★Communication(沟通)
A discussion on the leadership would be incomplete without addressing the topic of communication—good, clear, honest communication. Leadership communication is distinct—it is up close and personal. Whether the message is inspirational, criticizing, or crisis driven, the form and the timing of the message are important. In fact, timing is everything. For real communication to occur, the message must be delivered and received. The receiver has to be in a frame of mind(一定的精神状态) to hear the message. Therefore, leaders must be very careful about when they transmit their message, particularly when it comes to communicating criticism. They must also be explicit(简洁) in the scope of their words. Not everyone needs to know the big picture, only what is pertinent(恰当的,相宜的) to do the job. Too much information can hide or distract the intended message. Timely and precise communication can correct a problem before it becomes serious.
Project managers spend 75%-90% of working time on communication.
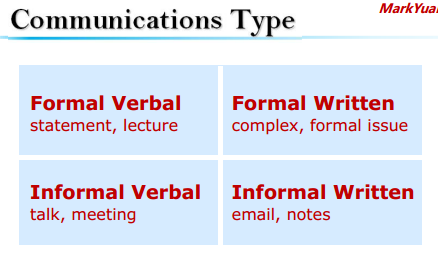
▷Communication forms(沟通形式)
Many forms of communication occur on project and within an organization.(verbal:口头的,语言的 written :书面的,文字的 vocal:音调的,发音的)
![]C(S`4BDQQ_YGIMX4DHFMBW.png](https://p.ananas.chaoxing.com/star3/origin/4a86081e3f62146be70b843b869e36bf.png)
☛How to carry out effective written and oral communication.(如何开展有效的书面和口头交流)
1.written communication---being heard and understood
2.Oral communication ---being understood(被理解)
3.Oral communication ---be bold(大胆说出来)
▷Communication Loop(沟通环理论)
Whether the message is inspirational, criticizing, the form(形式) and the timing(及时性)of the message are important. Generally speaking, communication contains three components: a source, symbols (to impart a message(承载信息) and receiver. The source could be the project leader; the symbols could be a written memo or a verbal announcement(书面备忘录或口头通知), and the receiver a subordinate(部属、下级). 
▶Source be explicit(明确)in the cope of their words. Be timely and precise to correct a problem before it becomes serious.
▶Symbol must consider the receivers background, experience and education. A written message sent to an audience that cannot read would be an ineffective method of communication. On the other hand, a message meant for one person that is announced in a group could do a lot of damage.
▶Receiver's obligation is to empathize(共情,同情), work with the sender, and try to connect and understand the message. Receivers need to indicate to the source that they understand the message. This will satisfactorily complete the transaction(交易).
工作环境中的交流
10个有效沟通的障碍因素
沟通的意义、原理以及方法
▷A interesting phenomeno assocaited with communication (一个有趣的沟通现象——漏斗效应)
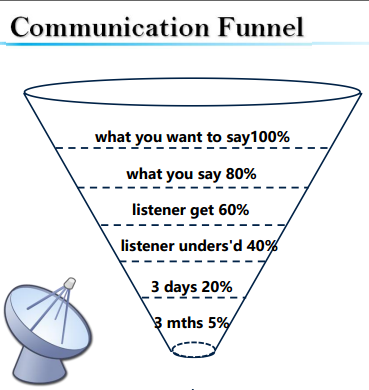
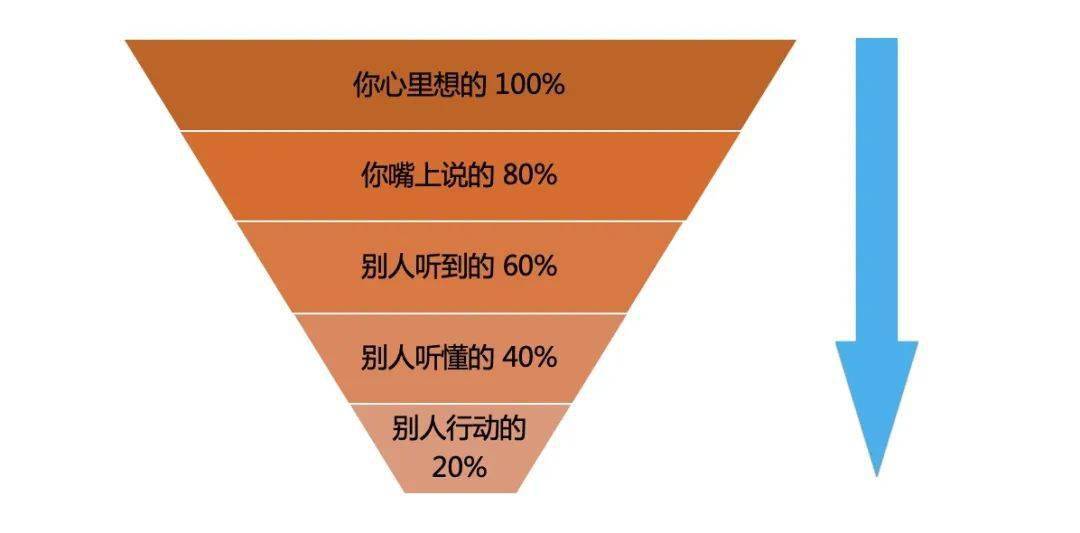
A joke: 一个黑人走进沙漠旅行,因为迷路而又累又渴,这时他发现了一盏阿拉丁神灯,擦了擦,一个精灵便出现了,精灵说:它在神灯里已被关了几千年了,今天黑人救了它,它要报答他,它可以满足黑人的一个要求,而且这个要求可以同时满足三个条件。
黑人想了想,便说:第一,因为肤黑老受歧视,他要变成白色的;第二,在沙漠太干渴了,他要有一辈子都喝不完的水;第三,他要每天能看见女人的臀部。
精灵想都没想,把黑人变成了一个白色的抽水马桶。
An example:




