Interest Rate vs. Inflation Rate
Interest rate (i, 利率) measures the cost/price of money and is expressed as a percentage per period of time.
Inflation rate (f, 通货膨胀率) is the increase in the average price for goods/services with a decrease in purchasing power of money.
Deflation rate (f, 通货紧缩率) is the decrease in the average price for goods/services with an increase in purchasing power of money.
Real Interest Rate vs. Apparent Interest Rate
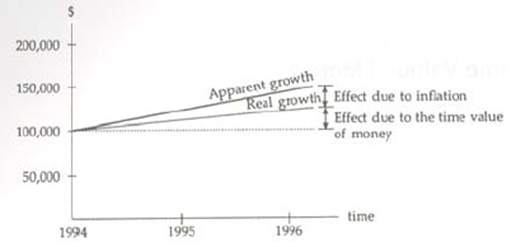
Real Interest Rate (ir) reflects only the time value of money, i.e., the real growth of earning power of money.
Apparent Interest Rate (market interest rate, im) is the combined effect due to inflation and the time value of money.
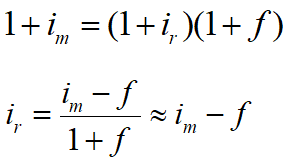
Simple Interest vs. Compound Interest
Simple Interest: The total interest earned/charged is linearly proportional to the initial amount of money (principal).
![]()
Compound Interest: The interest earned/charged in a period is based on the total amount (principal plus accumulated interest) at the beginning of this period.
![]()
Nominal Interest Rate vs. Effective Interest Rate
Nominal Interest Rate (r): The stated interest rate on a stated interest period (e.g. month, quarter), normally on an annual basis.
Effective Interest Rate (i): The calculated interest rate on the stated interest period which is not equal to the actual interest period.
Number of Compounding Periods (m): The stated interest period divided by the actual interest period.
![]()
Rate of Return (ROR, 收益率)
ROR measures the profitability of a project over a period of time, expressed as a percentage.
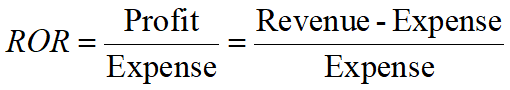
Minimum Attractive Rate of Return (MARR, ic,基准收益率) is the expected ROR decided by the top management of a firm.
is (i0, 社会基准折现率) is basic ROR of the society.
Determination of MARR
Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)
![]()
λ — Percentage of the total capital obtained from debt;
CDebt — Cost of debt financing;
CEquity— Cost of equity financing;

