-
1 Intercultural&nbs...
-
2 Case Study
-
3 Critical Thi...
-
4 Discussion
-
5 Further Study
1. Definition
Intercultural Communication studies how people from different cultural backgrounds communicate with each other. It covers knowledge from many disciplines, including psychology, philosophy, anthropology and sociology. The American anthropologist Edward T. Hall is said to be the father of Intercultural Communication. He once said that the ultimate reason for intercultural communication is to learn more about how one’s ownsystem works. So, the primary objective of this course is to arouse ourcultural awareness, build cultural confidence, and besides, be well-preparedfor intercultural communication.
2. History
Intercultural communication is as old as history. It occurs whenever there is communication between people from different cultural backgrounds, as what happened on the Silk Road in ancient China, in Marco Polo’s stay, Monk Jianzhen’s mission to Japan, and Zheng He’s seven voyages to the Western Seas. But as a discipline, its history is rather short. The term was first proposed by Edward T. Hall in his publication The Silent Language in 1959. Ever since, it developed very fast. Because of convenient transportation systems, innovative communication systems, economic globalization and widespread migrations, it has become a necessity for college students today to know more knowledge about intercultural communication, so as to communicate effectively with people from other countries and solve problems across cultures.
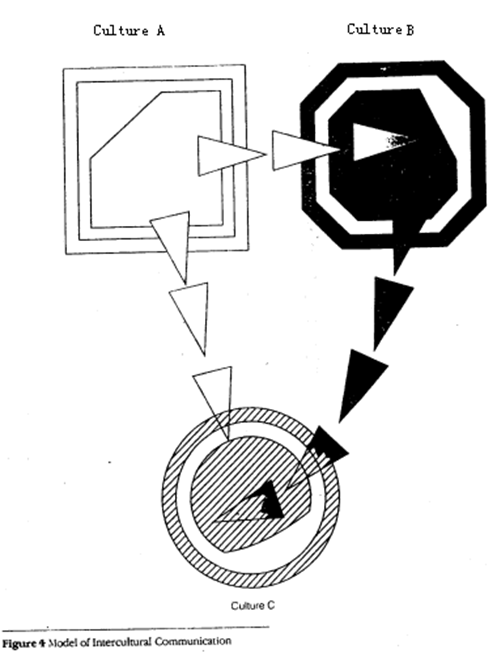
3. Model of Intercultural Communication
Two American scholars, Samovar and Porter, illustrated model of intercultural communication through the following picture. Culture A and culture B are closer in distance and similar in shape, one square, the other octagon. They bear more similarities compared with culture C, which is farther away and different in shape. So it will be easier for people from these two cultures to communicate with each other.
That is to say, the more similarities two cultures share, the less influence culture will have on communication. Therefore, the less messages will be changed during communication. The less the cultures are alike, the more likely the messages will be changed. Misunderstanding in intercultural communication often arises here.
4. Two obstacles in intercultural communication
There are two obstacles that hinder successful intercultural communication. One is stereotype, the other is ethnocentrism.
Stereotype is a fixed idea or image that many people have of a particular type of person or thing, but which is often not true in reality. Ethnocentrism is the ideas and beliefs of one particular culture, and the using of these to judge other cultures. Both stereotypes and ethnocentrism are harmful in intercultural communication. They block us from seeing the goodness in other cultures, even lead us to errors in decision making that may carry the potential for negative consequences.


