Internal Rate of Return (IRR, 内部收益率)
IRR is the breakeven rate at which the NPW of a project is zero.
It represents the real ROR of the project over its life.
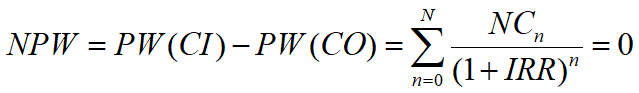
Decision Rule of IRR
If IRR ≥ ic, the project is economically justified.
If IRR < ic, the project is not accepted.
Calculation of Internal Rate of Return
Polynomial Equation Method
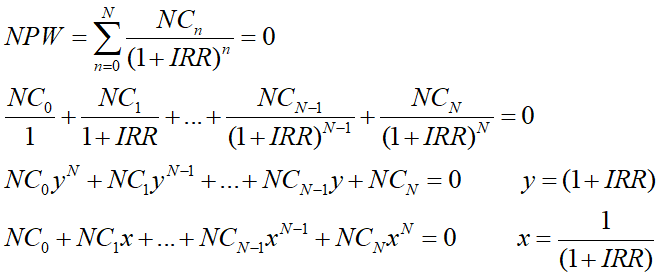
Linear Interpolation Method (Trial and Error Method)
Multiple Real Positive Root Problem of IRR
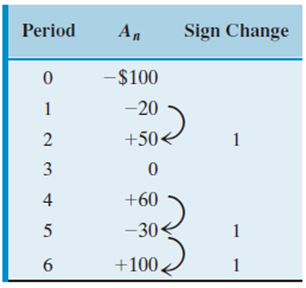
Descartes’ Rule of Signs on Net Cash Flow
Single real positive root: only one sign change occurs in the net cash flow series.
Multiple real positive roots: more than one sign change occurs in the net cash flow series.
The number of real positive roots is never greater than the number of sign changes in the net cash flow series.
Accumulated Cash Flow Sign Test
If the accumulated cash flow series starts negatively and changes sign only once, then a unique real positive root exists.
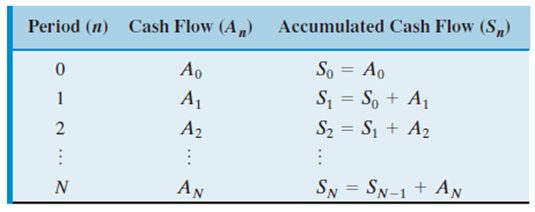
External Rate of Return (ERR)
ERR is a rate external to the project at which the NCs can be reinvested.
The objective is to seek the unique modified IRR* in case of multiple IRRs.
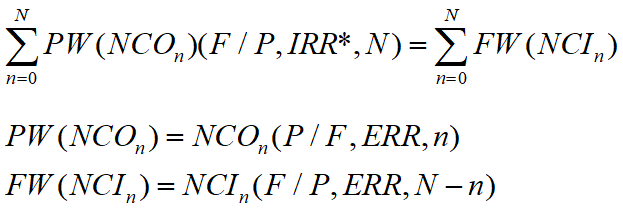
ERR method is not subject to the problem of multiple IRRs. It can usually be solved directly.
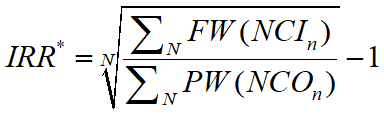
Decision Rule
If IRR* ≥ ic, the project is economically justified.
If IRR* < ic, the project is not accepted.
The IRR* may be different by using cash flows or net cash flows, however, it will not affect the final results.
When ERR ≥ ic, the change of ERR will not change the result of accepting the project or not.
When ERR < ic, the change of ERR may change the result of accepting the project or not.
However, a firm usually like a larger MARR than ERR, which is a ROR commonly obtained by other firms. Therefore, ERR normally should be equal to MARR.

