Summary
Coordination compounds are a class of compounds that contain a central atom or ion, usually a metal.surrounded by a cluster of ions or molecules called ligand, Ligands can be classified as monodentate and polydentate. The bonding between the metal atom and the ligands is called coordination bond. A complexion, called inner sphere, is held with outer sphere by ionic force, The ruler for naming coordination compounds is reference to the lnorganic Nomenclature Committee of the international Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
The valence bond theory assumes that hybridized orbitals are formed by the combination and rearrangement of empty orbitals of central metal atom , each of the ligands contributes a pair of electrons to the empty hybridized orbitals of the central metal to form a coordination bond. Coordination compounds can be classified as outer-orbital and inner-orbital complex. The valence bond theory can account reasonably well for the structure and magnetic properties of metal complexes .
According to crystal field theory , the d orbitals are split into two higher-energy and three lower-energy orbitals in an octahedral complex. The energy difference between these two sets of d obitals is the crystal field splitting energy . Electrons spins tend to be parallel with weak-field ligands and paired with strong-field ligands. The model can be used to understand , interpret and predict the magnetic behavior ,colors and some structures of coordination complexes.
Coordination equilibrium is one of the chemical equilibriums. For the reaction of the coordination com.pound formation:
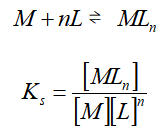
Ks is called the equilibrium constant for the coordination compound formation, also called the stability constant . The larger the Ks, the more stable the coordination compound.
Once the concentration of M and L are changed, the balance may be disturbed and shifted to a new equilibrium position. If the re-oxide equilibrium , acid-base equilibrium ,precipitation equilibrium are present in the same reacting system , the complex formation equilibrium will be moved.
A polydentate ligand can coordinate with a central metal atom to form coordination compound called chelate. Because the chelate contains five or six-membered ring in the structure, hence,its stability is very great. The more the cyclical structure in a chelate , the greater its stability.
Coordination compounds that contain a central metal atom or ion surrounded by biological ligands play important roles in vivo. They are essential in the storage and transport of oxygen, as electron transfer agents,as catalysts,and is photosynthesis. Coordination compounds are useful in medical areas-for example, in treatment of metal poisoning and as ant-tumor agents.


