√Asset management ratios, also referred to as asset utilization or asset efficiency ratios, measure a firm's ability to manage the assets at its disposal.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
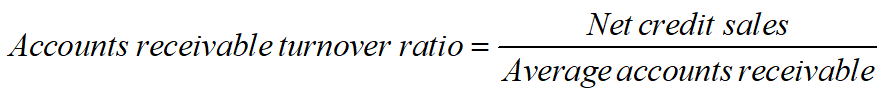
指标内涵:The trade between increased sales and the associated costs of longer collection periods and more uncollectable receivables.
※Turnover 贸易额,流通量 Annual turnover:年营业额
赊销收入指的是没有立即收到货款的主营业务收入。赊销收入净额是指销售收入中扣除了现销及销货退回、销货折扣与折让后的余额——Net credit sales=sales-cash sales-sales return-sales discounts
The tradeoff
Higher receivables turnover ratios imply that a firm is managing its accounts receivable efficiently. But a high accounts receivable turnover ratio may indicate that the credit sales policy is too restrictive. Manager should consider whether a more lenient policy lead to enhanced sales.
A low or declining accounts receivable turnover ratio may indicate the firm is either becoming lax in its efforts to collect receivables or is not writing off receivables that are unlikely to be ultimately collected. By performing an aging of the receivables account, where receivables are sorted by the length of time outstanding, managers can assess likelihood of collecting outstanding receivables. Those receivables that have been outstanding the longest time often have the lowest likelihood of eventual collection.
Solution for a low or declining accounts receivable turnover ratio
performing an aging of the receivables accounts
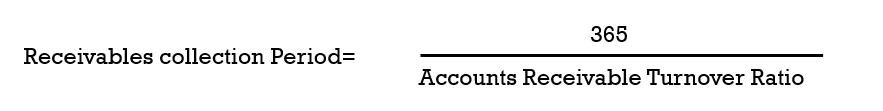
指标内涵:If the receivables collection period exceeds a firm's credit terms, this may indicate that a firm is inefficient in collecting its credit sales or is granting credit to marginal customers.
Inventory Turnover Ratio
![]()
A low, declining ratio may suggest the firm has continued to build up inventory in the face of weakening demand or may be carrying and reporting outdated or obsolete inventory that could only be sold at reduced prices, if at all.
Computer inventory system----allow firms to keep inventory levels to a minimum

Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio
![]()
In general, as long as a firm pays its bills in a timely manner and satisfies its financial obligations to its suppliers, the lower the payable turnover ratio the better.
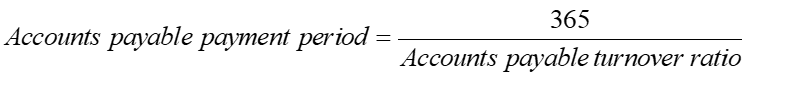
In general, high account payable payment periods are beneficial to the firm as account payable are a low cost source of funds for the firm.
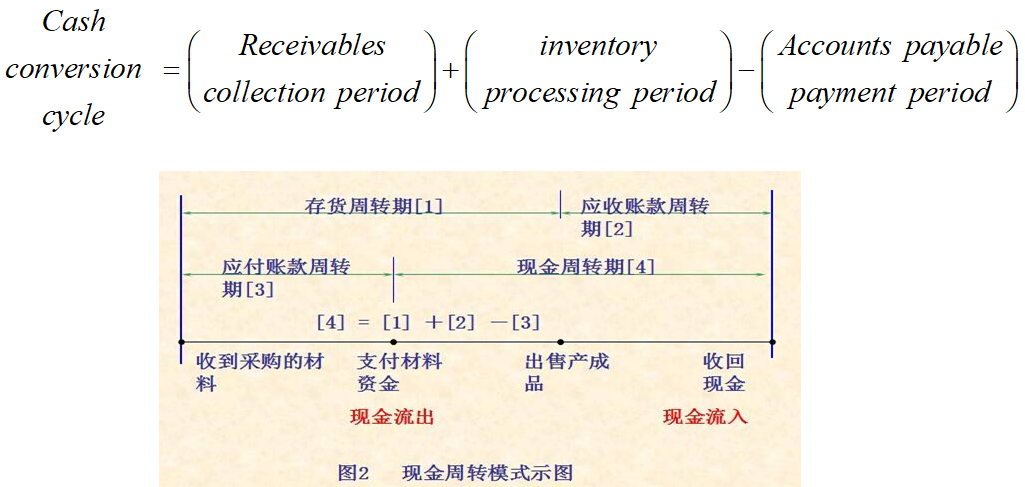
Cash conversion cycle
Asset Turnover Ratios
Measure how efficiently management using its fixed assets and total assets to generate sales.
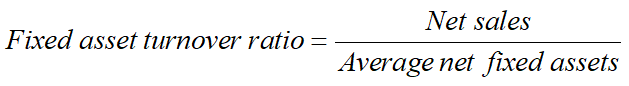
Question: If fixed asset turnover ratio =2,meaning?
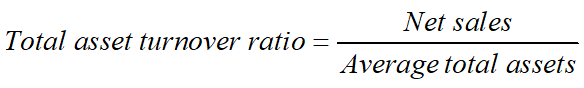
Question: Does high asset turnover ratio indicate highly efficient management ability regarding asset management?


