Read More
Text B The Donner Party

1. Early in April, 1846, 87 pioneers led by George Donner, a well-to-do 62-ycar-old farmer, set out from Springfield, Illinois, for California. Like many emigrants, they were ill-prepared for the dangerous trek. The pioneers’ 27 wagons were loaded with foods, liquor, and built-in beds and stoves.
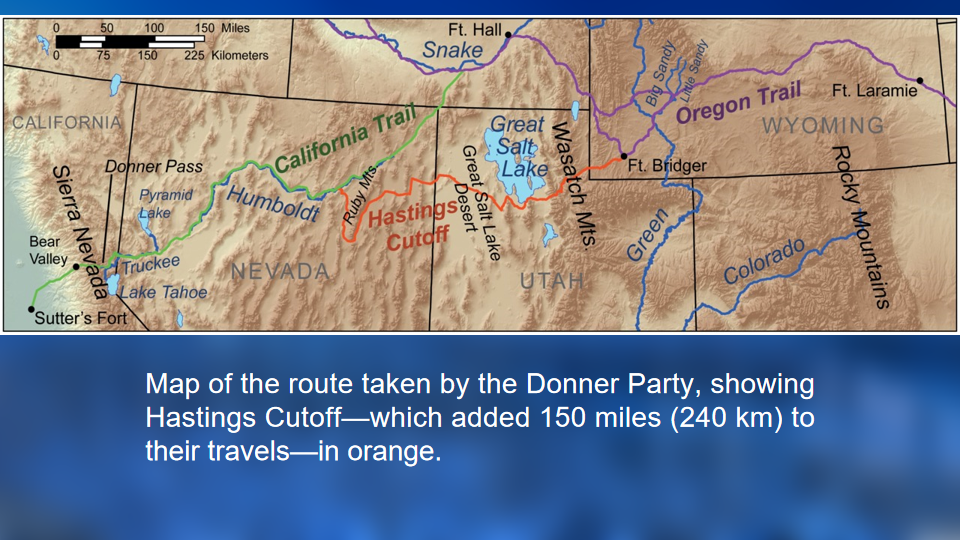
2. On July 20, at Fort Bridger, Wyoming, the party decided to take a shortcut. Lansford Hastings, had suggested in a guidebook that pioneers could save 400 miles by cutting south of the Great Salt Lake. Hastings himself had never taken his own shortcut. He was trying to overthrow California's weak Mexican government and hoped to bring in enough emigrants to start a revolution.
3. Soon huge boulders, arid desert, and dangerous mountain passes slowed the expedition to a crawl. During one stretch, the party traveled only 36 miles in 21 days. A desert crossing that Hastings said would t
ake two days actually took six days and nights.
4. Twelve weeks after leaving Fort Bridger, the Donner Party reached the eastern Sierra Nevada Mountains and prepared to cross Truckee Pass, the last remaining barrier before they arrived in California’s Sacramento Valley. On October 31, they climbed the high Sierra ridges in an attempt to cross the pass, but five-foot high snow drifts blocked their path.
5. Tapped, the party built crude tents and tepees covered with clothing, blankets, and animal hides. To survive, the Donner party was forced to eat mice, their rugs, and even their shoes. In the end, surviving members of the party escaped starvation only by eating the flesh of those who died.
6. In mid-December, a group of 12 men and
5 women made a last-ditch effort to cross the pass to find help. They took only a 6-day supply of r
ations, consisting of finger-sized pieces of dried beef -- two pieces a person per day. During a severe storm, two of the group died. The surviving members of the party “stripped the flesh from their bones, roasted and ate it, averting their eyes from each other, and weeping.” More than a month passed before seven frost-bitten survivors reached an American settlement. By then, the rest had died and two Indian guides had been shot and eaten.
7. Relief teams immediately sought to rescue the pioneers still trapped near Truckee Pass. During the winter, four successive rescue parties broke through and brought out the survivors. The situation that the rescuers found was unspeakably gruesome. Thirteen were dead. Surviving members of the Donner party were delirious from hunger and overexposure. One survivor was found in a small cabin next to a cannibalized body of a young boy. Of the original 87 members of the party, only 47 survived.

Big Cottonwood Canyon, located several miles south of the Donner route in the heart of the Wasatch mountains of Northern Utah
Questions for Discussion or Reflection
(1) Were George Donner and his party well-prepared when they started their trip?
(2) Why did the party decide on a shortcut?
(3) How did those trapped members of the party survive at last?
(4) What happened to the Donner Party finally?


