的
return on stockholders'equity股东权益报酬率
overall accomplishment综合业绩
numerator分子
return on total assets总资产报酬率
efficiency效率
formulary公式
activity ratio活动性比率
segment部分
inventory turnover存货周转率
be tied up in inventory投放在存货上
minimizing最小化
uncollectible不能回收的
uncollectible accounts坏账
appropriate适当的
breakdown崩溃;衰竭
accounts receivable turnover应收账款周转率
stability ratio稳定性比率
long-term solvency长期偿债能力
stability稳定性
evidence证据
debt ratio负债比率
disadvantage缺点
additional其他的,多余的
debt-to-equity ratio权益负债率
perspective看法;角度
time-interest earned ratio已获利息倍数
coverage范围;规模
pretax income税前利润
Notes
1.Dividend payments depend on how profitable operations are,and stock prices depend on the market's assessment of the company's future prospect.股息支付依赖于所取得的经营利润,而股价则依赖于市场对公司未来发展前景的评估。该句为并列复合句,由and连接的两个分句形成并列句,在第一个分句中,从句how profitable operations are作动词短语depend on的宾语。
2.They also want to know about profitability because the profitable operations that drive stock prices to higher levels also provide the cash to repay loans and finance growth.他们当然也关心盈利能力,因为经营利润会使股价上升到更高水平,从而有足够的资金偿还贷款及支持财务增长。该句为主从复合句。主句为They also want to know about profitability。由because引导的是原因状语从句,在原因状语从句中,that drive stock prices to higher levels为定语从句,修饰其先行词,即原因状语从句中的主语部分the profitable operations,谓语为provide。
3.Trend Analysis,also called Horizontal Analysis,shows the changes in a company's financial condition and operating results in percentages as well as in dollar amounts from one year to the next.趋势分析,也称为横向分析,显示公司从一个年度到另一年度的财务状况与经营成果在百分比及金额上的变化。该句为简单句。主语为Trend Analysis,半系词为shows,后面的成分全部为表语。主语之后有过去分词起定语作用,而表语部分有一个短语as well as,意为“以及”,起连接作用。
4.To compute the trend changes,we must select the base year,whose amounts are set equal to the base-year amount or to 100 percent.为了计算变化趋势,我们必须选定一个基准年份,并把它的数额设定为基准数额或相当于100%。该句为主从复合句。句首的不定式短语为目的状语,主句为we must select the base year,其后是一个由whose引导的非限制性定语从句,修饰base year。
5.In this method,we must define the total figures as the base,and set it equal to 100 percent,then compute the percentage of each item of that figure.在这种方法中,我们必须定义合计数为基准数据,并把它当成100%,然后计算每个项目对基准数据的百分比。该句为简单句,主语为we,三个并列谓语分别由动词define,set以及compute来表示。
6.For instance,the use of this ratio usually shows the lower liquidity of a company with a high investment in inventory that would not be revealed in the current ratio.例如,使用这个比率通常可以发现巨额投资于存货的公司具有较低的流动性。这是流动比率所不能揭示的问题。该句为主从复合句。主句为主系表结构,shows可看作半系词,后面的成分为表语。在表语中又含有一个由that引导的定语从句,修饰inventory。
7.Activity ratios are used to give a general idea of the length of the segments of a company's operating cycle so that the liquidity of selected current assets may be evaluated.活动性比率通常用来给出公司经营周期每个部分的长度,从而能够评价所选定流动资产的流动性。该句为主从复合句,主句为主谓宾结构,从句是由so that引导的目的状语从句。
8.The accounts receivable turnover reflects the efficiency with which the company collects its receivables and converts them back into cash.应收账款周转率表明了公司收回款项并把它们转换为现金的效率。该句为主从复合句,主句为主谓宾结构,其宾语the efficiency由一个“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句来修饰。
9.Up to a point,stockholders prefer a higher debt ratio when the company borrows money from creditors at interest rate that is lower than the return the company can earn in its operations.在一定程度上,当利息率低于公司能从它的经营中得到的回报率时,股东更喜欢一个较高的负债比率。该句为主从复合句。主句为stockholders prefer a higher debt ratio,由when引导的是时间状语从句,在该时间状语从句中,又带有一个由that引导的定语从句。另外,the company can earn in its operations之前省略了一个在句中作宾语的关系代词that或which.
