What is Constructivist Theory?
The constructivist theory believes that learning is a process in which the learner constructs meaning based on his/her own experiences and what he/she already knows.
John Dewey(杜威) (1859-1952)believed that teaching should be built based on what learners already knew and engage learners in learning activities. Teachers should balance an understanding of the habits, characteristics as well as personalities of individual learners with an understanding of the means of arousing learners’ interests and curiosity for learning (Archambault, 1964).
If you would like to read more about the constructivist theory, please click the link for more information:
2. What is Socio-cultural theory?
This theory was first introduced by Vygotsky (1978). It is “a theory of mind” about how humans think through the creation and use of mediating tools or a theory on recognition which emphasizes“the central role that social relationships and culturally constructed artifacts play organising uniquely human forms of thinking.
Here are the key concepts for your understanding of the theory:
mediation: the interation between the mind and the outside world (or oneself)
‘ all forms of human mental activity are mediated by material and/or symbolic means that are constructed within and through cultural activity’
To conclude, mediation can happen through material tools, through interations with another person or through the use of symbols.
ZPD
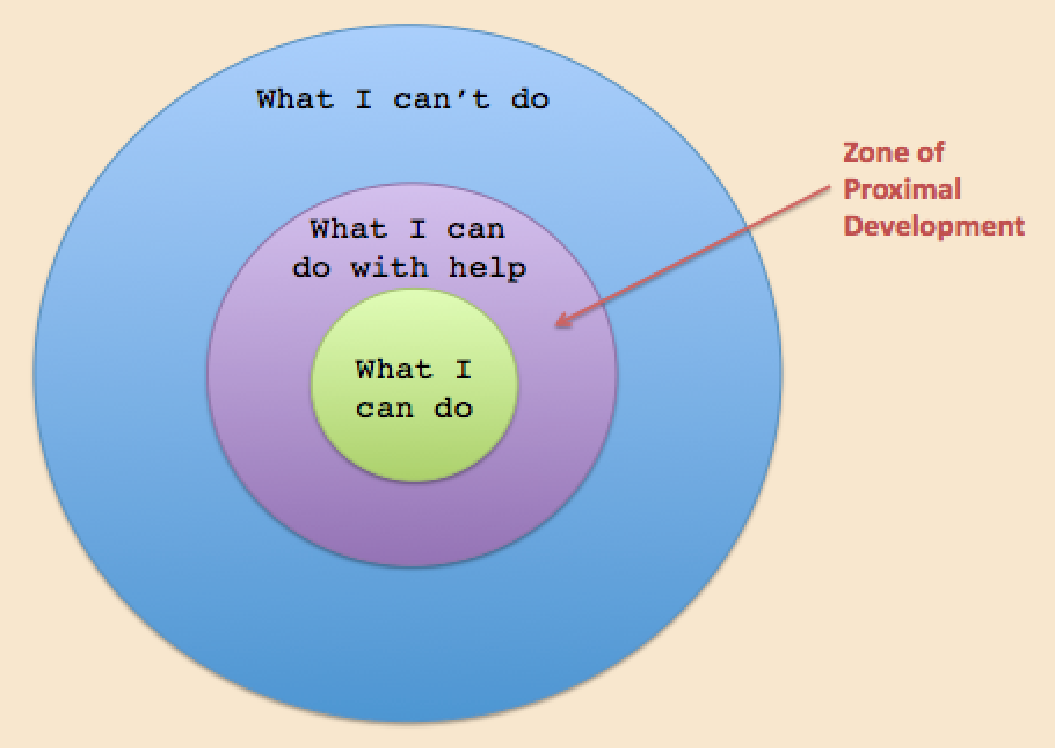
The zone of proximal development is "the distance between the actual developmental level as determined by independent problem solving and the level of potential development as determined through problem solving under adult guidance, or in collaboration with more capable peers.”
Scaffolding
所谓「鹰架」/「脚手架」(Scaffolding)是指提供符合学习者认知层次的支持、导引和协助,以帮助学习者由需要协助而逐渐能够独立完成某一任务,进而使其由低阶的能力水准发展到高阶的能力水准。鹰架观念源自于维果茨基(Vygotsky)的潜在发展区域 (the Zone of Proximal Development, 或ZPD)概念, 他认为孩童的能力有实际能力(“现实发展水平”level of actual development)和潜在能力(“潜在发展水平”level of potential development)两种。
To conclude:
With the teacher’s scaffolding through questions or explanations or with a more capable peer’s support, the learner can move to a higher level of understanding and extend his/her skills and knowledge to the fullest potential.
Learning is best achieved through the dynamic interaction between the teacher and the learner or between learners.



