Project management life cycle
项目管理生命周期
★Initionation(发起阶段): :Define scope; Assess Scope; Determine resourses needed; Identify stakehoders; ask for approval( 界定范围;评估范围;确定所需资源;识别干系人;项目审批)
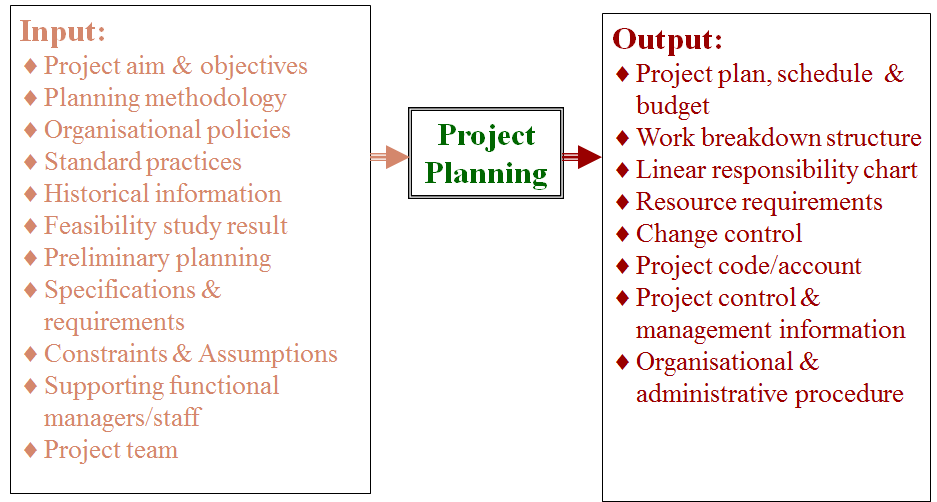
★Plannning(计划阶段) : Planning is considered to be the most important phase of project management, therefore one of the most important responsibilities of the project manager. A project plan provides the basis for its implementation, control & termination. The plan is a point of reference for specific project objectives, performance specifications, duration & milestones, organizational structure, resource requirements & budget. It is a vehicle for assigning team members’ role & duty.It helps individual know when his/her tasks is done.Planning forces one to think through the entire project, enables more efficient use of resources.Plans are more effective when they are developed by or at least with the help of doers.(计划被认为是项目管理中最重要的阶段,因此也是项目经理最重要的职责之一。项目计划为其实施、控制和终止提供依据。计划是特定项目目标、绩效规范、工期和里程碑、组织结构、资源需求和预算的参考点。它是进行团队成员角色定位和职责分配的工具。它有助于个人了解他/她的任务何时完成。计划迫使一个人对整个项目进行思考,能使资源得到更有效的利用。当计划由实干家制定或至少在实干家的帮助下制定时才会更加有效。)
☛A project planner should be CRAP:
Creative – imaginative in the adoption of ideas & techniques and developing tools to match project needs. (创造性——富有想象力地使用想法、技术以及开发工具来满足项目需求。)
Responsive – ever conscious of time constraint; quick to identify & solve problems with the participation & support of others(反应迅速——时刻意识时间限制;在他人参与和支持下快速发现并解决问题)
Analytic – able to grasp uncertainty & risks, and identify contributory factors and variables
(分析型——能够把握不确定性和风险,并识别促成因素和变量 )
Persuasive – effective in communication: initiate, coordinate & integrate
(说服力——有效沟通:发起、协调、整合)
★ Executing and Controlling(执行和控制阶段) : A major portion of the project work takes place during this stage. Time, cost and specification measures are used for control. Is the project on schedule, on budget, and meeting specifications? What are the forecasts of each of these measures ? What revisions /changes are necessary? Controlling goes through the entireprocess it includes checking the progress , comparing to what was planned and taking necessary action. (项目的大部分工作在这一阶段完成。时间、成本和规范方面的措施被用来进行控制。项目是否按计划、按预算进行、是否符合规格?对这些指标的预测是什么?需要进行哪些修订或者更改?控制贯穿整个过程,它包括检查绩效、与计划进行比较以及采取必要的措施。)
★Closing(收尾阶段): It includes the two activities: delivering the project product to the customer and redeploying project resources. Delivery of the project might include customer training and transfering documents.Redeployment usually involves releasing project equipment/materials to other projects and finding new assignments for team members.(它包括两项活动,向客户交付项目产品和重新部署项目资源。项目交付可能包括客户培训和转交档案资料。重新部署通常涉及将项目设备和材料分配到其他项目,并为团队成员找到新的任务)


