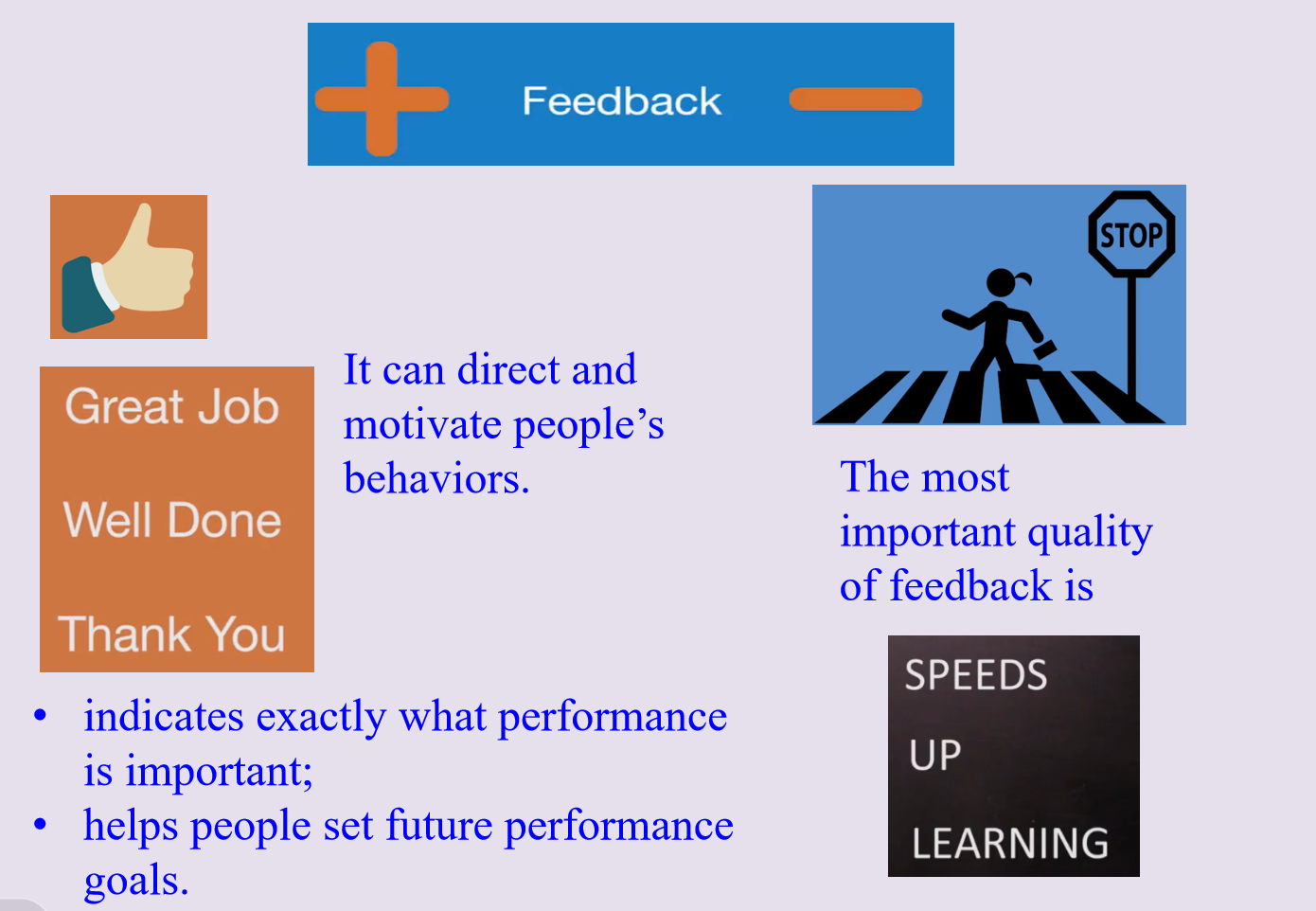
Giving feedback
•The aim of this section is to explore the different ways feedback is given in different cultures. Feedback styles can range from very direct in countries such as Germany or Holland, to very indirect in Japan an dThailand. This variation can cause significant difficulties for international teams because if you come from a culture such as Sweden where feedback is quite direct and clear, you will not necessarily understand that your Britishi partner is very concerned when all he or she says is that they have "a bit of a problem" with something. What is important to learn is the ability to observe the individual and tailor your feedback to their cultural and personal expectations, so that they understand what is going on but are not upset or confused by the way you say it.
 Videos to watch:
Videos to watch:
1) Whenever you give any feedback, the purpose is to improve the performance. Here are five rules to follow in giving feedback:
2) The secret to giving great feedback:
3) Direct feedback:
4) Indirect feedback:


