NP-completeness
Frpm: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NP-completeness
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from NP-complete)
| This article may be confusing or unclear to readers. (July 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
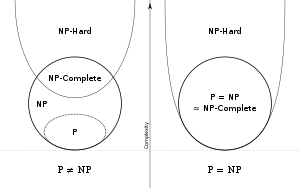
Euler diagram for P, NP, NP-complete, and NP-hard set of problems. The left side is valid under the assumption that P≠NP, while the right side is valid under the assumption that P=NP (except that the empty language and its complement are never NP-complete, and in general, not every problem in P or NP is NP-complete)
In computational complexity theory, a problem is NP-complete when it can be solved by a restricted class of brute force search algorithms and it can be used to simulate any other problem with a similar algorithm. More precisely, each input to the problem should be associated with a set of solutions of polynomial length, whose validity can be tested quickly (in polynomial time),[1] such that the output for any input is "yes" if the solution set is non-empty and "no" if it is empty. The complexity class of problems of this form is called NP, an abbreviation for "nondeterministic polynomial time". A problem is said to be NP-hard if everything in NP can be transformed in polynomial time into it, and a problem is NP-complete if it is both in NP and NP-hard. The NP-complete problems represent the hardest problems in NP. If any NP-complete problem has a polynomial time algorithm, all problems in NP do. The set of NP-complete problems is often denoted by NP-C or NPC.
Although a solution to an NP-complete problem can be verified "quickly", there is no known way to find a solution quickly. That is, the time required to solve the problem using any currently known algorithm increases rapidly as the size of the problem grows. As a consequence, determining whether it is possible to solve these problems quickly, called the P versus NP problem, is one of the fundamental unsolved problems in computer science today.
While a method for computing the solutions to NP-complete problems quickly remains undiscovered, computer scientists and programmers still frequently encounter NP-complete problems. NP-complete problems are often addressed by using heuristic methods and approximation algorithms.
Contents
Overview[edit]
NP-complete problems are in NP, the set of all decision problems whose solutions can be verified in polynomial time; NP may be equivalently defined as the set of decision problems that can be solved in polynomial time on a non-deterministic Turing machine. A problem p in NP is NP-complete if every other problem in NP can be transformed (or reduced) into p in polynomial time.
It is not known whether every problem in NP can be quickly solved—this is called the P versus NP problem. But if any NP-complete problem can be solved quickly, then every problem in NP can, because the definition of an NP-complete problem states that every problem in NP must be quickly reducible to every NP-complete problem (that is, it can be reduced in polynomial time). Because of this, it is often said that NP-complete problems are harder or more difficult than NP problems in general.
Formal definition[edit]
See also: formal definition for NP-completeness (article P = NP)
A decision problem is NP-complete if:
can be shown to be in NP by demonstrating that a candidate solution to can be verified in polynomial time.
Note that a problem satisfying condition 2 is said to be NP-hard, whether or not it satisfies condition 1.[3]
A consequence of this definition is that if we had a polynomial time algorithm (on a UTM, or any other Turing-equivalent abstract machine) for , we could solve all problems in NP in polynomial time.
Background[edit]
The concept of NP-completeness was introduced in 1971 (see Cook–Levin theorem), though the term NP-complete was introduced later. At the 1971 STOC conference, there was a fierce debate between the computer scientists about whether NP-complete problems could be solved in polynomial time on a deterministic Turing machine. John Hopcroft brought everyone at the conference to a consensus that the question of whether NP-complete problems are solvable in polynomial time should be put off to be solved at some later date, since nobody had any formal proofs for their claims one way or the other. This is known as the question of whether P=NP.
Nobody has yet been able to determine conclusively whether NP-complete problems are in fact solvable in polynomial time, making this one of the great unsolved problems of mathematics. The Clay Mathematics Institute is offering a US$1 million reward to anyone who has a formal proof that P=NP or that P≠NP.
The Cook–Levin theorem states that the Boolean satisfiability problem is NP-complete. In 1972, Richard Karp proved that several other problems were also NP-complete (see Karp's 21 NP-complete problems); thus there is a class of NP-complete problems (besides the Boolean satisfiability problem). Since the original results, thousands of other problems have been shown to be NP-complete by reductions from other problems previously shown to be NP-complete; many of these problems are collected in Garey and Johnson's 1979 book Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness.[4]
NP-complete problems[edit]
Some NP-complete problems, indicating the reductions typically used to prove their NP-completeness
Main article: List of NP-complete problems
An interesting example is the graph isomorphism problem, the graph theory problem of determining whether a graph isomorphism exists between two graphs. Two graphs are isomorphic if one can be transformed into the other simply by renaming vertices. Consider these two problems:
Graph Isomorphism: Is graph G1 isomorphic to graph G2?
