√Liquidity ratios indicate a firm's ability to pay its obligations in the short run.
Current ratio
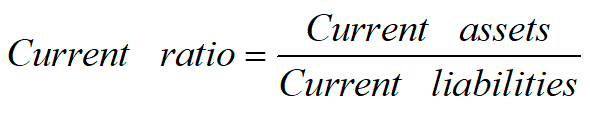
分子:numerator 分母:denominator
Question: If a company's current ratio is over 1, does it mean that the company can repay its current liabilities when they are due?
A declining current ratio may indicate a declining trend in a firm's liquidity. Excessively high current ratios, however, may indicate a firm may have too much of its long-term investor-supplied capital invested in short-term low-earning current assets.
A firm's accounting methods, particularly inventory valuation(FIFO or LIFO) , may affect its current ratio.
——Question: by how?
Firms can also manage their current ratio to some degree(Equal absolute changes in the numerator and denominator may lead to apparent improvements or deterioration in ratios that do not reflect real changes in performance).
Finally, current ratios may hide important liquidity differences among firms(different portions in current assets).
Question:
Why does a company with a stable current ratio have a constantly declined quick ratio?
Quick ratio
视频导入:
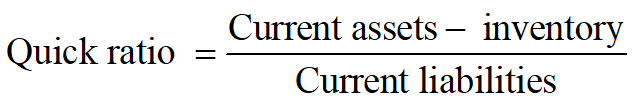
The ratio for excluding inventory is that it is the least liquid of a firm's current assets and may not be as readily available to meet a short-term maturing obligation as the other more liquid current assets.
Cash ratio
![]()
Analyzing a cash ratio, however, could be helpful for assessing a firm's liquidity when the firm needs to pay most or all of its current liabilities with cash in the near term.


