√Debt management ratios characterize a firm in terms of the relative mix of debt and equity financing and provide measures of the long-term debt paying ability of the firm.
Debt ratio
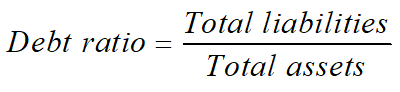
Creditors prefer a low or moderate debt ratio ;
Stockholders may want more leverage because it magnifies expected earnings.
*Financial leverage is a process that involves borrowing resources that are paired with existing assets and utilized to bring about a desired outcome to a financial deal.
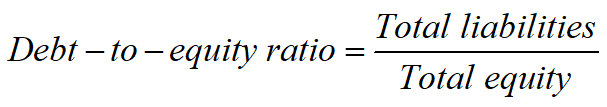
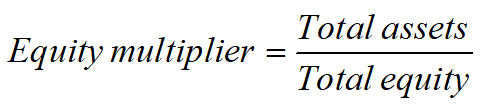
Debt Management Ratios
Long-term Debt Ratio
is computed by divided a firm’s long-term debt, usually defined as all non-current liabilities, by its total assets. By excluding current liabilities, this ratio may provide better insight into a firm's debt management policy.
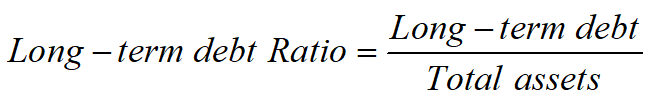
√Leverage ratios characterize a firm in terms of its relative amount of debt financing, but they do not indicate the firm's ability to meet its debt obligations.
Interest Coverage Ratio
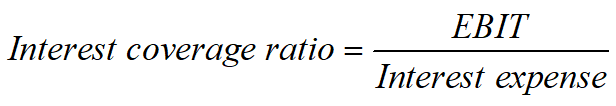
√The ratio measures the extent to which operating income can decline before the firm is unable to meet its annual interest costs.
Question:
Why is EBIT used other than net income when computing this ratio?
Cash Flow Coverage Ratio
![]()
√The cash flow coverage ratio is an earnings-based ratio, since firms pay debt and other financial obligations with actual cash (not earnings), cash flow ratios may provide a better indication of a firm's ability to meet these obligations.
Question:
Why is depreciation added back when computing this ratio?


