Leadership
★What's leadership (什么是领导力)
Leadership is the ability to inspire confidence and support among the people who are needed to achieve organizational goals.
Leadership is at the core of the construction management profession. Of course this is true to all other professions. As we know most projects are in a constant state of flux and tend to move from one crisis to another, project success is depend on the leadership of the construction manager. It is through the project manager's leadership that the project team stayed focused on the task at hand, supports each other, communicates, and continues to subordinate individual needs to the interest of the project. Good project managers are clear and honest communicators; they are teachers,not sergeant(警士). Leadership can be interpreted by the following aspects.

▶Flexibility(灵活性)
As the project moves forward, leaders need to adjust their strategies. For example, any changes and innovations are encouraged early in the life of the project, but during peak construction the focus needs to be on production. Manager needs to move with the proceeding of project, the team’s mood, the weather, and public sentiment. They need to respond to daily events, such as the schedule delay, the changing culture, the additional request of the owner, so they need to be equipped with the virtue(美德,优秀品质) of flexibility(灵活性).
▶Morale building(士气激励)

As we know, dividing(分裂,分开) the enemy to weak them is a wise strategy, but dividing one's own team is a mistake. Division from within can be disastrous to a project. Rewarding each subordinate efforts without arousing any petty jealousies(嫉妒)or disturbing(搅乱) the team's internal relationship. Celebration is also necessary for the moral. Projects milestones and team achievements are good reasons for celebration. Look to cultivate a “team first” mood. Team first employees are always on the look out to do what is best for the project. Encourage this type of behavior and get rid of the people who refuse to cooperate with team members or who are selfish. It is also very important for project manager to successfully represent the group at the next hierarchical level(层级). Effective project manager know how to work with the large organization to get the necessary resources that their project requires. This frees up those working under them to concentrate on the project itself and not worry about the availability of the office support.In order to encourage your team members, you need to know what they need.
♥需求理论(一):马斯洛需求层次理论
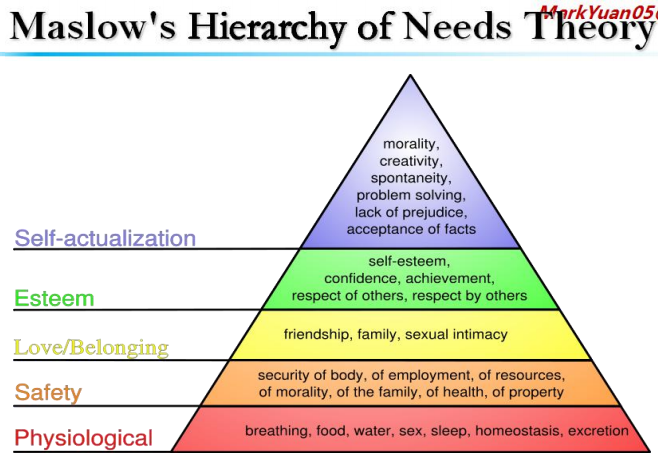
(马斯洛的需求层次理论:人类需求通常可以被描绘成金字塔内的五个等级。从层次结构的底部向上,需求分别为:生理(空气、食物和衣服........),安全(工作保障........),社交需要(友谊.......),尊重和自我实现。五种需要是最基本的,与生俱来的,构成不同的等级或水平,并成为激励和指引个体行为的力量。 需要层次越低,力量越大,潜力越大。随着需要层次的上升,需要的力量相应减弱。高级需要出现之前,必须先满足低级需要。
马斯洛需求层次理论
♥需求理论(二):麦克利兰的“三需求”理论
![_RQ}OCLI$J5]DVDC45_29F3.png](https://p.ananas.chaoxing.com/star3/origin/1edac00c33bb05071f5b6c3acd3e00e7.png)
(大卫·麦克利兰(David McClelland)"三需求”理论):人的需求分为了三类:对亲和/归属需求(Need for Affiliation); 对成就需求(Need for Achievement); 对权力需求(Need for Power)
▶Order and discipline(秩序和纪律)
Both material (a place for everything and everything in its place) and social (a place for everyone and everyone in his or her place) order must be maintained(物和人都必须要有一定的秩序). Material order is necessary to prevent waste and support the work of the organization. It includes a well-laid-out site with specific areas about the handling and storage of material and equipment(例如好的整洁的施工现场布置). It also includes good housing practices(好的内务). Social order means that every worker has a clearly defined job description. This includes job site orientation, identification of the immediate supervisor. It means that every worker is given instruction about the daily work environment and sense of the other work(in other words - who am I , what should I do ?)
