Introduction
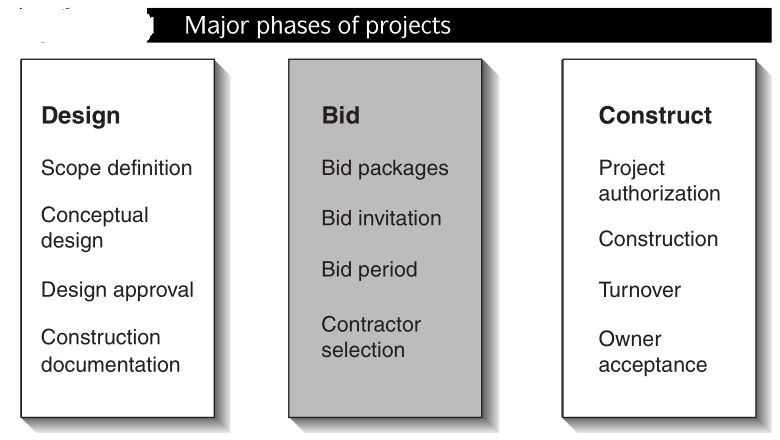
About Bidding
★Motivation to bid(投标动机)
Motivation to bid varies on a number of factors. The greatest one is the profit; each company wants to receive good return on its investment. Aside from the profit motivation, companies may bid on projects for other reasons. If it wants to establish relationship with a new client or maintain one with an established client, a company may bid on a less profitable project. A project that is unusual and can add variety to the company portfolio(代表集,公文包) will spark(火花,引发) interest even if the profit margins look low. If the project has high public influence or benefits the community, the company may view it as a marketing strategy. In one word, sometimes, the bidder concern short-term goal of profits, sometimes long-term goals, such as client relationship, or community recognition.
☛ Bidding is affected by economy(投标活动受经济的影响)
The bidding is affected by the economic ups and downs. In a strong economic market, contractors are able to choose which projects to bid on. In a slow economic market, the contractors have to bid on less desirable work.
投标(Bid):是指投标人(卖方) 应招标人的邀请,根据招标通告或招标单所规定的条件,在规定的期限内,向招标人递盘的行为。目前,大多数国家政府机构和公用事业单位通过招标购买设备、材料和日用品等。在进行资源勘探、开发矿藏或招商承建工程项目时,也常采用招标方式。
招标(Invitation for bids ;tender) :是指招标人(买方)事先发出招标通告或招标单,品种、数量和有关的交易条件,提出在规定的时间、地点,准备买进的商品名称、件,邀请投标人(卖方)参加投标的行为。【法律依据】《招标投标法》第三条,在中华人民共和国境内进行下列工程建设项目包括项目的勘察、设计、施工、监理以及与工程建设有关的重要设备、材料等的采购,必须进行招标。
★Formation of the bidding price(投标价格形成)
Once a company decides to bid on a project, it always enters the following process. Estimators ask prices from a number of subcontractors. The subcontractors do material takeoffs from the drawings and specifications that result in the quantities required on the job. Theses quantities are then multiplied by the unit cost. This total cost is the cost for materials. A similar exercise is done for labor and equipment. The total costs of materials plus labor plus equipment is the direct cost of the work.
The estimator then adds administrative costs for running the job at the job site ,such as the expense involved in marketing the company, necessary legal and accounting expenses. These are the field indirect costs of the work. Layered on are the overhead and the profit(reasonable profit for the job is determined based on the analysis of market and its motivations for doing the work.)
● Direct costs + Indirect costs= Cost of the work
(Direct costs are those clearly assigned to the aspect of the project that generated the costs, including labor and materials; Indirect costs generally are linked to two features: overhead, selling and general administration)
● Cost of the work+ X% for profit= Total cost to the owner
★Qualification of bidders(投标人资格审查)
Before a company is awarded a job, even if it is the low bidder, it will like to put through a qualification process. There are two methods of qualifying bidders: pre-bid and post-bid qualification. Pre-bid qualification requires the interested contractor to submit information about the firm before the bid documents are released. Post-bid qualifications are submitted with the bid and reviewed by the owner during the bid opening and analysis. In either case, qualification is determined by the evidence of capacity from previous jobs, financial strength and stability, personnel availability and safety record.
Construction managers usually keep a current list of qualified contractors and subcontractors so that they can quickly produce a bidders' list for the owner.
The number of bidders varies but generally is between five and seven for each major trade. With specialty trades it may not be possible to get so many bidders, but a minimum of three is necessary to judge the bids fairly. The goal is to keep the number small enough to generate interest for each contractor while providing enough competition so that the owner feels he or she got the best price available.
★Bidder conferences (投标人会议)
The meetings are between the buyer and all prospective(可能的,潜在的) sellers prior to submittal of a bid or proposal. Sometimes they are called contractor conferences, vendor conferences, and pre-bid conferences.
They are used to ensure that all prospective sellers have a clear and common understanding of the procurement (both technical and contractual requirements), and that no bidders receive preferential(优惠的) treatment
★Analysis of bids (评标)
Once all the bids have been received, the construction manager tabulates them into spread sheet and makes them comparable. Such comparisons may consist of the base bid, alternates, addenda, unit price,and value engineering suggestions.
★Award of the contract(合同授予)
Award of the contract can be as simple as accepting the lowest bidder. However many factors should still be considered. For example, if the low bidder is too far from the other bidders, the suspicion that he or she has missed something will raise. Minor clerical errors are usually okay for correction; but in general, if a bidder has not met the requirements of the bid, the bid will be rejected. In all cases, the owner has the right to reject or accept the bids.
Reviewing questions(复习思考):
1. Why firm bid? in other words, what motivate a constructor to bid ?
2. what information should be included in a invitation to bid
3. what is the function of a pre-bid conference?
4.How to form a bidding price?


