-
1 概述
-
2 教学视频
一、概念
Hypoxia refers to reduction of oxygen supply to tissue or an impaired use of oxygen by tissues leading to changes in their metabolism,function,and structure.
组织供氧不足或用氧障碍导致机体产生相应的功能、代谢和形态改变的病理过程称为缺氧。
二、常用血氧指标
1 血氧分压 (partial pressure of oxygen,PO2):物理溶解于血液中的氧所产生的张力。
2 血氧容量 (oxygen binding capacity, CO2max):标准条件下,100ml血液中的Hb完全氧化后的最大携氧量。
3血氧含量(oxygen content,CO2):100ml血液的实际携氧量。
4 血氧饱和度(oxygen saturation,SO2):Hb与氧结合的百分数。
三、缺氧的分类、原因、血氧变化特点
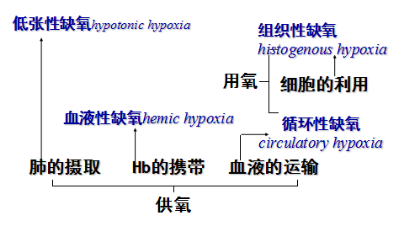
ØHypotonic Hypoxia: It is characterized by a low arterial partial pressure of oxygen.
CAUSES:²Low partial pressure of O2 in the inspired air
²Abnormal pulmonary function
²Shunts in the pulmonary circulation or a Right-to-left shunt in the heart
ØHemic Hypoxia: It is mainly caused by the low oxygen capacity of blood oeing to decreased total hemogloboin or altered hemoglobin consyituents.
CAUSES:²Anemia
²Carboxyhemoglobinemia
²Methemoglobinemia
²High affinity of Hb for O2
ØCirculatory Hypoxia: It is failure to transport adequate oxygen to the tissues. due to slow blood flow to the tissues such as in cardiac failure, or circulatory shock and localized impairment of flow (arterial spasm, embolism). It is also called hypokinetic hypoxia.
CAUSES:²General circulatory:heart failure
²Local circulatory :embolism
ØHistogenous Hypoxia: It s the inability of cells to take up or utilize oxygen from the bloodstream.despite of the fact that the oxygen supply is enough.
CAUSES:²Histotoxication
²Mitochondria injury
²Decreased synthesis of respiratory enzymes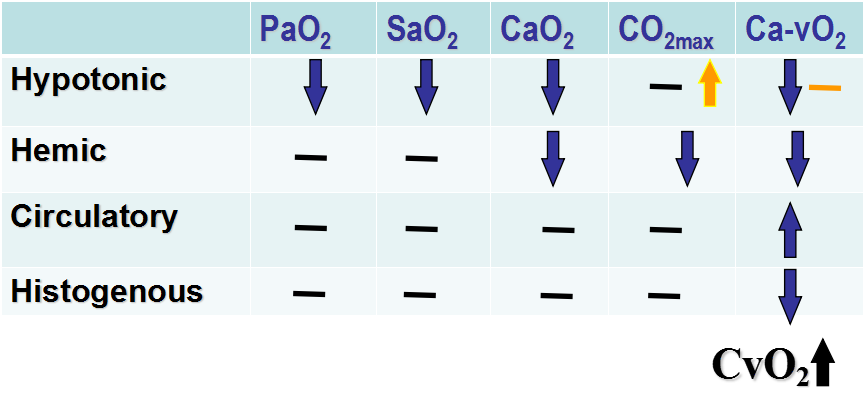
四、缺氧时机体的功能代谢变化
Mild hypoxia induces mainly the adaptive responses; while severe hypoxia leads to functional and metabolic disturbances. There are some differences in adaptive responses and disturbances between acute and chronic hypoxia, and among different types of hypoxia.
Ø Respiratory System
1 Adaptive responses
Hyperventilation occurs when PaO2 is lower than 60 mmHg. Low PaO2 stimulates peripheral chemoreceptors, increasing pulmonary ventilation
via a reflex mechanism, which enhances the alveolar partial pressure of oxygen.
2 Disturbances
² High Altitude Pulmonary Edema
Pulmonary edema might occur in a few days after arriving at 4. 000 m above sea level. Its mechanism is not fully understood. Perhaps the pulmonary hypertension caused by uneven hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction results in high pressure pulmonary edema, and the damage of endothelial cells caused by increased blood flow leads to high permeability pulmonary edema,the latter is confirmed by the presence of large amounts of proteins,macrophages and vasoactive substances in the broncho-alveolar s
lavage fluid.
² Respiratory Depression
Severe hypoxia may inhibit respiratory center, pres
thus decrease pulmonary ventilation.
Ø Hemic System
1 Increase of erythrocytes
2 Decrease of the affinity of Hb for oxygen (2,3-DPG)