What is contract?(什么是合同)
A contract is simply an agreement between two or more people in which a person agrees to perform or provide a specific task or service to another person in exchange for something in return.
世界需要契约精神
Contract types(合同类型)
In order to minimize the risks effectively, the owner must decides what type of contract to use, besides of a delivery method. There are three basic types of contracts: single fixed price, unit price, and cost plus a fee.
1. Single fixed price(固定总价合同)
In a single fixed price, the contractor agrees to provide a specific amount of work for a specific amount of money. Both parties try to fix the conditions of the project as precisely as possible. It is usually used with the traditional delivery method. The designer prepares a complete set of documents. According to the documents, the owner bids out or negotiates with a contractor. A final price is agreed to, and the work begins.
Advantages:
☝The owner knows the final cost of the project before the work begins.
Disadvantages:
☟High demanding of the accuracy of the contract documents, if the scope of the project changes or if errors exist in the documents, the contract needs to be renegotiated; this will impose a lot of risk on the owner and the contractor.
2. Unit price (单价合同)
In a unit price contract the owner and the contractor agree that the price is decided by the quantities of the project and the bidding unite price. The owner, usually the designer provides estimated quantities for the project, asking contractors to bid on the job by figuring unite prices for these items and calculating the final price. The owner compares the final price and selects the lower bidder. It is usually used in heavy engineering project, such as earth dams, subways. Because the quality of the work can be define but the actual quantities are difficult to determine in advance.
Advantages:
☝Less risk to both the bidder and the owner. Payments will be based on the actual quantities.
☝It eliminate s the risk of negotiating and renegotiating a fixed price Work can begin before the design is complete, thus speeding up the project.
Disadvantages:
☟If the estimated quantity is quite different, the owner will have to spend more money.
A case:
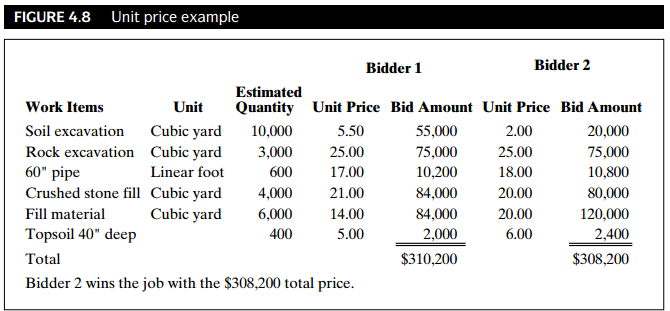
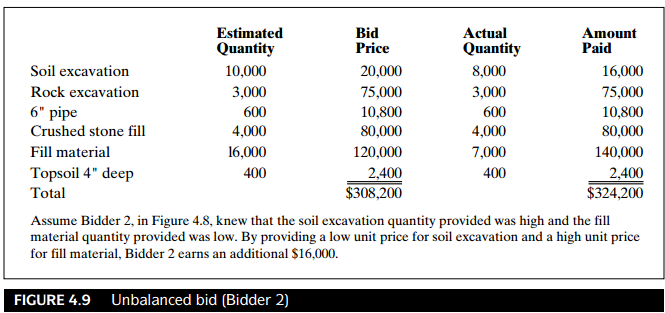
☟Actual quantities must be measured in the field. This requires the owner’s presence.
3. Cost plus fee (reimbursable) (补偿合同)
In a cost plus fee contract arrangement, the contractor is reimbursed by the owner for his or her work costs and receives an additional fee. The fee can be negotiated or just a percentage of the costs.
This contract makes sense when the scope of the project is difficult to define or when it is important to fast-track the project. The contractor can start the work without a clearly defined project scope since all costs will be reimbursed and a profit guaranteed.
常见的四种施工合同类型
Contract changes(合同的变更)
In all types of contracts we have discussed, an agreement is established between the owner and the contractor. To some degree the contract is based on the design and knowledge about the project. If conditions change, however the contract has to change accordingly. There are three major reasons why contract change will occur.
▶Because of a change in owner requirements, the scope of the project increases or decreases.
▶Because of the conditions unforeseen when the contract was signed. The work must be performed differently.
▶Because of omission in the documents or design, the design has to be adjusted.
Reviewing questions(复习思考):
Just talk about the contract types and their advantages & disadvantages.
Why contract change always happen?