Subgraph Isomorphism: Is graph G1 isomorphic to a subgraph of graph G2?
The Subgraph Isomorphism problem is NP-complete. The graph isomorphism problem is suspected to be neither in P nor NP-complete, though it is in NP. This is an example of a problem that is thought to be hard, but is not thought to be NP-complete.
The easiest way to prove that some new problem is NP-complete is first to prove that it is in NP, and then to reduce some known NP-complete problem to it. Therefore, it is useful to know a variety of NP-complete problems. The list below contains some well-known problems that are NP-complete when expressed as decision problems.
Travelling salesman problem (decision version)
To the right is a diagram of some of the problems and the reductions typically used to prove their NP-completeness. In this diagram, problems are reduced from bottom to top. Note that this diagram is misleading as a description of the mathematical relationship between these problems, as there exists a polynomial-time reduction between any two NP-complete problems; but it indicates where demonstrating this polynomial-time reduction has been easiest.
There is often only a small difference between a problem in P and an NP-complete problem. For example, the 3-satisfiability problem, a restriction of the boolean satisfiability problem, remains NP-complete, whereas the slightly more restricted 2-satisfiability problem is in P (specifically, NL-complete), and the slightly more general max. 2-sat. problem is again NP-complete. Determining whether a graph can be colored with 2 colors is in P, but with 3 colors is NP-complete, even when restricted to planar graphs. Determining if a graph is a cycle or is bipartite is very easy (in L), but finding a maximum bipartite or a maximum cycle subgraph is NP-complete. A solution of the knapsack problem within any fixed percentage of the optimal solution can be computed in polynomial time, but finding the optimal solution is NP-complete.
Solving NP-complete problems[edit]
At present, all known algorithms for NP-complete problems require time that is superpolynomial in the input size, and it is unknown whether there are any faster algorithms.
The following techniques can be applied to solve computational problems in general, and they often give rise to substantially faster algorithms:
Approximation: Instead of searching for an optimal solution, search for a solution that is at most a factor from an optimal one.
Randomization: Use randomness to get a faster average running time, and allow the algorithm to fail with some small probability. Note: The Monte Carlo method is not an example of an efficient algorithm in this specific sense, although evolutionary approaches like Genetic algorithms may be.
Restriction: By restricting the structure of the input (e.g., to planar graphs), faster algorithms are usually possible.
Parameterization: Often there are fast algorithms if certain parameters of the input are fixed.
Heuristic: An algorithm that works "reasonably well" in many cases, but for which there is no proof that it is both always fast and always produces a good result. Metaheuristic approaches are often used.
One example of a heuristic algorithm is a suboptimal greedy coloring algorithm used for graph coloring during the register allocation phase of some compilers, a technique called graph-coloring global register allocation. Each vertex is a variable, edges are drawn between variables which are being used at the same time, and colors indicate the register assigned to each variable. Because most RISC machines have a fairly large number of general-purpose registers, even a heuristic approach is effective for this application.
Completeness under different types of reduction[edit]
In the definition of NP-complete given above, the term reduction was used in the technical meaning of a polynomial-time many-one reduction.
Another type of reduction is polynomial-time Turing reduction. A problem is polynomial-time Turing-reducible to a problem if, given a subroutine that solves in polynomial time, one could write a program that calls this subroutine and solves in polynomial time. This contrasts with many-one reducibility, which has the restriction that the program can only call the subroutine once, and the return value of the subroutine must be the return value of the program.
If one defines the analogue to NP-complete with Turing reductions instead of many-one reductions, the resulting set of problems won't be smaller than NP-complete; it is an open question whether it will be any larger.
Another type of reduction that is also often used to define NP-completeness is the logarithmic-space many-one reduction which is a many-one reduction that can be computed with only a logarithmic amount of space. Since every computation that can be done in logarithmic space can also be done in polynomial time it follows that if there is a logarithmic-space many-one reduction then there is also a polynomial-time many-one reduction. This type of reduction is more refined than the more usual polynomial-time many-one reductions and it allows us to distinguish more classes such as P-complete. Whether under these types of reductions the definition of NP-complete changes is still an open problem. All currently known NP-complete problems are NP-complete under log space reductions. All currently known NP-complete problems remain NP-complete even under much weaker reductions.[5] It is known, however, that AC0 reductions define a strictly smaller class than polynomial-time reductions.[6]
Naming[edit]
According to Donald Knuth, the name "NP-complete" was popularized by Alfred Aho, John Hopcroft and Jeffrey Ullman in their celebrated textbook "The Design and Analysis of Computer Algorithms". He reports that they introduced the change in the galley proofs for the book (from "polynomially-complete"), in accordance with the results of a poll he had conducted of the theoretical computer science community.[7] Other suggestions made in the poll[8] included "Herculean", "formidable", Steiglitz's "hard-boiled" in honor of Cook, and Shen Lin's acronym "PET", which stood for "probably exponential time", but depending on which way the P versus NP problem went, could stand for "provably exponential time" or "previously exponential time".[9]
Common misconceptions[edit]
The following misconceptions are frequent.[10]
"NP-complete problems are the most difficult known problems." Since NP-complete problems are in NP, their running time is at most exponential. However, some problems provably require more time, for example Presburger arithmetic.
"NP-complete problems are difficult because there are so many different solutions." On the one hand, there are many problems that have a solution space just as large, but can be solved in polynomial time (for example minimum spanning tree). On the other hand, there are NP-problems with at most one solution that are NP-hard under randomized polynomial-time reduction (see Valiant–Vazirani theorem).
"Solving NP-complete problems requires exponential time." First, this would imply P ≠ NP, which is still an unsolved question. Further, some NP-complete problems actually have algorithms running in superpolynomial, but subexponential time such as O(2√nn). For example, the independent set and dominating set problems for planar graphs are NP-complete, but can be solved in subexponential time using the planar separator theorem.[11]
"All instances of an NP-complete problem are difficult." Often some instances, or even most instances, may be easy to solve within polynomial time. However, unless P=NP, any polynomial-time algorithm must asymptotically be wrong on more than polynomially many of the exponentially many inputs of a certain size.[12]
"If P=NP, all cryptographic ciphers can be broken." A polynomial-time problem can be very difficult to solve in practice if the polynomial's degree or constants are large enough. For example, ciphers with a fixed key length, such as Advanced Encryption Standard, can all be broken in constant time (and are thus already known to be in P), though with current technology that constant may exceed the age of the universe. In addition, information-theoretic security provides cryptographic methods that cannot be broken even with unlimited computing power.
Properties[edit]
Viewing a decision problem as a formal language in some fixed encoding, the set NPC of all NP-complete problems is not closed under:
It is not known whether NPC is closed under complementation, since NPC=co-NPC if and only if NP=co-NP, and whether NP=co-NP is an open question.[13]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
Citations[edit]
^ Cobham, Alan (1965). "The intrinsic computational difficulty of functions". Proc. Logic, Methodology, and Philosophy of Science II. North Holland.
^ J. van Leeuwen (1998). Handbook of Theoretical Computer Science. Elsevier. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-262-72014-4.
^ J. van Leeuwen (1998). Handbook of Theoretical Computer Science. Elsevier. p. 80. ISBN 978-0-262-72014-4.
^ Garey, Michael R.; Johnson, D. S. (1979). Victor Klee (ed.). Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness. A Series of Books in the Mathematical Sciences. San Francisco, Calif.: W. H. Freeman and Co. pp. x+338. ISBN 978-0-7167-1045-5. MR 0519066.
^ Agrawal, M.; Allender, E.; Rudich, Steven (1998). "Reductions in Circuit Complexity: An Isomorphism Theorem and a Gap Theorem". Journal of Computer and System Sciences. 57 (2): 127–143. doi:10.1006/jcss.1998.1583. ISSN 1090-2724.
^ Agrawal, M.; Allender, E.; Impagliazzo, R.; Pitassi, T.; Rudich, Steven (2001). "Reducing the complexity of reductions". Computational Complexity. 10 (2): 117–138. doi:10.1007/s00037-001-8191-1. ISSN 1016-3328.
^ Don Knuth, Tracy Larrabee, and Paul M. Roberts, Mathematical Writing Archived 2010-08-27 at the Wayback Machine § 25, MAA Notes No. 14, MAA, 1989 (also Stanford Technical Report, 1987).
