i) Financial Accounting StandardsBoard (FASB)
(1) Generally Accepted AccountingPrinciples (GAAP)
1. The Economic Entity Assumption
2. The Cost Principle
3. The Going Concern Assumption
4. The Monetary Unit Assumption
ii) Securities and ExchangeCommission (SEC)
iii) International AccountingStandards Board (IASB)
(1) International Financial ReportingStandards (IFRS)
b) Ethics in Accounting andBusiness
i) Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
ii) Public Company AccountingOversight Board (PCAOB)
The Relationship among IFRS FOUNDATION, IASB,IFRS AC, and IFRS IC
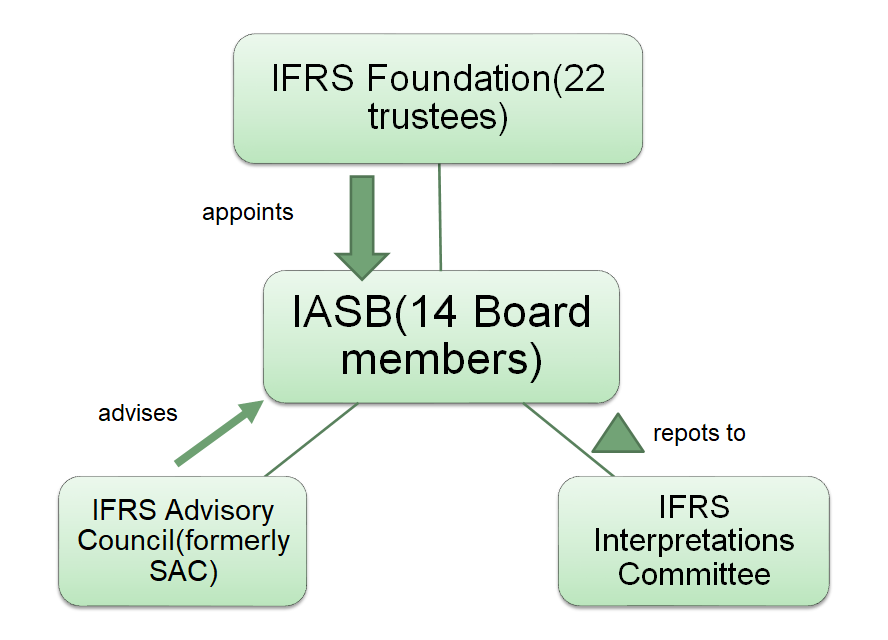
IFRS Foundation Trustees
https://www.iasplus.com/en/resources/ifrsf/governance/ifrsf-trustees
International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
https://www.iasplus.com/en/resources/ifrsf/iasb-ifrs-ic/iasb
IFRS Interpretations Committee
https://www.iasplus.com/en/resources/ifrsf/iasb-ifrs-ic/ifrs-ic
IFRS Advisory Council
https://www.iasplus.com/en/resources/ifrsf/advisory/ifrs-advisory-council
International Financial Reporting Standards
https://www.iasplus.com/en/standards/ifrs
IFRS最新更新信息
http://app.news.esnai.com/tags.php?tag=IFRS&page=1
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/ifrs.asp
GAAP
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
https://www.iasplus.com/en/resources/regional/fasb
US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
https://www.iasplus.com/en/resources/regional/sec
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB)
https://www.iasplus.com/en/resources/regional/pcaob
Over the years, accounting standards have been developed by different accounting authorities. The ultimate purpose of accounting standards is to establish a common set of procedures and rules in preparing financial statements, thereby preventing misunderstandings between and among the preparers and users of accounting information.
As we have said in a previous topic, financial accounting is concerned with the preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles or GAAP. So, what is GAAP?
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
Generally accepted accounting principles or GAAP are rules, conventions, procedures, and standards that are accepted in a community. With that said, generally accepted accounting standards vary in different locations. For example, U.S. GAAP is only applicable and is the acceptable set of accounting standards in the United States. Canada has its own GAAP; Australia has its own. Every country has its own set of accepted accounting standards.
Financial accounting, as opposed to managerial accounting, strictly follows GAAP. Managerial accounting follows many standards and procedures in many fields of business, such as economics, financial management, accounting, and others, depending on the need of the management.
In the United States, GAAP consists of rules and standards established by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). However, there is a current move to shift towards International Financial Accounting Standards (IFRS).
International Financial Reporting Standards
International Financial Reporting Standards or IFRS are published by the International Accounting Standards Board, an independent standard-setting organization based in London. IFRS have been adopted by many countries, in a vision to establish a common set of accounting standards around the world.
The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) is formerly known as the International Accounting Standards Council (IASC) which has developed International Accounting Standards (IAS) during its existence. The IASB has adopted many of the IAS and retained their names. New standards are published as IFRS.
Accordingly, IFRS consists of the IAS that were retained and new IFRS. As of now there are 41 standards: IAS 1, 2, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 16 to 21, 23, 24, 26, 27, 28, 29, 32, 33, 34, 36 to 41, and IFRS 1 to 13.
Where are IAS 3, 4, 5, and the other missing IAS? They have been fully withdrawn and superseded by the latest standards. For example: IAS 3 on Consolidated Financial Statements is now under IAS 27 and 28; IAS 4 Depreciation Accounting is now under IAS 36; IAS 22 Business Combinations has been replaced by IFRS 3, etc.
Conclusion
Generally accepted accounting standards set the rules and procedures to be followed when preparing and interpreting financial statements.
The two most influential bodies when it comes to setting accounting standards are: the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) in the United States, and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) based in London, England.
Accounting standards vary in different countries; however, there is a current move towards worldwide adoption of the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).