10.The numerator of the time-interest earned ratio is usually pretax operating income;that is,income before income taxes,to which interest expense is added back.已获利息倍数公式的分子通常是税前经营利润;也就是说,所得税前利润,在此基础上利息被加回。该句为主从复合句,主句为主系表结构。分号之后的that is可视为插入语,income before income taxes可看作短语,解释其主句之意,to which interest expense is added back是由“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句,修饰income taxes。add to为固定搭配,意为“增加”。
Exercises
Section 1:Know the Concepts
1.Classify each of the following statements as True or False.
(1)A firm with a current ratio of 2 would be in a healthy situation.
(2)A manufacturing company's stocks should always be included in a calculating its liquidity.
(3)A bank which had lent money to a company would be happy if its timeinterest earned ratio rose.
(4)The higher the percentage of a company for gearing,the smaller is its longterm debt.
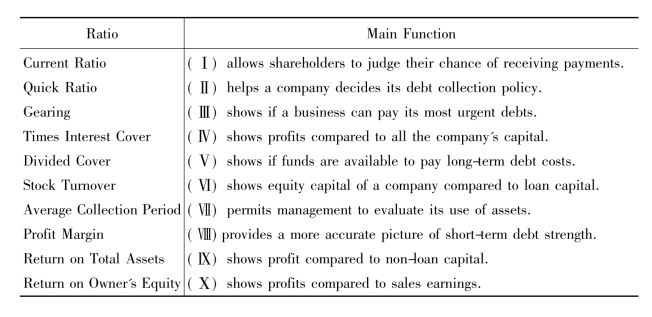
2.Match the ratios listed in the text with their main functions.
3.Translate the following terms into Chinese.
(1)trend analysis
(2)return on total asset
(3)times-interested earned ratio
(4)inventory turnover
(5)accounts receivable turnover
(6)current ratio
(7)quick ratio
(8)acid test ratio
Section 2:Practical Application
1.If a firm's current assets are$1,000,000 and its current liabilities $500,000,calculate its current ratio.What does this ratio tell you?
2.You are given the following balance sheet and income statement for 2002 and 2003:
Table A
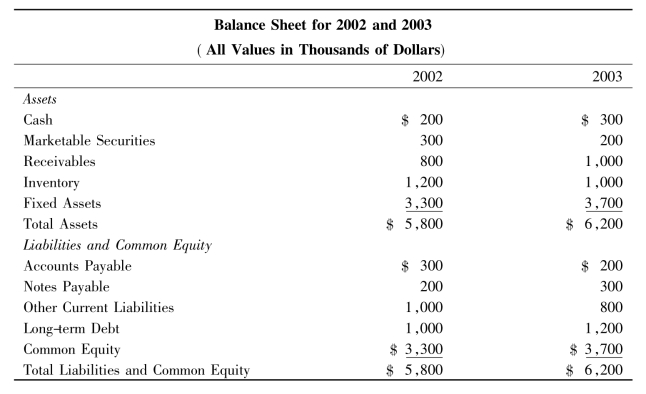
Table B

Depreciation Amounts to$50,000 in 2003
(1)Using the financial information presented in Table A,calculate the following ratios for 2002:
(a)the current ratio
(b)the debt to equity ratio
(c)the acid-test or quick ratio
(2)Analyzing both the income statement(Table B)and the balance sheet (Table A),calculate the following ratios for 2003:
(a)time-interest earned ratio
(b)rate of return on sales
(c)return on total assets
3.Selected financial ratios for a firm and its industry are as follows:
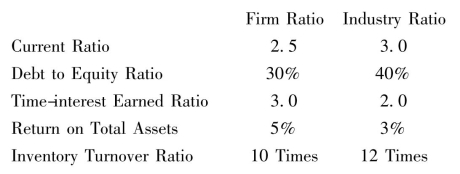
Compare the financial ratios of the firm and the industry and discuss their strengths and weaknesses.
课文翻译