^ Knuth, D. F. (1974). "A terminological proposal". SIGACT News. 6 (1): 12–18. doi:10.1145/1811129.1811130.
^ Ball, Philip. "DNA computer helps travelling salesman". doi:10.1038/news000113-10.
^ Bern (1990); Deĭneko, Klinz & Woeginger (2006); Dorn et al. (2005); Lipton & Tarjan (1980).
^ Hemaspaandra, L. A.; Williams, R. (2012). "SIGACT News Complexity Theory Column 76". ACM SIGACT News. 43 (4): 70. doi:10.1145/2421119.2421135.
^ Talbot, John; Welsh, D. J. A. (2006), Complexity and Cryptography: An Introduction, Cambridge University Press, p. 57, ISBN 9780521617710,
The question of whether NP and co-NP are equal is probably the second most important open problem in complexity theory, after the P versus NP question.
Sources[edit]
Garey, M.R.; Johnson, D.S. (1979). Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness. New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-1045-5. This book is a classic, developing the theory, then cataloguing many NP-Complete problems.
Cook, S.A. (1971). "The complexity of theorem proving procedures". Proceedings, Third Annual ACM Symposium on the Theory of Computing, ACM, New York. pp. 151–158. doi:10.1145/800157.805047.
Dunne, P.E. "An annotated list of selected NP-complete problems". COMP202, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Liverpool. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
Crescenzi, P.; Kann, V.; Halldórsson, M.; Karpinski, M.; Woeginger, G. "A compendium of NP optimization problems". KTH NADA, Stockholm. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
Dahlke, K. "NP-complete problems". Math Reference Project. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
Karlsson, R. "Lecture 8: NP-complete problems" (PDF). Dept. of Computer Science, Lund University, Sweden. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 19, 2009. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
Sun, H.M. "The theory of NP-completeness" (PPT). Information Security Laboratory, Dept. of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu City, Taiwan. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
Jiang, J.R. "The theory of NP-completeness" (PPT). Dept. of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Central University, Jhongli City, Taiwan. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
Cormen, T.H.; Leiserson, C.E.; Rivest, R.L.; Stein, C. (2001). "Chapter 34: NP–Completeness". Introduction to Algorithms (2nd ed.). MIT Press and McGraw-Hill. pp. 966–1021. ISBN 978-0-262-03293-3.
Sipser, M. (1997). "Sections 7.4–7.5 (NP-completeness, Additional NP-complete Problems)". Introduction to the Theory of Computation. PWS Publishing. pp. 248–271. ISBN 978-0-534-94728-6.
Papadimitriou, C. (1994). "Chapter 9 (NP-complete problems)". Computational Complexity (1st ed.). Addison Wesley. pp. 181–218. ISBN 978-0-201-53082-7.
Bern, Marshall (1990). "Faster exact algorithms for Steiner trees in planar networks". Networks. 20 (1): 109–120. doi:10.1002/net.3230200110..
Deĭneko, Vladimir G.; Klinz, Bettina; Woeginger, Gerhard J. (2006). "Exact algorithms for the Hamiltonian cycle problem in planar graphs". Operations Research Letters. 34 (3): 269–274. doi:10.1016/j.orl.2005.04.013..
Dorn, Frederic; Penninkx, Eelko; Bodlaender, Hans L.; Fomin, Fedor V. (2005). "Efficient Exact Algorithms on Planar Graphs: Exploiting Sphere Cut Branch Decompositions". Proc. 13th European Symposium on Algorithms (ESA '05). Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 3669. Springer-Verlag. pp. 95–106. doi:10.1007/11561071_11. ISBN 978-3-540-29118-3..
Lipton, Richard J.; Tarjan, Robert E. (1980). "Applications of a planar separator theorem". SIAM Journal on Computing. 9 (3): 615–627. doi:10.1137/0209046..
Further reading[edit]
Scott Aaronson, NP-complete Problems and Physical Reality, ACM SIGACT News, Vol. 36, No. 1. (March 2005), pp. 30–52.
Lance Fortnow, The status of the P versus NP problem, Commun. ACM, Vol. 52, No. 9. (2009), pp. 78–86.
| hide Important complexity classes (more) | |
|---|---|
| Considered feasible | |
| Suspected infeasible | |
| Considered infeasible | |
| Class hierarchies | |
| Families of classes | |