Key terms:
1.APEC:
The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation is an inter-government forum facilitatingeconomic growth and prosperity, cooperation, trade and investment in theAsia-Pacific region, and operates on the basis of non-bindingcommitments, open dialogue and equal respect for the views of all participantsregardless of the size of their economy. Thelocation of the meeting is rotated annually among the members. In 2014, theforum was held in Beijing, China.
2.WTO:
World Trade Organization is an international organization designed to superviseand liberaliseinternational trade. The WTO came into being on Jan.1, 1995, and is thesuccessor to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which wascreated in 1948, and continued to operate for almost five decades as a de factointernational organization.
Way to achieve its goal:
1. administering trade agreements;
2. acting as a forum for trade negotiations;
3. settling national tradedisputes;
4. reviewing national trade policies;
5. assisting developing countries in tradepolicy issues, through technical assistanceand training programmes;
6. cooperatingwith other international organizations.

3.OECD:
The Organization forEconomic cooperation and Development, established in 1961, has now 30countries, with an annual budget for 2013 is EUR 354 million.
Extended Reading Material
Role of Government vs Economy
Canada
Canada closely resembles the US in its market-oriented economic system, patter of production, and affluentliving standards.The State is to control budget and to set the rules for it and collects most of the personal and corporate income taxes.The federal government also provides services like,old age security (OAS)payments, employment insurance(失业保险)payments, student loans(助学贷款) to Canada's people.Further,agricultural subsidies and funding to crown corporations like the CanadianBroadcasting Corporation (CBC),Via Rail,and Canada Post are also done by the government of Canada.The government also manages the Canada Pension Plan(CPP),which is funded by mployer and employee contributions.Besides,the government is responsible for allocating money to the provinces to deliver other services such as health,education and social services.
Thus,despite being a market economy,Canada does have a significant room for government intervention and the government has indeed a significant impact on how public services are delivered.
Australia
The role of government in Australia today has less influence on the market than they did before.Its function now is to provide a stable interal and exteral (balance under which the market can function.This is achieved through the use of fiscal,monetary (货币的)and microeconomic reform.)
Australia currently operates under a mixed economic system.This means that the government has partial (control over the economy and has the ability to influence the markets.
New Zealand
New Zealand government is involved in economy in a range of different ways.The main ones are as a regulator,as a gatherer of taxes,as an owner of enterprises,and as a provider of services and income.
Most economic activity in New Zealand is people and firms doing business with each other.The government's role is to regulate those interactions.Some of this regulation is through general laws,like the law of contract,which bring people together to do business.Other regulation involves civil laws (民法)which are about outlining people's rights and responsibilities in relation to each other.
As tax-gatherer,the government colleets about $32 billion in taxes every year. The revenue is used to fund goverment programmes like heath and ducation,to pay debts, and to build public infrastructure such as roads.
The converse to the goverment's role as tax-atherer is as the provider of goods and the public.Major examples of th edirect provision of services are education,health services and the police force.
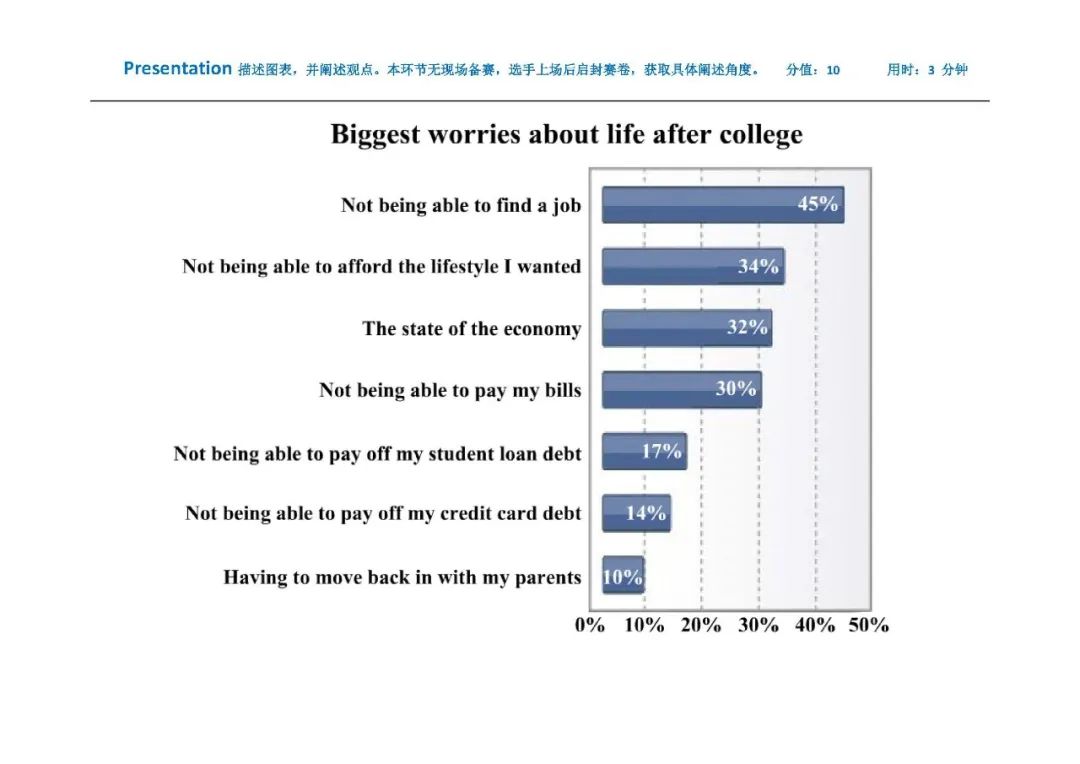
How to describe a graph?
National Competition for Skills of Vocational Education