Benefit/Cost Ratio Analysis
Benefit/Cost Ratio (B/C Ratio, 效益费用比)
The B/C ratio is a ratio of discounted benefits to discounted costs.
The B/C ratio represents the ability of earning benefits to the public with monetary expenses of the government.
The B/C ratio analysis is normally used for the evaluation of public projects in which the NCs may be negative.
Conventional Benefit/Cost Ratio (B/C Ratio)
![]()
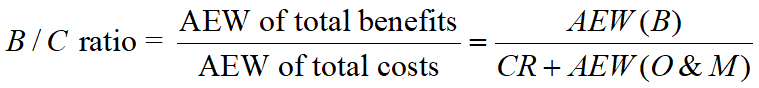
Decision Rule
B/C ratio ≥ 1, the project is worthwhile.
B/C ratio < 1, the project is not accepted.
Modified Benefit/Cost Ratio (B*/C* Ratio)
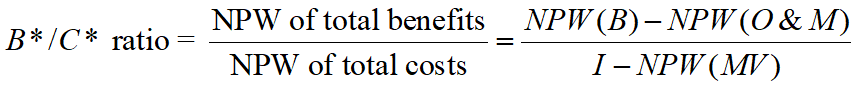
![]()
Decision Rule
B*/C* ratio ≥ 1, the project is worthwhile.
B*/C* ratio < 1, the project is not accepted.
Inconsistence of B/C ratio and B*/C* ratio
Comparison of B/C ratios may lead to wrong decisions.
The best way is to use the incremental analysis.
Incremental Analysis with Benefit/Cost Ratio
Computing the incremental benefits/costs of two alternatives in case of inconsistent ranking problem.
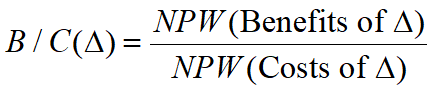
∆: incremental cash flow, ∆ = B – A, if investment of B is larger than that of A.
B/C (∆) or B*/C* (∆) ≥ 1, the project with larger investment should be selected.
B/C (∆) or B*/C* (∆) < 1, the project with lower investment should be selected.
Economic Benefits & Economic Costs
Economic Benefits (经济效益)
All Contribution of the project which is good on national economy.
Direct Benefits: The revenues obtained from the project by selling goods/services to public.
Indirect Benefits: The benefits which cannot be directly measured, such as the improvement on social development, environment enhancement, etc.
Economic Costs (经济费用)
All expenditures that the national economy need to pay for the project.
Direct Costs: The monetary disbursements expensed during the life cycle of the project.
Indirect Costs: The social resources spent within the project which cannot be directly measured.
Transfer Payment (转移支付)
Payment without actually expend social resources, which is transferred within the sectors of national economy.
Transfer Payment will not be counted in the benefits and costs.
Taxes, subsidies, interests
Shadow Price (影子价格)
The change of price will cause the gain of someone and the loss of other one. It will not change the total benefits and costs of the society.
The shadow price of goods/services reflect the "willingness to pay" of consumer on the goods/services.
The shadow price of resources reflect the "opportunity cost" that the resources are invested on this project.
Input & Output of Goods/Services
Foreign Trade Goods:
Exports: Free on Board price (离岸价)
Imports: Cost Insurance and Freight (到岸价)
Non-Foreign Trade Goods:
Market Pricing
Government Pricing: Cost Decomposition (成本分解)
Special Inputs:
Shadow Wage (影子工资): the shadow price of labor cost
Shadow price of land (土地的影子价格): the opportunity cost of using the land
Shadow price of natural resources (自然资源的影子价格)
Coefficients of Shadow Price
Shadow Exchange Rate (影子汇率)
Basic ROR of society (社会折现率): is (i0)
National Economic Evaluation
Commons of Financial Evaluation & National Economic Evaluation
Evaluation Method: NPW and IRR
Evaluation Rule: With & Without Comparison (有无对比) by considering the opportunity cost
Analysis Period: Same
Differences of Financial Evaluation & National Economic Evaluation
Viewpoint: Project/investor & National economy
Benefits & Costs: Only direct & Both direct and Indirect, as well as the different categories
Analysis Contents: Profitability analysis/debt analysis/financial viability analysis & Profitability analysis only
Price: Market price & Shadow price
ROR standards: ic & is
Benefits & Costs Adjustments
Capital Investment
Working Capital
Operating Cost
Operating Revenue
Evaluation Indexes
ENPV
EIRR

