This part is mainly about two topics:
1) What makes a good language teacher?
2) How can one become a good language teacher?
1. Three groups of elements contributing to the qualities of a good language teacher (Parrot, 1993):
ethic devotion, professional qualities, personal styles
Here are some adjectives to describe each element:
ethic devotion
kind, well-prepared, caring, enthusiastic, warm-hearted, hard-working
professional qualities
creative, resourceful, accurate, disciplined, authoritative, well-informed, professionally-trained, fair, reflective, speaking clearly
personal styles
dynamic, patient, attentive, flexible, intuitive, humourous
2. Reflective Model
The most important and most difficult part of the making of a good language teacher is the development of professional competence. A language teacher’s professional competence involves more factors and longer learning time, and may never be really finished. A "reflective model" can demonstrate the development of professional competence.

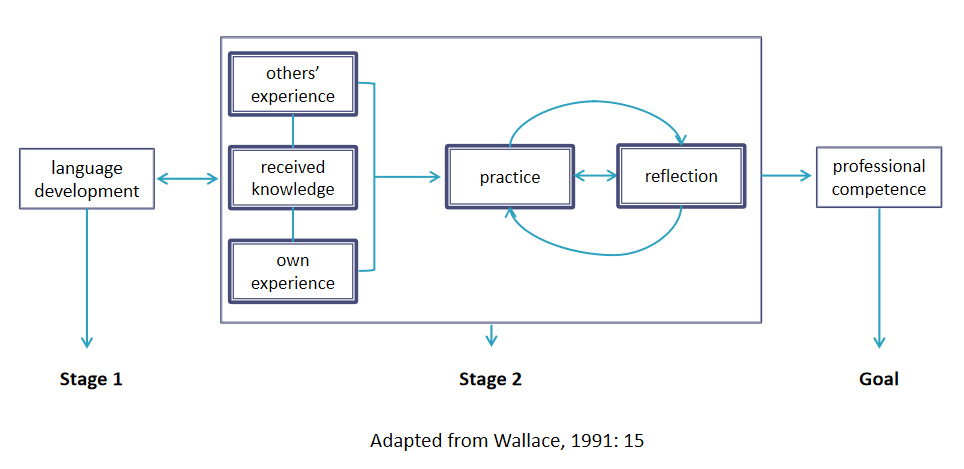
The development of professional competence for a language teacher involves stage 1, stage 2, and goal.
1) Stage 1: Language development
All English teachers are supposed to have a sound command of English. Since language is always changing, language development can never come to an end.
2) Stage 2: learning, practice and relfection
Learning: This is the purposeful preparation a language teacher normally recieves before he/she starts the teaching practice, including:
a. Learning from other's experiences (empirical knowledge gained through reading and observations)
b. Learning the received knowledge (language learning theories, educational psychology, language teaching methodology, etc.)
c. Learning from one's own experiences as a learner
Practice: The learning stage is followed by practice. There are two sense of practice:
a. Pseudo practice: a short period of time assigned to do teaching practice as part of one's pre-service education.
b. Real practice: the real classroom teaching that a teacher undertakes after he/she finishes formal education.
Relfection: Teachers benefit from practice if they keep on reflecting on what they have been doing.
Teachers reflect on their work not only after they finish a certain period of practice, but also while they are doing the practice.
3) Goal:
Ideally, a teacher should be able to attain his/her professional competence after practice and reflection.
With the ever-deepening of our understanding of teaching and learning, and with the ever changing needs of the society, of education, of students, and of the teaching requirements, one must keep on learning, practicing and reflecting. Therefore, professional competence as an ultimate goal does not seem to have an end.
3. Extensive reading
“The most basic aim of education is to foster virtue. We will fully implement the Party's educational policy, carry out the basic task of fostering virtue through education, and nurture a new generation of capable young people with sound moral grounding, intellectual ability, physical vigor, aesthetic sensibility, and work skills who will fully develop socialism and carry forward the socialist cause.”---From Xi Jinping's report to the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China
育人的根本在于立德。全面贯彻党的教育方针,落实立德树人根本任务,培养德智体美劳全面发展的社会主义建设者和接班人。
Follow the PPT and review the two parts with the aid of your textbook:
Watch the video and try to understand the responsibility shoulded by the teachers:


