1. Why CLT?
The ultimate goal of foreign language teaching is to enable students to use the foreign language in work or life when necessary. However, we may find there are some differences between language used in real life and language learned under the traditional pedagogy:

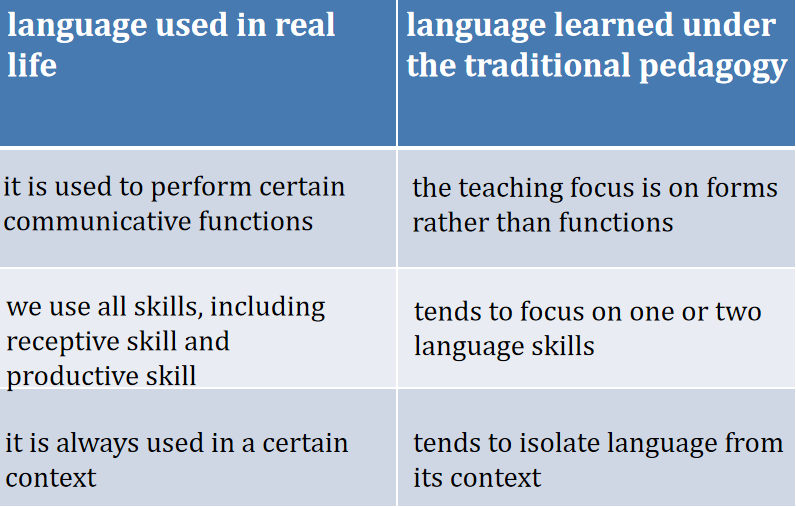
In order to bridge the gap between language used in real life and language learned under the traditional pedagogy, teachers are suggested to adopt the communicative language teaching.
2. Communicative competence
The goal of CLT is to develop students' communicative competence, including both the knowledge about the language and the knowledge about how to use the language appropriately in communicative situations.
Hedge discussed five components of communicative competence. They are linguistic competence, pragmatic competence, discourse competence, strategic competence and fluency.
Linguistic competence: it is concerned with knowledge of the language itself, its form and meaning. Linguistic competence is an integral part of communicative competence. It is wrong to think that communicative language teaching does not aim for high standard of linguistic correctness.
Pragmatic competence: it is concerned with the appropriate use of the language in social context. That is to say, the choice of vocabulary and structure (language forms) depends on the social context.
Discourse competence: it refers to one's ability to create coherent written text (in written language) or conversation (in spoken language) and the ability to understand them. In other words, language learners should be able to effectively employ or comprehend the cohesive markers (first, second, at last, etc.) and reference words (it, they, that) in the context.
Strategic competence: it refers to communication strategies, one employs when there is communication breakdown due to lack of resources. For example, using a similar phrase, gestures, a longer explanation.
Fluency: it means one's ability to 'link units of speech together with facility and without strain or inappropriate slowness or undue hesitation'. Teaching learners lexical phrases or chunks of language can help learners produce the language more fluently, for the reason that lexical phrases or chunks can reduce processing difficulty in people's mind.
3. Implications
Importantly, you, as pre-service teachers are expected to make some implications for language teaching and learning based on your understanding of the five components. Here are some examples:

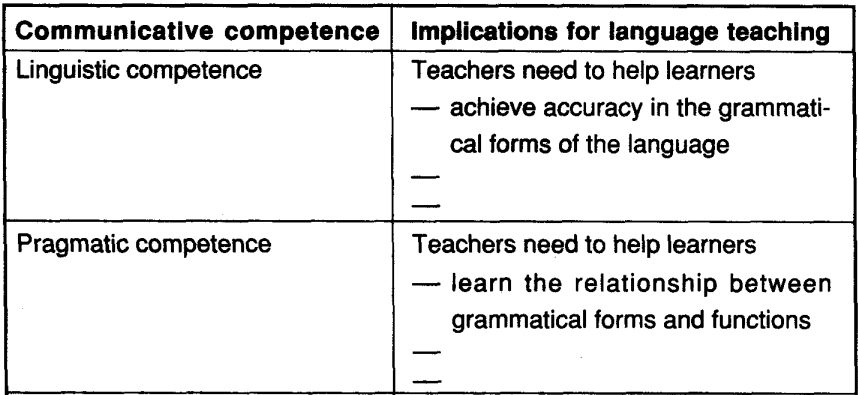
You can join the discussion below and make implications for language teaching especially from the perspective of a teacher:


