About quality and QM
Quality is a much more complicated term than it appears. Dictionary definitions are usually inadequate(不充分) in helping a quality professional(质量专业人员) understand the concept. It seems that every quality expert(专家) defines quality in a somewhat different way. There are a variety of perspectives(视角) that can be taken in defining quality (e.g. customer's perspective, specification-based perspective基于规范的视角). A modern definition of quality derives from(起源于) Juran's "fitness for intended use." This definition basically says that quality is "meeting or exceeding customer expectations." Deming states that the customer's definition of quality is the only one that matters.
ISO(International Standard Organization):质量是“反应实体满足客户明确和隐含需求的能力的特性总和”。实体的内涵丰富,可以是具体的实物,也可以指对应的活动、过程或组织等。明确需求是指在标准、规范、图样、技术要求、合同和其他文件中用户明确提出的要求与需要。隐含需求是指用户对实体的期望以及公认的、不必明确的需求。特性是指实体所特有的性质,反映了实体满足需要的能力。
what is quality?
why is quality important?
★Quality management
Quality management is the totality(整体,全部) of functions involved in the determination and achievement of quality (includes quality assurance and quality control).
Modern quality management believes that quality should be planned, designed, and biult-into——not inspected into the project's deliverables(可交付物)
Modern quality management approaches recognize the importance of:
Customer satisfaction (顾客满意度)
Continuous improvement(持续改进)
Prevention over inspection(预防胜于检查)
Management responsibility(管理责任)
▶Quality control tools
收集质量数据,分析和确定质量问题,控制和改进质量水平的常用7种工具:
![6WGWFV]6AC53)V9H4~ACM5P.png](https://p.ananas.chaoxing.com/star3/origin/3ebc266dd6cb92208b8609e314550446.png)
(因果图;流程图;核检表
帕累托图;直方图;控制图
散点图)
▶Total Quality management(TQM) (全面质量管理)
TQM is a new concept in the construction industry, but it has made a significant impact during the past two decades. Although dozens of books and hundreds of articles have been published about the TQM philosophy, its essence can be summed up in just two guiding concepts: customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
The concept of customer satisfaction goes far beyond the traditional idea of providing an acceptable product to the owner for whom we are working. The customers are considered to be everyone involved in the building process from designers to subcontractors and employees. TQM encourages innovation and cooperation. Ideas flow more freely, and decisions are made with more input from all of the parties involved.
Continuous improvement means making every job better than the last one. Ask“is there a better way to perform this task? If so learn from the experience and share it with other members of the project team. This attitude can be seen at every level in the TQM Company.
TQM is a philosophy, not a business plan. TQM is everyone's responsibility and everyone's reward.

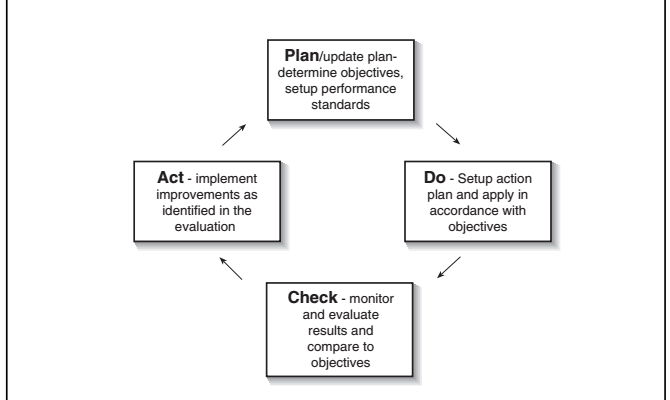
PDCA - A useful manangement tool
Reviewing questions(复习思考):
1、Write out your understanding of TQM
2、what's PDCA?


