-
1.1前 言
-
1.2Chapter 1 Overview of Accounting
-
1.2.11.1 Accounting History
-
1.2.21.2 Accounting Definition and Function
-
1.2.31.3 Accounting Standards
-
1.2.41.4 Categorization of Accounting
-
1.2.51.5 Accounting Postulations
-
1.2.61.6 Accounting Principles
-
1.3第一章 会计概述
-
1.3.11.1 会计的历史
-
1.3.21.2 会计的定义与功能
-
1.3.31.3 会计标准
-
1.3.41.4 会计分类
-
1.3.51.5 会计假设
-
1.3.61.6 会计原则
-
1.4Chapter 2 Accounting Recognition and Measurement
-
1.4.12.1 Accounting Elements and Equations
-
1.4.22.2 Accounting Subjects and Account
-
1.4.32.3 Double Entry System
-
1.5第二章 会计确认与记量
-
1.5.12.1 会计要素与会计等式
-
1.5.22.2 会计科目与账户
-
1.5.32.3 复式记账系统
-
1.6Chapter 3 Accounting Process
-
1.6.13.1 Accounting Cycle
-
1.6.23.2 The Journal
-
1.6.33.3 The Ledger
-
1.6.43.4 Adjusting Entries
-
1.6.53.5 Trial Balance
-
1.7第三章 会计程序
-
1.7.13.1 会计循环
-
1.7.23.2 日记账
-
1.7.33.3 分类账
-
1.7.43.4 调整分录
-
1.7.53.5 试算平衡表
-
1.8Chapter 4 Current Assets
-
1.8.14.1 Assets
-
1.8.24.2 Current Assets
-
1.8.34.3 Cash
-
1.9第四章 流动性资产
-
1.9.14.1 资产的概念
-
1.9.24.2 流动资产
-
1.9.34.3 现金
-
1.10Chapter 5 Accounts Receivable
-
1.10.15.1 Receivables
-
1.10.25.2 Accounts Receivable
-
1.11第五章 应收账款
-
1.11.15.1 应收款项
-
1.11.25.2 应收账款
-
1.11.35.2.1 应收账款的确认
-
1.11.45.2.2 应收账款的入账金额
-
1.11.55.2.3 应收账款的处置
-
1.12Chapter 6 Inventory
-
1.12.16.1 Inventory and Its Classification
-
1.12.26.2 Determine Inventory Quantities
-
1.12.36.3 Basic Issues in Inventory Valuation
-
1.13第六章 存 货
-
1.13.16.1 存货及其分类
-
1.13.26.2 存货数量的确定
-
1.13.36.3 存货计价的基本方法
-
1.14Chapter 7 Non-current Assets
-
1.14.17.1 Fixed Assets
-
1.14.27.2 Depreciation of Fixed Assets
-
1.14.37.3 Intangible Assets
-
1.14.47.4 Long-term Investment
-
1.15第七章 非流动性资产
-
1.15.17.1 固定资产
-
1.15.27.2 固定资产的折旧
-
1.15.37.3 无形资产
-
1.15.47.4 长期投资
-
1.16Chapter 8 Liabilities and Equity
-
1.16.18.1 Concept of Liabilities
-
1.16.28.2 Current Liabilities
-
1.16.38.3 Long-term Liabilities
-
1.16.48.4 Owner's Equity
-
1.16.58.5 The Nature of Owner's Equity
-
1.16.68.6 Sources of Owner's Equity
-
1.17第八章 负债与权益
-
1.17.18.1 负债的概念
-
1.17.28.2 流动负债
-
1.17.38.3 长期负债
-
1.17.48.4 所有者权益
-
1.17.58.5 所有者权益的特点
-
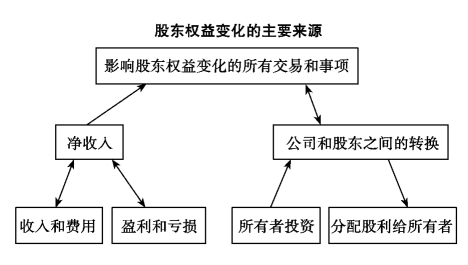
1.17.68.6 所有者权益的来源
-
1.18Chapter 9 Revenue and Expenses
-
1.18.19.1 Revenue
-
1.18.29.2 Expenses
-
1.18.39.3 Gains and Losses
-
1.19第九章 收入与费用
-
1.19.19.1 收入
-
1.19.29.2 费用
-
1.19.39.3 收益和损失
-
1.20Chapter 10 Financial Statements
-
1.20.110.1 Overview of Financial Statements
-
1.20.210.2 The Balance Sheet
-
1.20.310.3 The Income Statement
-
1.20.410.4 The Statement of Cash Flows
-
1.21第十章 财务报表
-
1.21.110.1 报表概述
-
1.21.210.2 资产负债表
-
1.21.310.3 利润表
-
1.21.410.4 现金流量表
-
1.22Chapter 11 Financial Statement Analysis
-
1.22.111.1 Objectives of Financial Statement Analysis
-
1.22.211.2 Trend Analysis
-
1.22.311.3 Common-size Analysis
-
1.22.411.4 Ratio Analysis
-
1.23第十一章 财务报表分析
-
1.23.111.1 财务报表分析的目的
-
1.23.211.2 趋势分析
-
1.23.311.3 结构分析
-
1.23.411.4 比率分析
-
1.24Chapter 12 Accounting in the New Epoch
-
1.24.112.1 International Accounting
-
1.24.212.2 Computerized Accounting System
-
1.24.312.3 Three Basic Software in Accounting
-
1.25第十二章 新时代会计
-
1.25.112.1 国际会计
-
1.25.212.2 电算化会计
-
1.25.312.3 三种基本会计软件
-
1.26Chapter 13 Accountants,Organizations and Examinati...
-
1.26.113.1 Profession of Accounting
-
1.26.213.2 Top Accounting Organizations
-
1.26.313.3 Accounting Examinations
-
1.26.413.4 Ethics and the Accounting Environment
-
1.27第十三章 会计人员、机构与考试
-
1.27.113.1 会计职业
-
1.27.213.2 世界顶级会计师事务所
-
1.27.313.3 会计考试
-
1.27.413.4 道德规范与会计环境
-
1.28Chapter 14 Accounting Language
-
1.28.114.1 Abbreviation and Acronyms缩略语及简称
-
1.28.214.2 British and American Accounting Vocabulary英美会...
-
1.28.314.3 Accounting Terms常用会计术语
-
1.28.414.4 Accounting Diagrams常见会计报表中英对照
-
1.29Keys to the Exercises
-
1.30附录一 《中华人民共和国会计法》
-
1.31附录二 《中华人民共和国会计法》知识问答
-
1.32Bibliography
1
实用会计英语
1.17.6
8.6 所有者权益的来源