

Students Addicted to Social Media Use?
American college students have an addiction problem. It's not drugs or alcohol that we have to worry about, but smartphones. Yes, this sounds out of touch, but there is data to back this up. In 2014, University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) released a national survey that showed 98% of college students use social media, and out of that number, 27% admit to using it more than 6 hours every day. This is a 7.3% increase from the original number of 19.9% in 2007.
Social media is not just a fun pastime for users; it is increasingly affecting the way we socialize. Before the advent of social media platforms, there was no real way to filter what kind of strangers you met without interacting with them first. This is uncomfortable, sure, but it’s also a vital part of networking and personal growth.
To streamline user experience and keep retention rates, social media platforms carefully supervise users' exposure to information and people. Certain sites like Tumblr and Reddit allow this process to be completely voluntary; it's up to their users to pick and choose who they follow or what communities they participate in.
Taking the opposite approach are sites like Facebook and YouTube, who are infamous for using hidden background algorithms to censor information that fits their users' consumption habits without them ever noticing.
Each of the sites' approaches led to the same outcome: the creation of digital echo chambers that isolate and magnify specific opinions and community cultures. Not only does this lead to the potentially dangerous spread of false information through otherwise discredited organizations, it also makes people less tolerant of opposing views and more hostile when discussing or interacting with those who have them.
College-aged individuals are remarkably vulnerable to Internet addictions. This dependency might even be promoted in schools. The unique combination of stress, new networking requirements and free time found in college life promotes reliance on social media and the Internet in general. Researchers are asking whether the growing cases of depression and anxiety can be blamed on social media's increasing presence in the college-aged population, or if it is a natural result of changing cultural and economic conditions.
Social media does have its advantages. That's why students are attracted to it, after all. In contrast to opinions claiming that it negatively influences social skills, there exists data that claims the opposite — that social media use among certain individuals is highly correlated with a well-maintained social life, and it may help older people maintain a close circle when they otherwise wouldn't be able to.
There are many questions about social media and its power, but as of now, it seems that moderation is key.




Notes on the Text
1. retention rate: 客户保持率,指企业继续保持与老客户交易关系的比例,也可理解为顾客忠诚度。企业留住老顾客的能力是企业保持市场份额的关键。
2. Tumblr: 汤博乐,目前全球最大的轻博客网站,也是轻博客网站的始祖。汤博乐成立于2007年,是一种介于传统博客和微博之间的全新媒体形态,既注重表达,又注重社交,更注重个性化设置,成为当前最受年轻人欢迎的社交网站之一。
3. Reddit: 红迪网,美国人气最高的新闻社区,用户(也叫redditors)能够浏览并且提交互联网上内容的链接,发布自己的原创或有关用户提交文本的帖子。其他用户可对发布的链接进行高分或低分的投票,得分突出的链接会被放到首页。另外,用户可对发布的链接发表评论,以及回复其他评论者。
4. communities: 本文中指的是互联网上的虚拟社区。
5. without them ever noticing:此句中noticing是动名词作without的宾语,them是noticing的逻辑主语。
6. echo chamber: 原本指的是录音时为制造回声效果而建立的回声室,现在常用来比喻人际交往过程中只承认或接受与自己的观点相近的回应。在本文中,“回声室”形象地体现了社交媒体上的一种普遍现象——由于相同的观点被人不断地重复、夸大,因此很难看到不同的观点。
Exercises
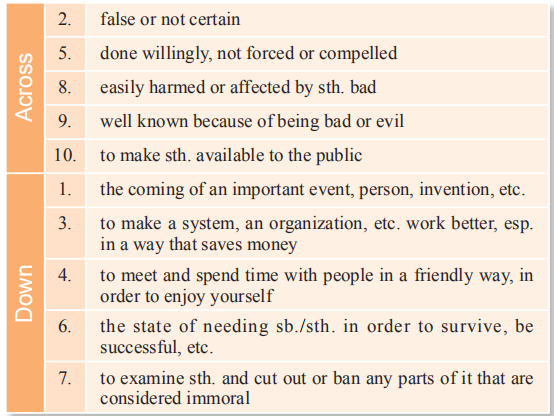
Task 3 Fill in the puzzle spaces with the words from Text A according to the explanations given in the table.
Task 4 Complete the following sentences with the words from Task 3. Change the word forms if necessary.
Task 5 Complete the sentences using derivatives of the words in the box. Change the word forms if necessary.
addicted | moderation | magnify | tolerant | exposure |


