Why do we need trade terms in international trade?
It is very important to agree the price of the transaction and the risks and responsibilities of the buyer and seller. In the long history of international trade, the form of "trade terms" has gradually evolved, which can better divide the risks, liabilities, costs and other contents of buyers and sellers.
1. Definitions and Functions of Trade Terms
Trade terms, also known as price terms or price conditions, refer to specialized terms that use phrases or English abbreviations to explain the price composition of goods and the division of risks, responsibilities, and costs between buyers and sellers in the process of goods handover. This definition has two meanings:
① Trade terms describe what constitutes the price of a commodity, for example, does it include freight charges? Who pays the insurance?
② Trade terms are special terms used by buyers and sellers on the place of delivery, risks, liabilities and costs during the delivery of goods.
2. Functions of Trade Terms
Trade term is a component of price clause , and price clause is the core of all terms . In international trade , the problems that importers and exporters have to solve are very complicated. In addition to specifying the price, both parties need to specify which party shall bear the freight, insurance and other related expenses, and which party shall bear the risk of goods damage, etc . The appearance of trade terms has clarified the responsibilities of both parties, simplified the transaction procedures, improved the transaction efficiency, effectively promoted the development of international trade, and played an important role in international trade.
International trade practices are some common practices and interpretations gradually developed in the long-term practice of international trade, which have become rules and provisions through the compilation and interpretation of relevant international organizations, and are familiar with, recognized and adopted by many countries or trade groups.
① It is not the common legislation of all countries, nor the law of any one country, so it does not have the compulsion of law.
② When both parties cite one international customer, it becomes legally valid, and both parties are subject to it . If the contract clause conflict with customers, the contract to be followed is as a basic principle
1. Warsaw Oxford Rules (1932)
Formulated by the International Law Association, these Rules have a total of 21 articles, mainly stating the nature of CIF sales contracts. The expenses, risks and responsibilities borne by both parties are specified.
Since the mid-19th century, The CIF trade term has been widely used, but disputes and controversies often arise in transactions due to its original lack of uniform provisions and interpretations of the respective obligations of the buyer and the seller. Thus, the International Law Association drafted and designated the Uniform Rules for CIF in Warsaw, the capital of Poland, in 1928, and then, at the Oxford Conference in 1932, the Rules were made 21 and renamed the Warsaw Oxford Rules of 1932, which are still in use today.
2.Revised American Foreign Trade Definition 1941
It is jointly developed by the American Chamber of Commerce , the American Chamber of Importers and the American Foreign Trade Association, and mainly applies to North And Latin American countries.
This practice has a greater impact in American countries. Special attention shall be paid to differences from other usages in trade with countries where such usages are adopted, and both parties shall specify in the contract the usages on which the trade terms are based.
It specifies six terms:
(1)Ex point of origin
(2) Free on Board
(3)Free along Side
(4)Cost and Freight
(5.)Cost, Insurance and Freight
(6)Ex Dock
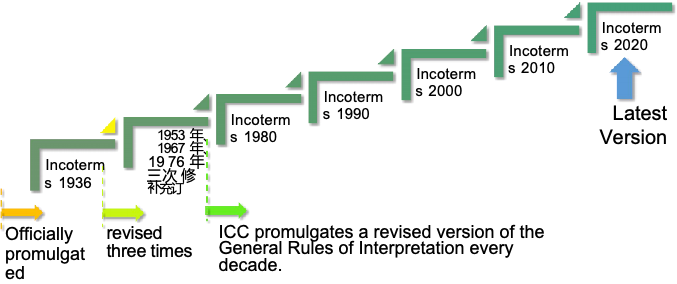
3. International Rules for the Interpretation of Trade Terms, INCOTERMS
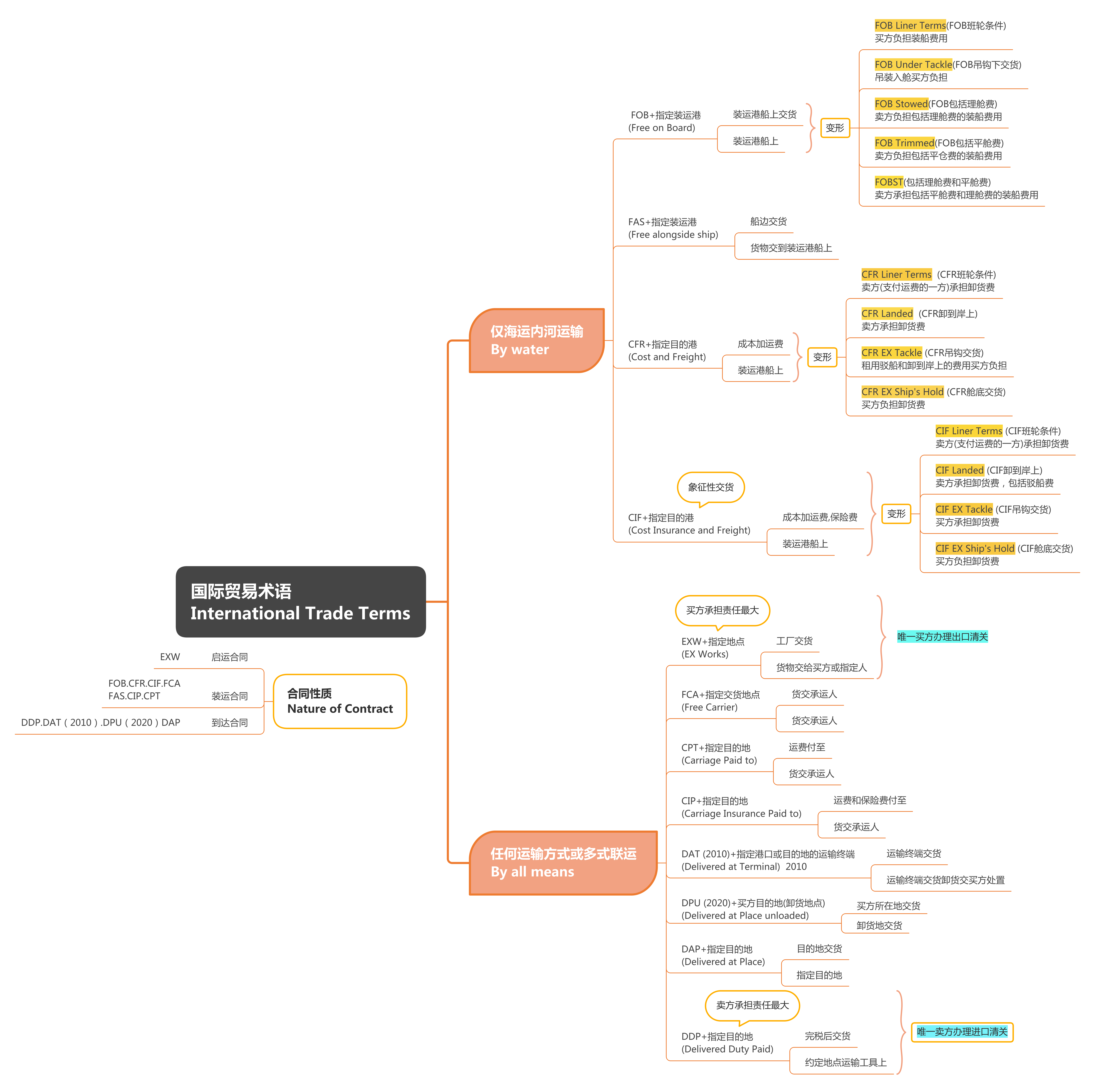
The General Rules for the Interpretation of International Trade 1936 were formulated by the International Chamber of Commerce in Paris in 1936. Subsequently, it has been amended many times to meet the needs of the development of international trade business. The 2020 General Rules include four groups of 11 trade terms.