Financial Analysis after Financing
From the viewpoint of equity investors, it evaluates profitability of equity investment which may be impacted by the financing plan.
Since the financing plan is concerned, the ability of debt repayment and the liquidity of the project will be conducted.
Besides, the financial viability will be analyzed to judge whether the project has enough funds over the service period.
Profitability Analysis (盈利能力分析)
The FIRRs of equity investment will be calculated to analyze the profitability of equity investor and individual investors .
The financing plan and repayment plan will impact the interest during construction, depreciation, financial cost, income tax, etc., and then impact the results of FIRRs.
Static indexes, such as Return on Investment Ratio (投资收益率) and Return on Equity Ratio (资本金收益率), may also be calculated.
Cash Flow of Equity Investor
Cash inflow: operating revenues
Cash Outflow: equity investment, operating cost, income tax, repayment of principal and interest, etc.
Net Cash Flow:
EOY 0: negative equity investment
EOY 1 - N:

Cash Flow of Individual Investors
Cash inflow: dividends
Cash Outflow: investment of individual investors
Net Cash Flow:
EOY 0: negative equity investment from individual investors
EOY 1 - N: positive dividends
The FNPV and FIRR of the project will be definitely increased by borrowing money, especially when the interest rate is lower than the MARR.
Normally, it is nonsense when the interest rate is larger than the MARR. However, it still can be meaningful since the equity investment can earn money.
Return on Investment Ratio (ROI, 投资收益率)
A measure of the ability that the investment, financed by debt or equity, earns a profit.

EBIT (息税前利润): Earnings before interest and tax.
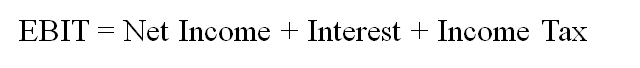
Return on Equity Ratio (ROE,资本金利润率)
A measure of the rate of return on common equity.
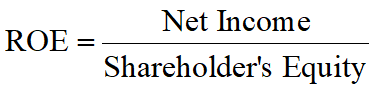
Net Income is the average annual net income or the net income of the normal years.
Debt & Liquidity Analysis (偿债能力分析)
The ability of a project/firm to pay its long-term liabilities will be indicated by Loan of Asset Ratio (资产负债率), Interest Coverage Ratio (利息备付率) and Debt-Service Coverage Ratio (偿债备付率) .
Current Ratio (流动比率) and Quick Ratio (速动比率) measure whether a project has a working capital to meet the liquidity obligations.
Interest Coverage Ratio (ICR, 利息备付率)
The extent to which fixed charges (interests) are covered by operating profits.
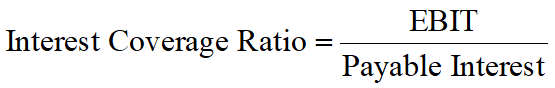
Interest and income tax are added back since they are earnings that are available to pay interest.
ICR should be calculated annually.
ICR should be at least larger than 1. The larger the ICR is, the higher the capacity to pay interest is.
Debt-Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR, 偿债备付率)
The extent to which the principals and interests are covered by operating profits.
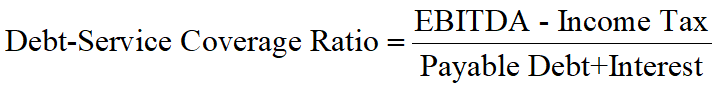
EBITDA (息税折旧摊销前利润): Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation and amortization.
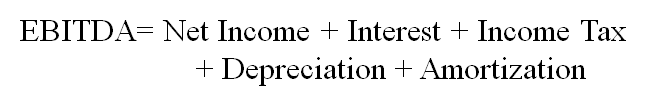
DSCR should be calculated annually and be at least larger than 1.
Loan of Asset Ratio (LOAR, 资产负债率)
A degree to which a firm is utilizing borrowed money to finance assets. It also known as the Debt ratio.
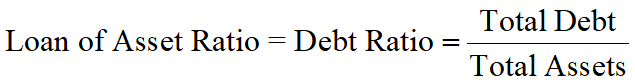
An investor often like a larger LOAR since the return should be leveraged whereas a lender prefers a low LOAR to avoid the risk that the debt cannot be repaid.
If the firm can not meet is debt payment schedule, the lenders will push the firm into bankruptcy and there will be nothing left for the equity holders.
Working Capital (Current) Ratio (流动比率)
The extent to which current assets can be converted to cash to meet current obligations.
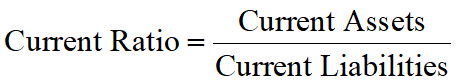
Short-term lenders frequently have a covenant requiring the firm to maintain or exceed a set current ratio or to have an absolute amount of working capital.
An acceptable current ratio generally is from 2 to 1.
Quick (Acid Test) Ratio(速动比率)
The extent to which a firm could pay all of its current liabilities which came due immediately.
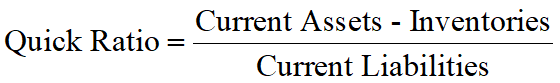
Inventories are typically the least liquidity of a firm’s current assets. Therefore, inventories are the assets on which losses are most likely to occur in case of liquidation.
Financial Viability Analysis (财务生存能力分析)
Financial viability of a project/firm requires that it should obtain enough funds during the operation stage.
The net cash flow of individual years may be negative. However, the cumulative net cash flow at the end of each year must be positive.
Financial viability in the initial years can be impacted by the repayment plan. If the net cash flow is negative, a short-term credit line.

