-
1 Thought Patt...
-
2 Case Study
So far, we have already learned different aspects about verbal communication, such as addressing, compliments, taboos and culturally loaded words, which will help you to have better communications with people by recognizing the cultural differences with linguistic signs. While during intercultural communication, there will always be some differences that cannot be recognized or presented superficially, and these differences take roots inside our mind and play a more decisive role. They are different patterns of thought.
Sometimes, we will find people from different cultures inscrutable not because of the words or grammar they use, but the different ways of communication, or to be more exact, that’s because the different thinking patterns encouraged by that certain culture.
Thinking patterns are not born to be with us, but influenced by the cultures we live in, and people of the same race may act differently when they grow up in different cultures. This phenomenon is reflected in some movies involving intercultural communication. Now let’s firstly enjoy a video clip from the movie The Farewell, and in this video you will see different responses to the serious topic of life – death.
Ok, have you found out the different thinking patterns in this movie? Yes, they are the typical high-context thinking pattern being more indirect and euphemistic, and the typical low-context thinking pattern, likely to be more direct and facts-oriented.
Facing the fact that her grandma has cancer, Bill, who migrated to America when she was 6 years old, advocate that grandma deserves the truth. While her parents and relatives who live in China and Japan for long time would like to keep it a secret to grandma, thinking that truth will cause a more serious suffering than the disease itself. You see, what a striking contrast between a typical Oriental thinking pattern and a Western thinking pattern.
Robert Kaplan, the famous linguist, used different shapes to demonstrate different thinking patterns in different cultures.
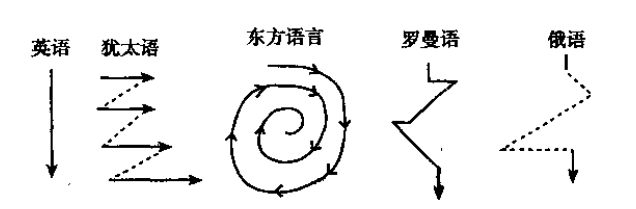
English Semitic Oriental Romance Russian
Figure 1 Sequencing Differences by Culture
As you can see in figure 1, English-speakers were likely to be more linear and direct than Semitic individuals who solve problems using a combination of tangential and semi-direct approaches. Asians employed a circular approach, Romance cultures used a more consistently circuitous approach, and Russians used a combination of direct and circuitous approach.
Learning one language is not only learning the grammar and vocabulary, but learning the logic and problem-solving approach embedded in its culture. Understanding and appreciation of differences among cultures in cognitive processing and problem solving will be a major step towards successful intercultural communication. And for the students, it will also help you make great progress in learning in terms of listening, speaking, reading, writing, and even translation.
Differences in Cultural Thought Patterns
• A culture’s worldview(世界观), belongs to the core part of culture, for it influences all aspects of our perception and consequently affects our belief and value system as well as how we think and act.
• Eastern culture’s worlview: holistic(整体的,全盘的), Chinese philosophers emphasized the “One”, the ”blending” and the “harmony”. The notion of stressing oneness or wholeness took root in the minds of Chinese people. intuitive wisdom
• Nature and Man are blended into one harmonious identity.(天人合一) They stress adapting to nature instead of conquering it.
• Traditional Chinese Medicine stresses the whole human body that is compose of different parts. Being part of nature, the human body, if it isn’t functioning well, needs to be broght back into balance. So medicine has to stimulate the body’s own resources which work to restore normality.
• Western culture’s worldview: dualistic(二元的), the ancient Greek philosophers tended to believe that the Universe is divided into two opposites and there is a clear-cut demarcation(划界) between the two: man and nature, subject and object, mind and matter, the divine and the secular(世俗). Christianity prevalent in the West helps explain this.
• Western Medicine lays emphasis on the parts that make up a man. The human body is taken as an object that can be studied and controlled.
• Reasoning is humankind’s highest faculty and achievement. There is also a strong reliance on “facts” as opposed to “opinions”.


