-
1 Outcome
-
2 Overview
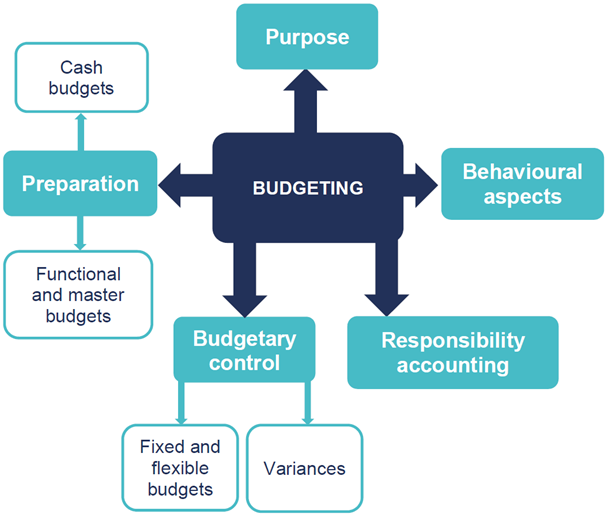
Outcome
}By the end of this session you should beable to:
ØExplain why organisations use budgeting
ØDescribe the planning and control cyclein an organisation
ØExplain the administrative proceduresused in the budgeting process
ØDescribe the stages in the budgeting process (including sources of relevant data, planning and agreeing draft budgets and purpose of forecasts and how they link to budgeting)
ØExplain the importance of motivation inperformance management
ØIdentify factors in a budgetary planningand control system that influence motivation
ØExplain the impacts of targets uponmotivation
ØDiscuss managerial incentive schemes
ØDiscuss the advantages and disadvantagesof a participative approach to budgeting
ØExplain top down, bottom up approaches to budgeting
ØExplain the importance of principalbudget factor in constructing the budget
ØPrepare sales budgets
ØPrepare functional budgets (production,raw materials usage and purchases, labour, variable and fixed overheads)
ØPrepare cash budgets
Øprepare master budgets (statement of profit or loss and statement of financial position)
ØExplain and illustrate 'what if' analysisand scenario planning
ØExplain the importance of flexiblebudgets in control
ØExplain the disadvantages of fixed budgets in control
ØIdentify situations where fixed orflexible budgetary control would be appropriate
ØFlex a budget to a given level of volume
ØCalculate simple variances between flexed budget, fixed budget and actual sales, costs and profits
ØDefine the concept of responsibility accounting and its significance in control
ØExplain the concept of controllable anduncontrollable costs
ØPrepare control reports suitable for presentation to management (to include recommendation of appropriate controlaction).
}and answer questions relating to these areas.