▶Goals and accountability(目标和问责制)
It is the job of the project leader to set goals (objective) 、related standards and ensure that they are being met. A group is highly perspective of its leader's behavior and reacts quickly to it(马首是瞻). E.G. Ancient general need to work harder than their subordinates, and set a good example. Leaders are responsible for the success and failure, but the people working for them is also accountable(负有责任的). To help establish this accountability, leaders should set clear expectation and goals for their people and monitor their performance.
![LS`MC]_U@8NTYN}EINJ}A62.png](https://p.ananas.chaoxing.com/star3/origin/67eb59566657aa7a762b1cb27d0a1ea1.png)
1、目标具体(Specific),指绩效考核要切中特定的工作指标,不能笼统。
2、目标可度量(Measurable),指绩效指标是数量化或者行为化的,验证这些绩效指标的数据或者信息是可以获得的。
3、目标可实现(Attainable),指绩效指标在付出努力的情况下可以实现,避免设立过高或过低的目标。
4、目标现实(Realistic),指绩效指标是实实在在的,可以证明和观察。
5、目标有时限(Time bound),注重完成绩效指标的特定期限。
▶Monitoring and supporting(监督和支持)
The monitoring system should be customized to the job situation and to the skill level of the worker, and should provide enough room so that workers can operate as independently as possible. ( Don't spur a willing horse) In life safety situation, there is no room for tolerance (容忍)and project leaders need to step in very quickly and provide direct scolds(斥责) and even dismissal(开除) if necessary. In normal situations, however, especially with senior, experienced people, leaders may need to stay back, observe and subtly guide their subordinates. In most cases it may be best to let people learn through self-correction.
Successful project teams are organized, prepared, and made up of people who are confident in their abilities. Workers develop confidence from a demonstrated ability and success in their assigned duties. Project leaders can support this confidence building by ensuring that each worker is appropriately supported, that the scope of each job is clear, and that measurements for success are understood. Reinforcing successful behavior through praise and discouraging unsuccessful behavior through criticism is also key.
▶Assignment and Promotion(任命和提拔)
That is to say develop and train future leaders. Organizations can develop their future leaders two ways (from within and from outside). From within are inherently stale(固有陈旧) because they allow people to progress in their careers without leaving. People appreciate an organization that is committed to(致力于) the advancement of its people. But by feeding the organization with new people, companies can keep themselves competitive and up to date on changes and the social advancement.
▶Communication Skills(沟通技能)(this issue willl be unfolded in the coming section 该议题将在下一节展开详细讨论)
▶Authorization (授权)
Authorization is one of the important tasks for managers. It means delegate the necessary power to subordinate personnel to complete a certain work. Different levels in an organization have different functions and powers, and authority will flow between different levels, resulting in authorization problems.
Authorization is a scientific and artistic process in which leaders achieve organizational goals by providing employees and subordinates with more autonomy(自主权).Authorization is the expansion and extension of leaders' wisdom and ability.
如何有效授权,授权有什么意义
7大优秀领导品质
如何成为优秀的领导者
★Leader vs Manager (领导者与管理者)
A manager is an individual who has received a title within the organization that permits her to plan, organize, direct, and control the behavior of others within her department or area of oversight. Leadership is less about administration and more about interpersonal relationships, which involves inspiring, motivating, influencing, and changing behaviors of others in pursuit of a common goal. Leaders embrace change; managers support the status quo(现状).Leaders aim for effectiveness; managers aim for efficiency.
领导与管理的不同


