Unit 2 The Colonial America


Unit Goals
※ To get familiar with the natural surroundings of the colonies.
※ To know the history and geographical locations of the colonies.
※ To acquire information about the daily life in the colonies in
general.
※ To learn the useful words and expressions that can describe the
colonial America.
※ To improve English language skills.
Before You Read
1. Do you still remember the story about the Puritans and the
Mayflower? Can you retell the story?
2. Decide whether each of the following is a Puritan belief according to what you learned in Unit 1.
Statements YES/NO
Puritans believed in predestination.
All men were born sinners.
They led pleasure-seeking lives.
They valued austere and simple life.
Puritans saw Bible as the infallible guide to everything.
3. What would have happened on the new land if the Westerners had never moved to the New World? Use your imagination!
Answer 1: ______________________________
Answer 2: ______________________________
Answer 3: ______________________________
4. Form groups of three or four students. Try to find, on the internet or in the library, more information about the colonial period of America which interests you. Get ready for a 5-minute presentation in class.
Start to read
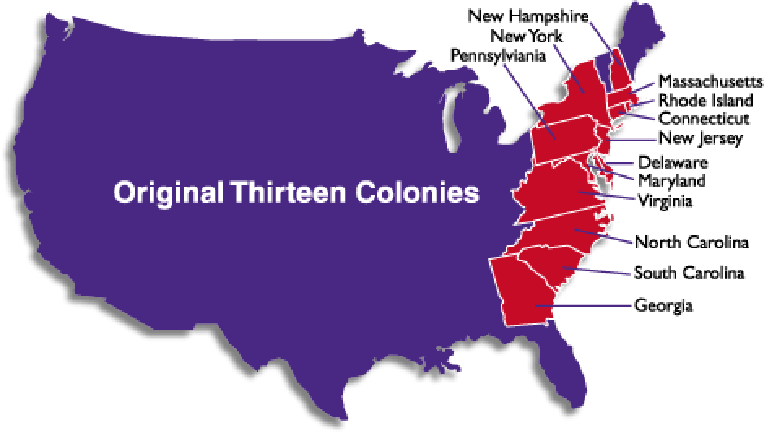
Text A The Original 13 Colonies
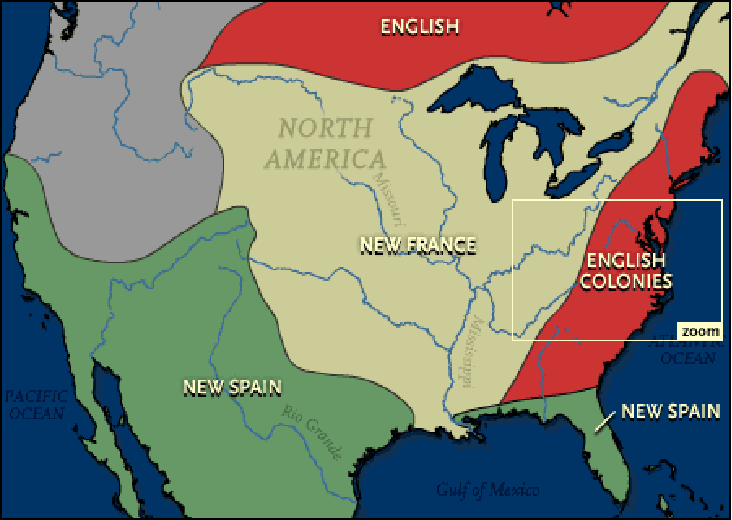
1. Within the span of a hundred years, in the 17th and early 18th centuries, a tide of emigration – one of the great folk wanderings of history – swept from Europe to America. This movement, impelled by powerful and diverse motivations, built a nation out of a wilderness and, by its nature, shaped the character and destiny of an uncharted continent.
2. Today, the United States is the product of two principal forces – the immigration of European peoples with their varied ideas, customs, and national characteristics and the impact of a new country which modified these distinctly European cultural traits. But, inevitably, the force of geographic conditions peculiar to America, the interplay of the varied national groups upon one another, and the sheer difficulty of maintaining old-world ways in a raw, new continent caused significant changes. These changes were gradual and at first scarcely visible. But the result was a new social pattern which, although it resembled European society in many ways, had a character that was distinctly American.
3. To the anxious travelers, the sight of the American shore brought almost inexpressible relief. Said one chronicler, ‘The air at twelve leagues’ distance smelt as sweet as a new-blown garden.’ The colonists’ first glimpse of the new land was a vista of dense woods. The virgin forest with its profusion and variety of trees was a real treasure-house which extended over 1,300 miles from Maine in the north to Georgia in the south. Here was abundant fuel and lumber. Here was the raw material of houses and furniture, ships and naval stores.
4. ‘Heaven and earth never agreed better to frame a place for man’s habitation.’ wrote John Smith (founder of the colony of Virginia) in praise of Virginia, the colony he helped found. As inviting as the climate were the native foods. The sea abounded in oysters and crabs, cod and lobster.
5. Virginia was the earliest permanent British colony in North America. New England was the second. In 1620, a group of Puritans sailed to the New World on the ship Mayflower. These Puritans came to be known as Pilgrims. They had separated from the Church of England and came to America for religious freedom. Before landing their leaders signed the Mayflower Compact. In this document, they agreed to make and obey just and equal laws for the common good. They landed at Plymouth in what is now Massachusetts and founded a colony there.

6. The Pilgrims suffered greatly during the first winter. Shelters were poor, disease widespread, and food scarce. About half the members died. Fortunately, the Indians proved friendly. In the following year, the colonists worked hard in the fields and had a good harvest. So in early autumn of 1621, they set aside a day for celebrating peace and plenty, and invited the Indians to join them. That was the first Thanks giving ever celebrated.

7. In 1629, Puritans founded the Massachusetts Bay Colony. Plymouth became part of Massachusetts Colony in 1691. Between 1629 and 1640, about 20000 more English colonists crossed the Atlantic Ocean to settle in New England. These Puritan settlers valued hard work and commercial success, and they also believed in the importance of education. These Puritanical values strongly influenced the culture of the American colonies and later of the United States. The Puritans also contributed to democracy in America. They held town meetings, where the adult males worked together to make laws.
8. From the foundation of the colonies beginning with the founding of Jamestown until the beginning of the Revolutionary War, different regions of the eastern coast had different characteristics. Once established, the thirteen British colonies could be divided into three geographic areas: New England, Middle, and Southern. Each of these had specific economic, social, and political developments that were unique to the regions.
Colonies: New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut.
9. The New England was basically founded by Puritans who had suffered a lot of religious persecution in England. They came to the New World for the sake of free worship. Harbors were located throughout the region. The area was not known for good farmland. Therefore, the farms were small, mainly to provide food for individual families. New England flourished instead with fishing, shipbuilding, manufacturing, and fur trading along with trading goods with Europe. People were considered relatively equal, at least in the eyes of God.
Colonies: New York, New Jersey , Pennsylvania , and Delaware.
10. Due to their geographical locations, these colonies had some of the characteristics of the South and some of the North. This area was excellent for farming and included natural harbors. Farmers grew grain and raised livestock. The Middle Colonies also practiced trade like New England, but typically they were trading raw materials for manufactured items.
Colonies: Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia.
11. Southern colonies grew their own food along with growing three major cash crops: tobacco, rice, and indigo. These were grown on plantations typically worked by slaves and indentured servants. The reason for establishing the colonies in the south was to provide Britain with a new trade market. Plantations kept people widely separate which prevented the growth of many towns. People in this area fell into several categories as for the hierarchical order, namely the aristocracy (wealthy but very few), the middle class farmers and the slaves.



